CUDA-based (compute unified device architecture-based) giant constellation coverage performance parallel computing method
A parallel computing and constellation technology, applied in the direction of reducing energy consumption, complex mathematical operations, climate sustainability, etc., can solve problems such as low computing efficiency, which is not conducive to the rapid design and optimization of giant constellations, real-time monitoring and operation and maintenance of constellation status, etc. achieve the effect of improving efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
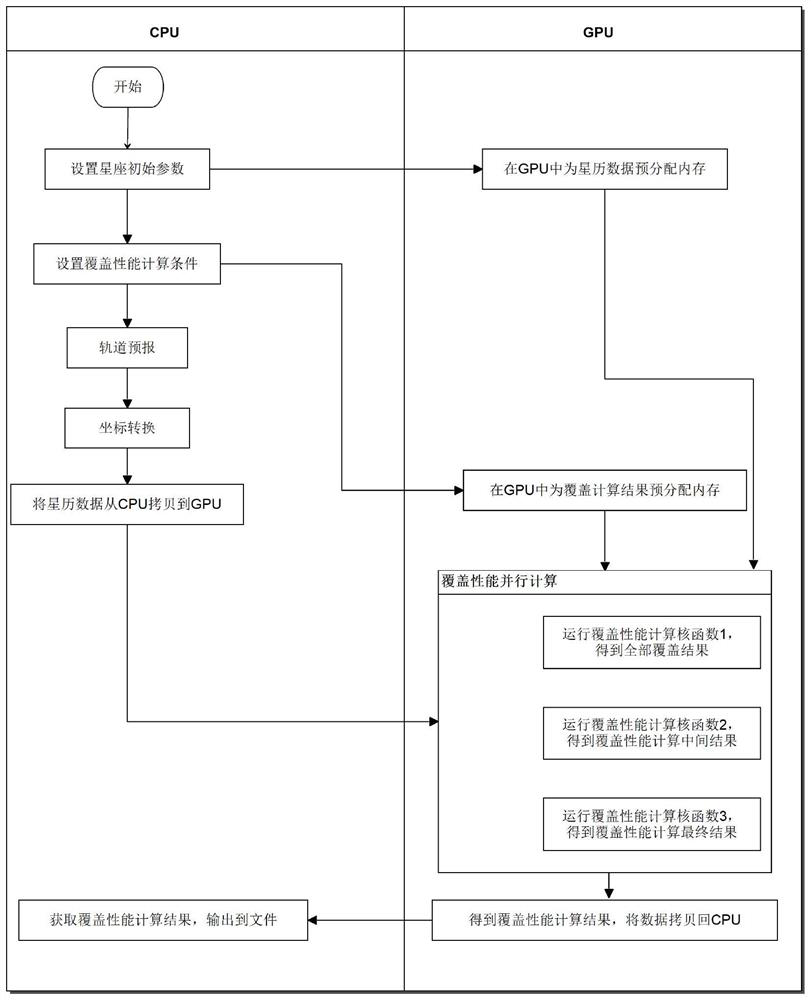
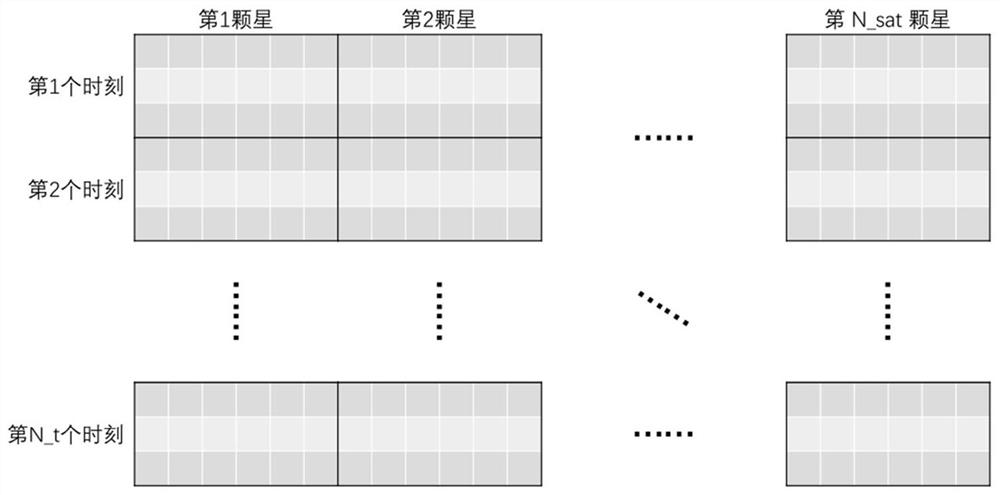
[0037]Step 1. Set the initial parameters of the constellation, including the initial epoch of the constellation, the total number of satellites in the constellation N_sat, the initial orbital number of each satellite in the constellation (orbit height h, eccentricity e, orbit inclination angle i, ascending node point Right ascension Ω, perigee angular distance ω, true perigee angle f). Then convert the number of orbits into position speed, and finally according to the set simulation duration and simulation time interval, there are N_t moments in total;
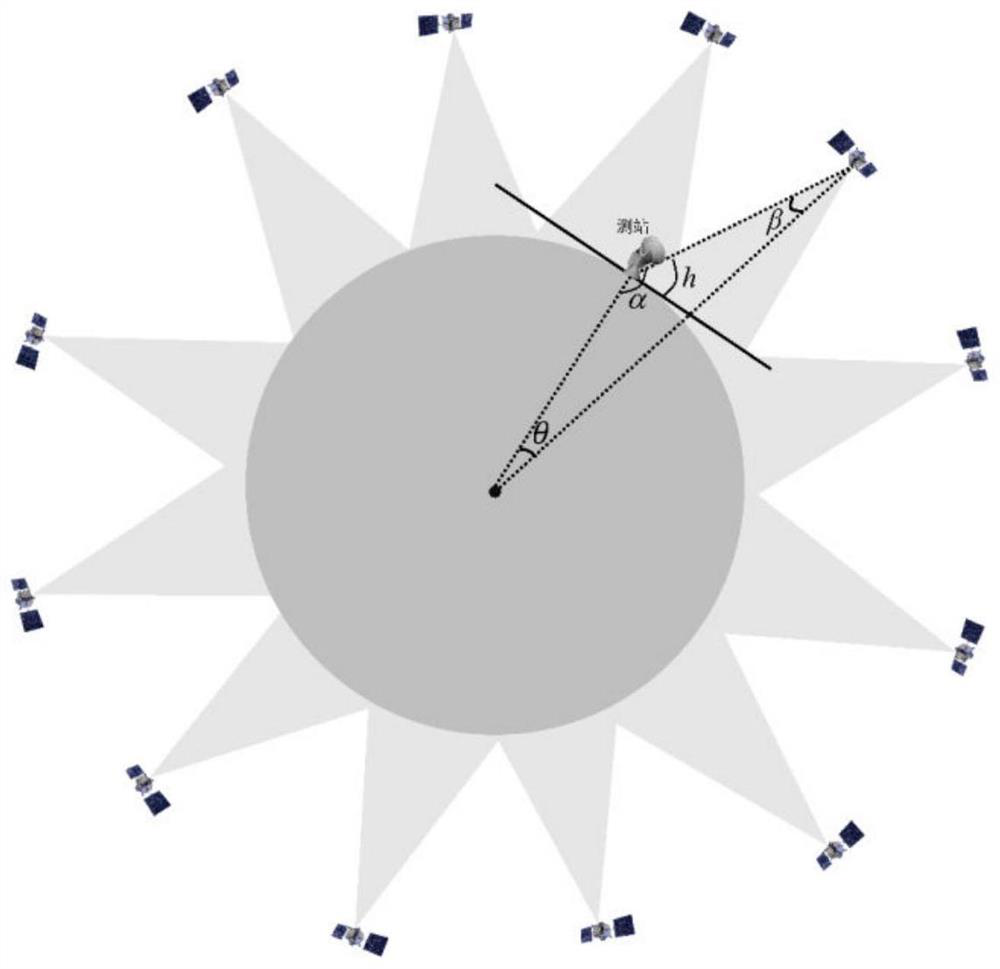
[0038] Step 2. Set the coverage performance calculation conditions, that is, the time for calculating coverage (which must be consistent with the ephemeris data) and the spatial resolution requirements: such as figure 2 shown, the beam angle 2β of the ground directional antenna 0 , and the cut-off elevation angle h for ground observations 0 ; Condition 1 for the coverage of the satellite to the ground station is: The visi...
Embodiment 2
[0054] The difference between the present embodiment 2 and the embodiment 1 is that in the step 1, according to the Walker-δ constellation T / P / F parameter, the initial orbital number of satellites is generated in batches; the specific process is:
[0055] 1) Set the number of reference star orbits (orbital height h, eccentricity e, orbital inclination i, ascending node right ascension Ω, perigee angular distance ω, true perigee angle f);
[0056] 2) Generate the initial orbital number of satellites in batches according to the set T / P / F parameters; if the ascending node right ascension of the reference star is recorded as Ω 0 , the corresponding phase is u 0 =ω 0 +f 0 , then the ascending node right ascension Ω and phase u of the jth satellite on the ith orbital plane in the constellation are:
[0057]
[0058]
[0059] Other steps and parameters are the same as in Example 1.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com