Three-D object recognition method and parts picking system using the method
A recognition method and technology of three-dimensional objects, applied in the field of parts grabbing system, can solve the problems of low recognition efficiency and long processing time.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
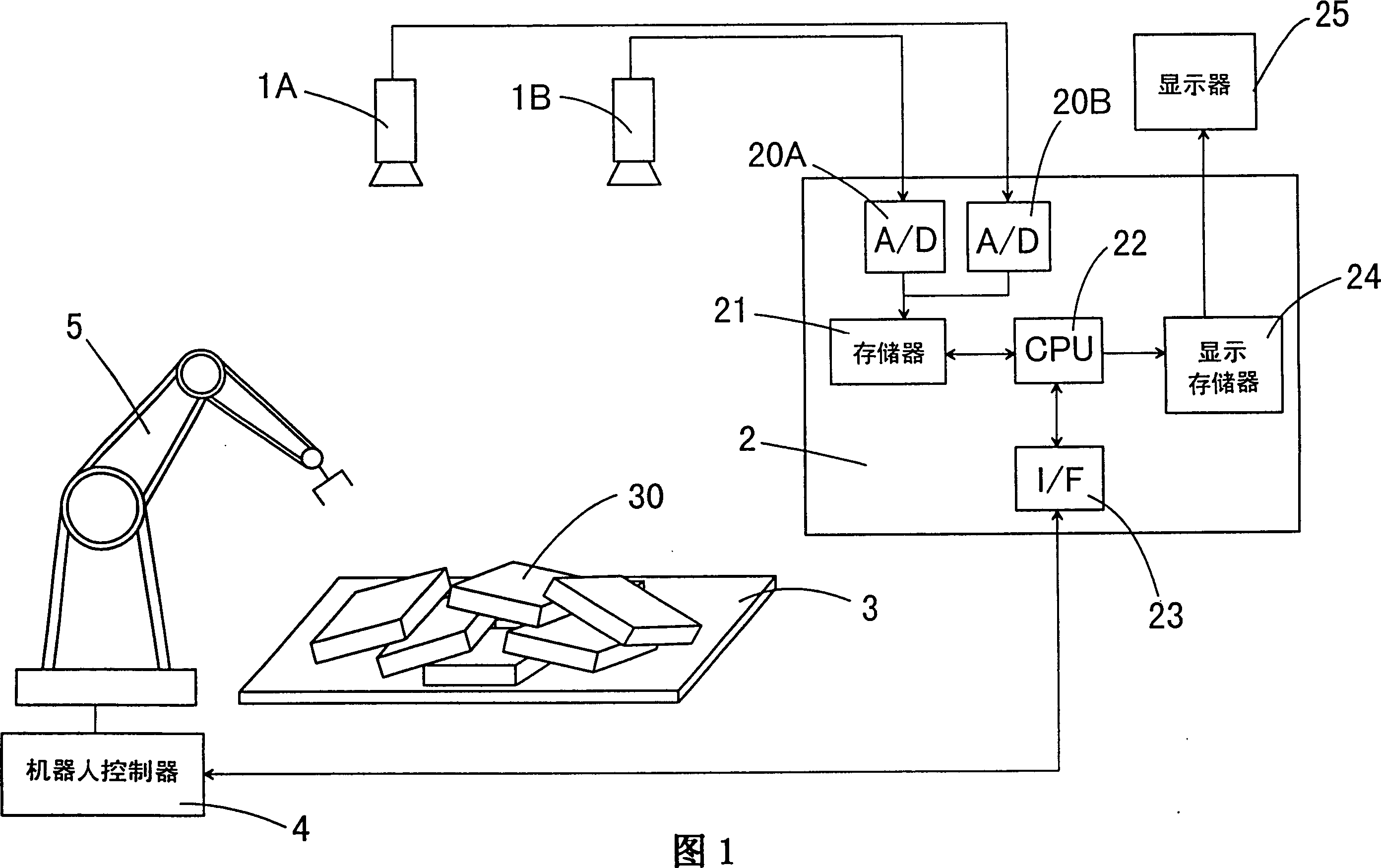
[0045]The three-dimensional object recognition method of the present invention can be well used in a part gripping system for conveying parts. For example, as shown in Figure 1, this part grasping system comprises a pair of TV cameras (1A, 1B); By using the image information provided by these TV cameras to carry out the image processing unit 2 of the three-dimensional object recognition method of the present invention; Have flexible robot 5 that can grasp parts 30 manipulator; And a robot controller 4, this robot controller 4 is used to control robot 5 according to the output that image processing unit 2 provides, makes manipulator grab parts from material box 30, wherein a plurality of parts 30 are piled up on the stage 3 in a random manner, and the grabbed parts are moved to the required positions.
