Compositions and methods for treating hemological disorders
A technology for blood disorders and red blood cells, applied in the field of compositions and methods for treating blood disorders, capable of solving problems such as not curing blood disorders
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
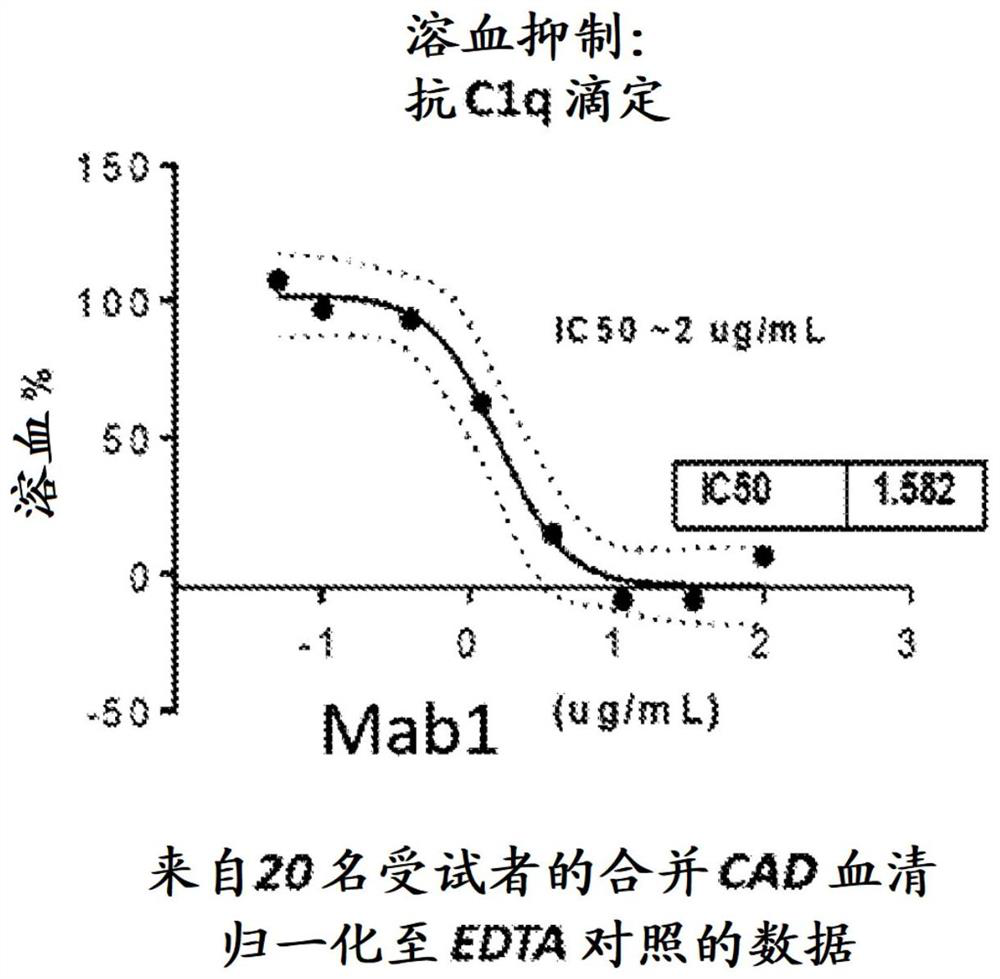
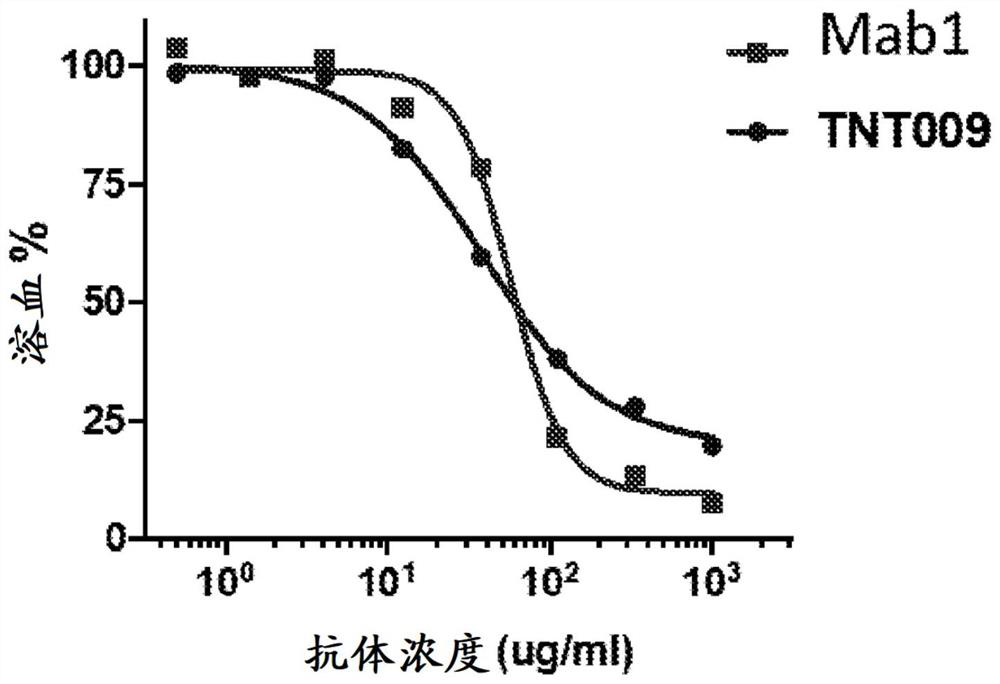
[0409] Example 1: Anti-Clq antibody inhibits complement-mediated hemolysis in blood samples from CAD
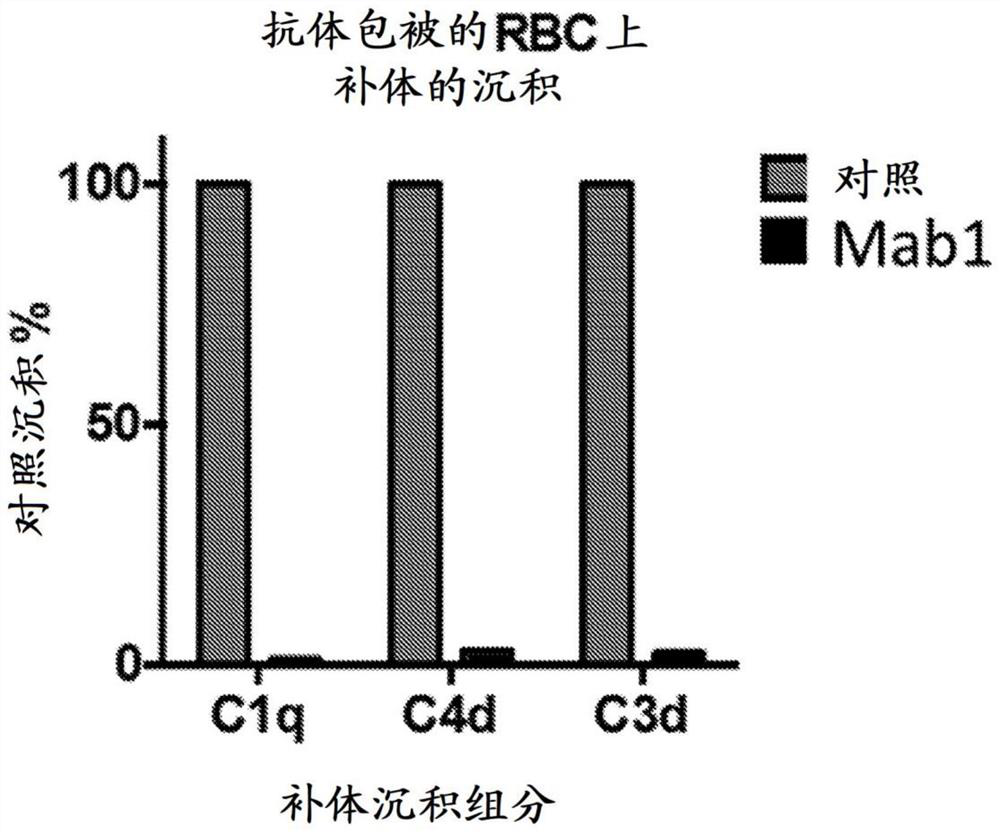
[0410] Individual CAD serum samples were pooled together for hemolysis and FAC experiments with anti-Clq antibody titration. Hemolysis was performed by sensitizing RBCs with pooled CAD serum (1 hour at 4°C - 10 μL serum + 10 μL RBCs). Addition of 200 μL of 20x normal human serum at 37 °C triggers lysis for 35 min. After lysis, the supernatant was removed and hRBCs were stained with anti-C3 antibody (CT-C3), anti-C1q antibody and anti-C4 antibody for 30 min, washed once, and stained with fluorescent secondary anti-goat antibody for FACS analysis.
[0411] In CAD, RBCs are coated by the three major classical complement "opsonins" (C1q, C4b and C3b) that drive RBC clearance through "extravascular lysis". C1q, C4b and C3b are recognized by the reticuloendothelial system in the spleen and liver for RBC removal. Also in CAD, RBCs become coated with C5b, which triggers the form...
Embodiment 2
[0412] Example 2: Anti-Clq antibodies inhibit hemolysis and complement deposition in blood samples from CAD patients
[0413] CAD and control plasma samples
[0414] Human CAD plasma samples from 8 subjects were obtained according to IRB-approved protocols. Control serum and plasma samples were obtained from Innovative Research (Novi, MI).
[0415] In vitro sensitization of human RBCs
[0416] RBCs (Innovative Research, MI) were washed and suspended in GVB++ buffer (Comptech, TX) (80 μL of packaged RBCs in 2 mL GVB++ buffer). 25 μL of human RBCs were mixed with 25 μL of 5x diluted CAD or normal serum and incubated at 4°C for 30 minutes. This step allows the binding of cold agglutinin antibodies from CAD subjects to human RBC surface antigens.
[0417] Three subjects showed robust IgG deposition, while seven subjects showed robust IgM deposition. One subject showed low signal of cell surface IgG and IgM.
[0419] Addition of normal human serum ...
Embodiment 3
[0426] Example 3 : Complement activation by PF4 / heparin via the classical pathway in plasma from patients with heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (HIT)
[0427]In HIT, RBCs are cleaved when the patient produces antibodies against heparin administered therapeutically in combination with the endogenous circulating protein PF4. To confirm that this cleavage is mediated by the classical pathway and not by the alternative pathway, differential sequestration studies using EDTA and EGTA were performed in vitro with plasma from HIT patients. The Mg2+-sensitive alternative pathway was inhibited by EDTA, but not by EGTA. like Figure 7A As shown in , addition of EDTA or EGTA to plasma prior to addition of PF4 / heparin abolished complement activation. Furthermore, Mg supplementation of EGTA-treated plasma did not rescue complement activation by PF4 / heparin. Plasma from healthy donors was incubated with or without C1 inhibitor (10 and 20 IU / mL) prior to incubation with PF4 / heparin, and ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com