Protein sequence design method of fixed skeleton based on graph network mask node classification
A protein sequence and design method technology, applied in sequence analysis, neural learning methods, biological neural network models, etc., can solve problems such as insufficient structural feature constraints of ProteinSolver, insufficient efficiency of network models, and increased structural constraints
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
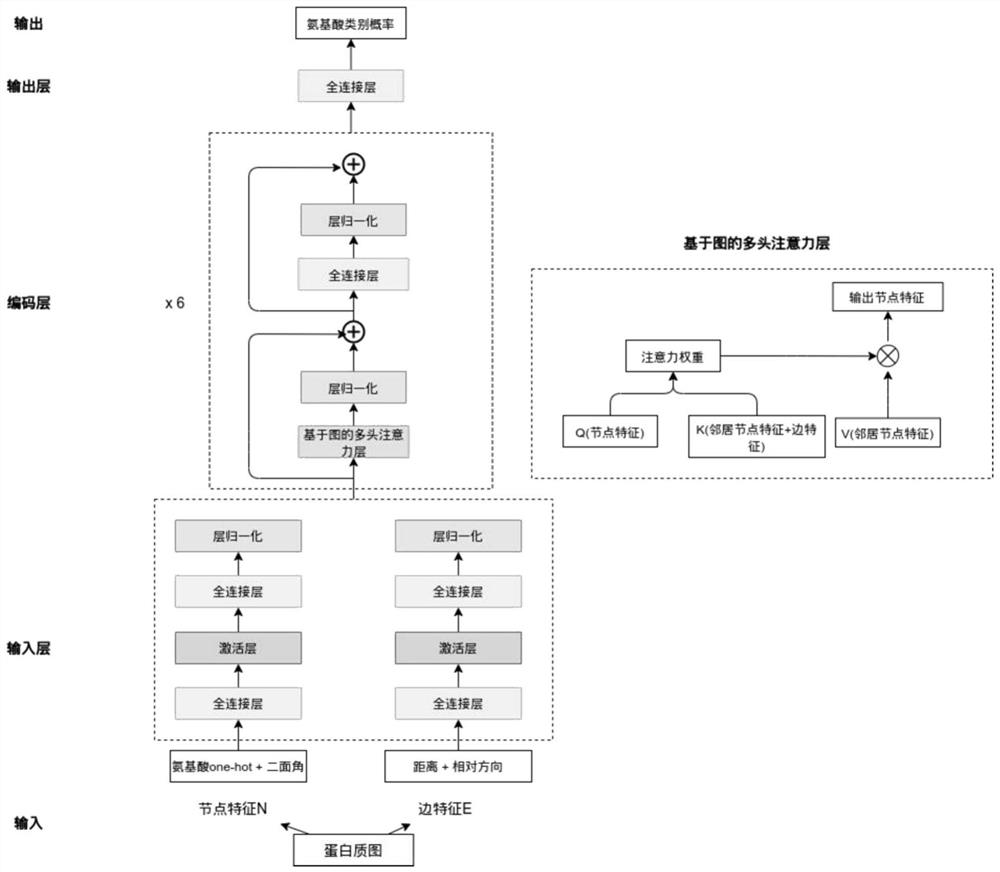
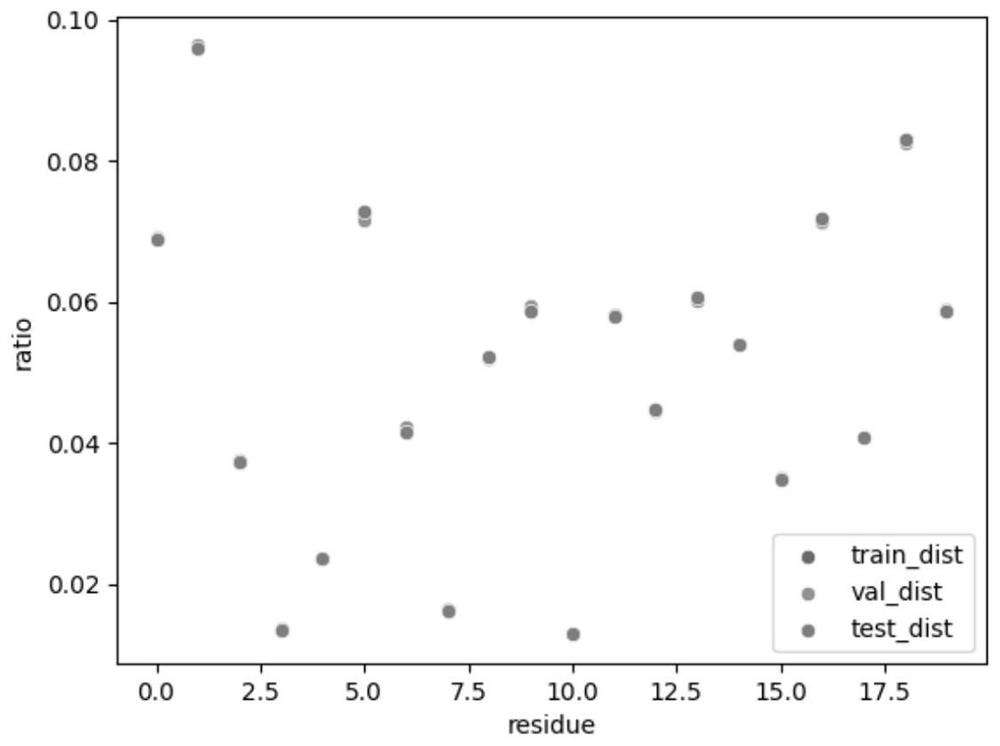
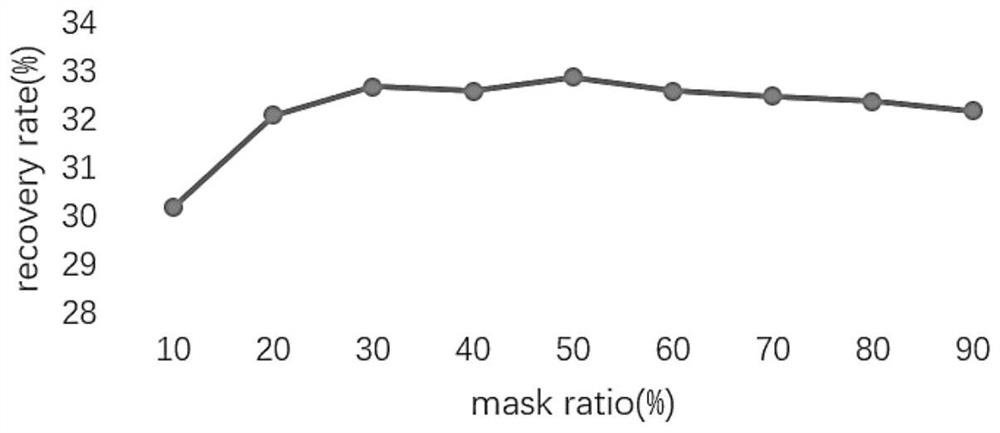
[0025] like figure 1 As shown, this embodiment relates to a fixed-skeleton protein sequence classification method based on graph network mask node classification, using the CATH 40% non-redundant data set, selecting sequences with a length of 50-500, according to 80:15 The ratio of :5 is divided into training set, validation set and test set. Then use the protein amino acid sequence in C α the coordinates of The distance is the standard to build the nearest neighbor map, i.e. when the two amino acids C α coordinates are less than , the two amino acids are neighbor nodes to each other, and when the number of neighbor nodes of the node is greater than 32, the distance C is selected α The nearest 32 amino acids serve as neighbor nodes. The feature dimension of the node feature of the created graph is 24, and the feature dimension of the edge feature is 4 respectively.
[0026] like figure 1 As shown, the graph network in this embodiment includes an input layer, an encodi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com