[0046] In the image processing unit 2, the obtained video signal is converted into a digital signal by the A / D converter (20A, 20B), and temporarily stored in the memory 21. Ne...
no. 2 example
[0116] As shown in FIG. 14, the parts gripping system of the second embodiment is basically equal to the parts gripping system of the first embodiment, except that a third camera 1C is used in addition to the television camera, and by using the third camera 1C The image processing unit with A / D converter 20C can perform Figure 15 The 3D object recognition method shown.
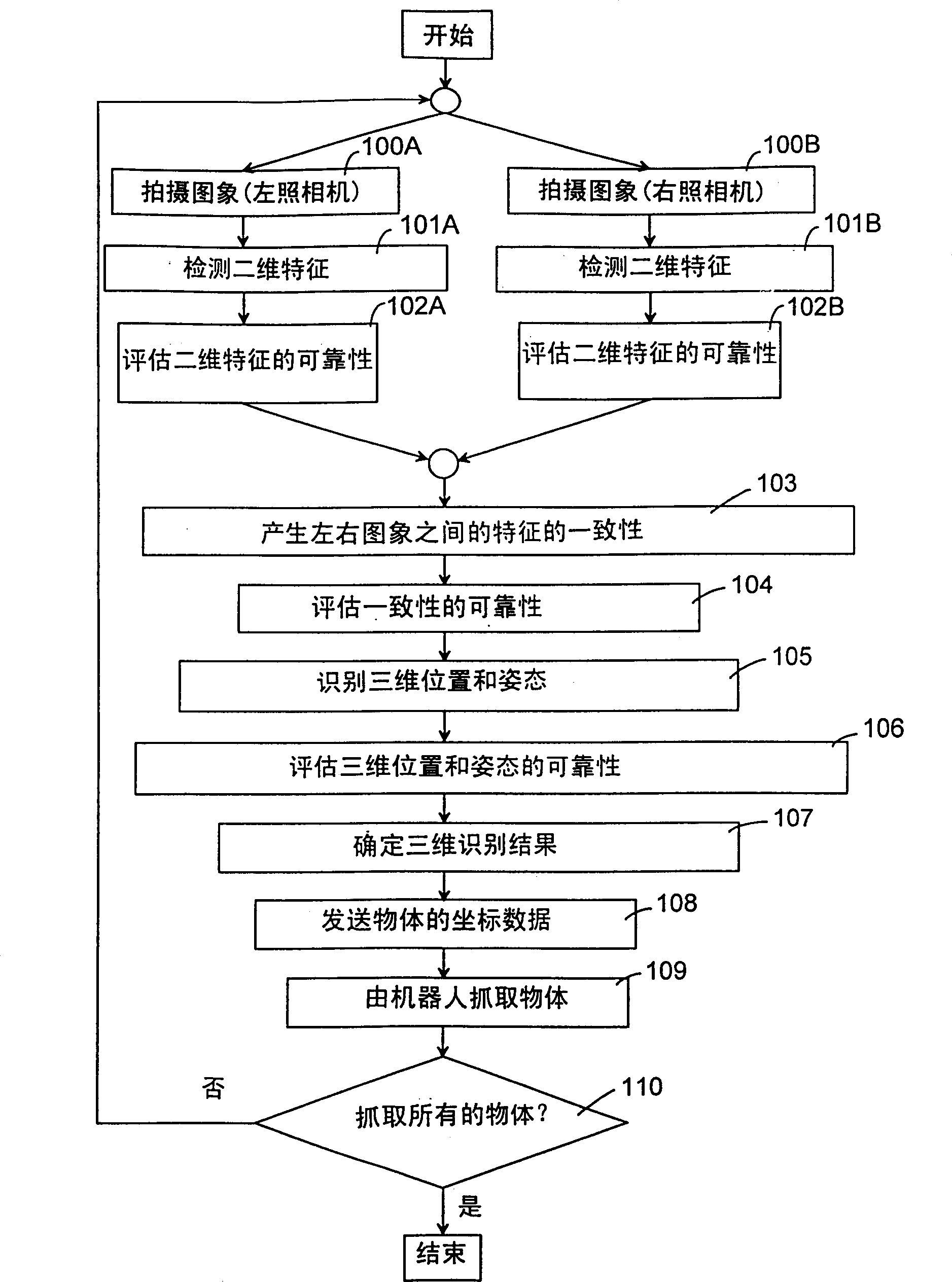
[0117] The three-dimensional object recognition method of the present embodiment includes the following steps: step 200A, photographing the left image; step 201A, detecting the two-dimensional features of the object on the left image; step 202A, evaluating the reliability of the two-dimensional features; step 200B, photographing The right image; step 201B, detecting the two-dimensional features of the object on the right image; step 202B, evaluating the reliability of the two-dimensional features. These steps are performed in the same manner as in the first embodiment. The method of this embodiment further ...
no. 3 example
[0126] The second embodiment described above illustrates that the recognition accuracy of the position and attitude of an object in three dimensions can be improved by creating consistency of two-dimensional features between the left and right images and between the left image and the third image. In this embodiment, the three-dimensional object recognition method is performed in consideration of the coincidence of the two-dimensional features between the generated right image and the third image.
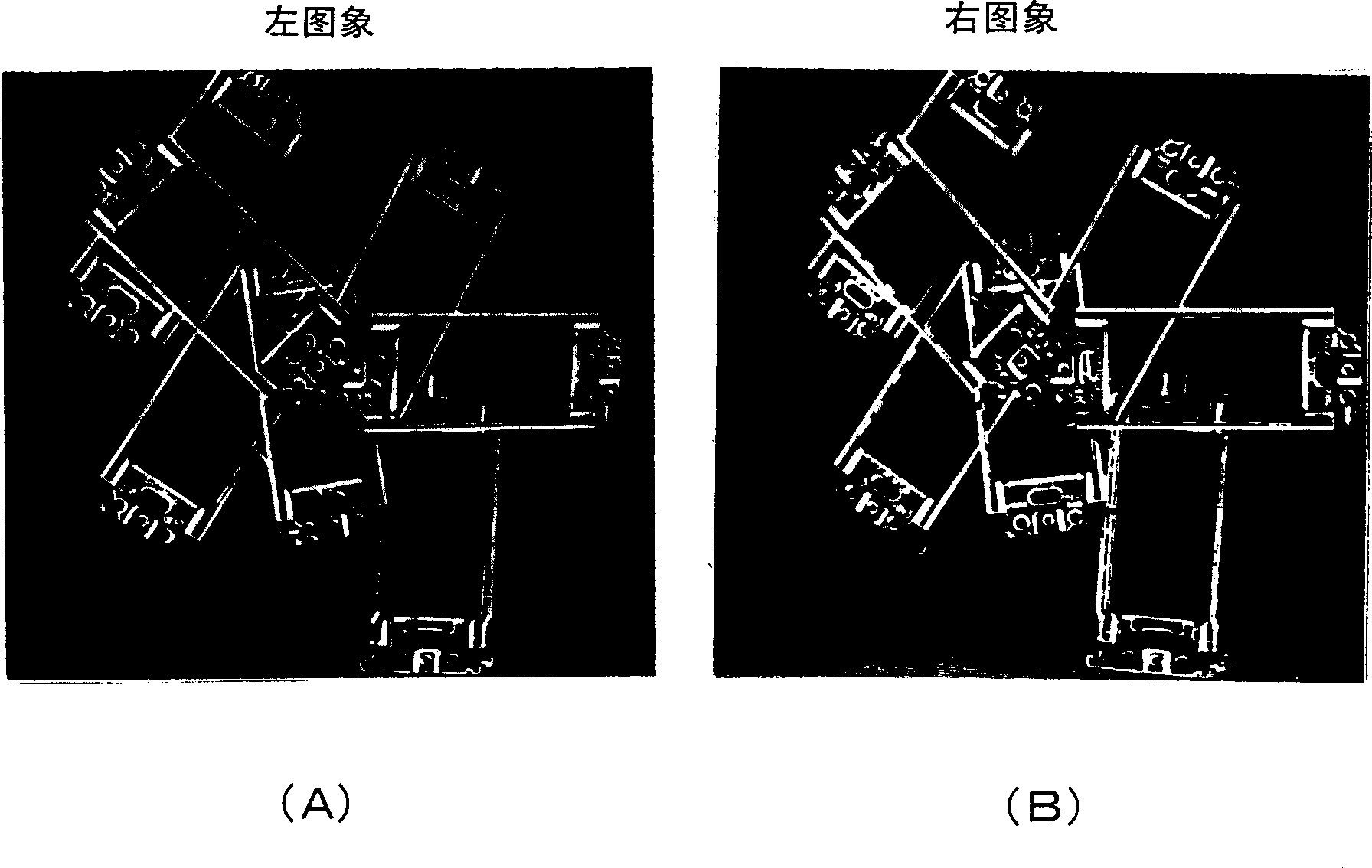
[0127] Specifically, as Figure 16 As shown, a case where a rectangular solid 50 is used as an object is illustrated, and two parallel straight line pairs (51, 52), (53, 54) are used as two-dimensional features of the object. First, an image of a rectangular solid is taken using three cameras 1A, 1B and 1C. Next, two parallel line pairs (51, 52), (53, 54) are extracted from each of the three images as two-dimensional features. The first process of generating consistency between t...
PUM
 Login to view more
Login to view more Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap