No-position sensor motor control device
A technology for control devices and motors, applied in motor control, AC motor control, control systems, etc., can solve problems such as estimated angle error, increased angle residual error, and difficulties
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0379] Hereinafter, the position sensorless motor control device of Embodiment 1 will be described.
[0380] The position sensorless motor controller of Embodiment 1 calculates the induced voltage value from the phase voltage equation of each phase of the stator winding, then calculates the deviation between the induced voltage value and the induced voltage reference value, and corrects the estimated angle θm so that the deviation converges to zero. Therefore, high-precision angle estimation can be realized with high resolution, angle estimation can be realized even when the phase voltage is saturated, and high-precision estimation can be realized even if motor constants such as induced voltage constants change.
[0381] In this document, the term "error" has the same meaning as "deviation".
[0382] First, the position sensorless motor control device of the first embodiment will be described.
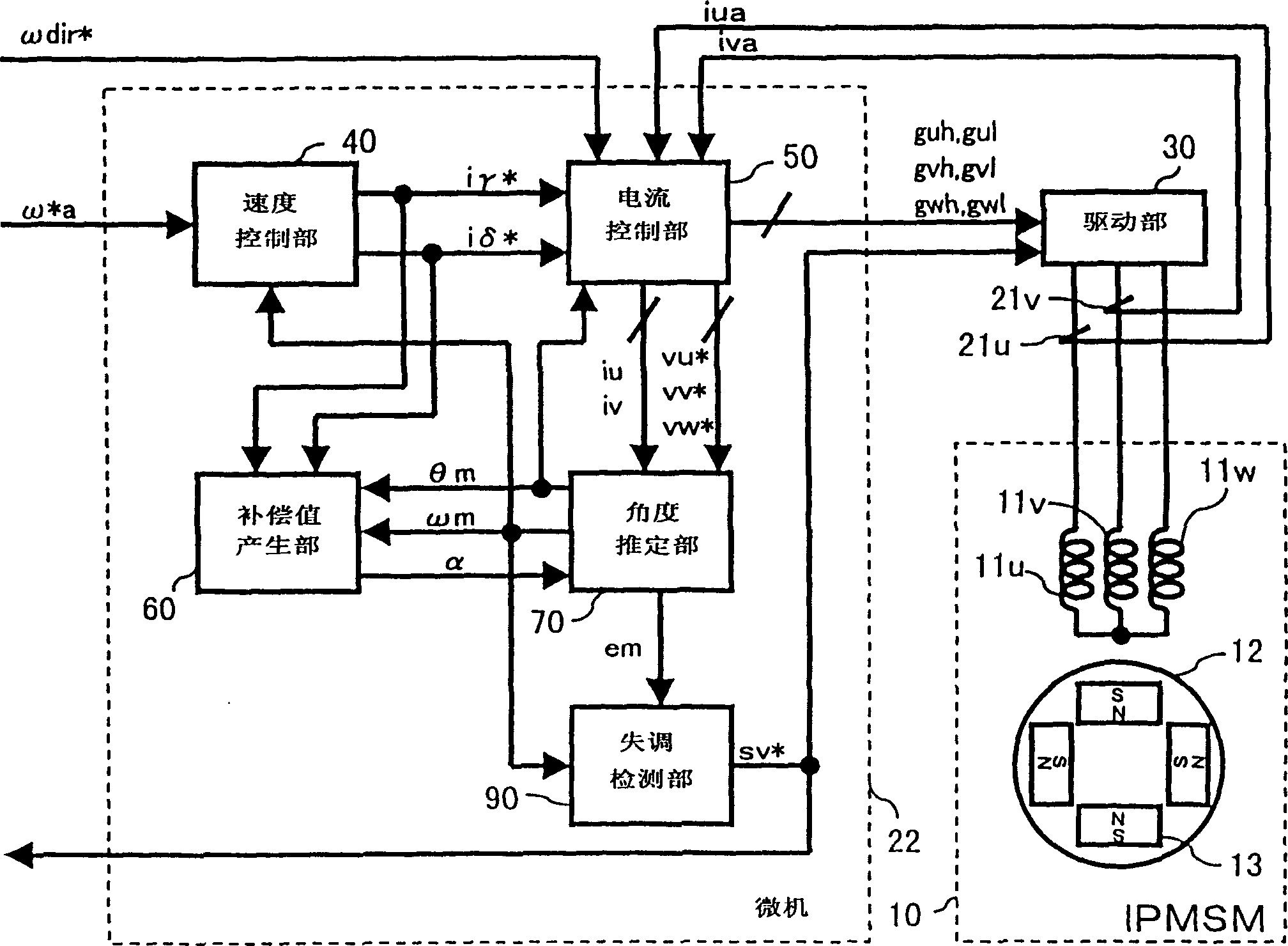
[0383] ( figure 1 illustrate)
[0384] figure 1 It is a block diagram showin...
Embodiment 2
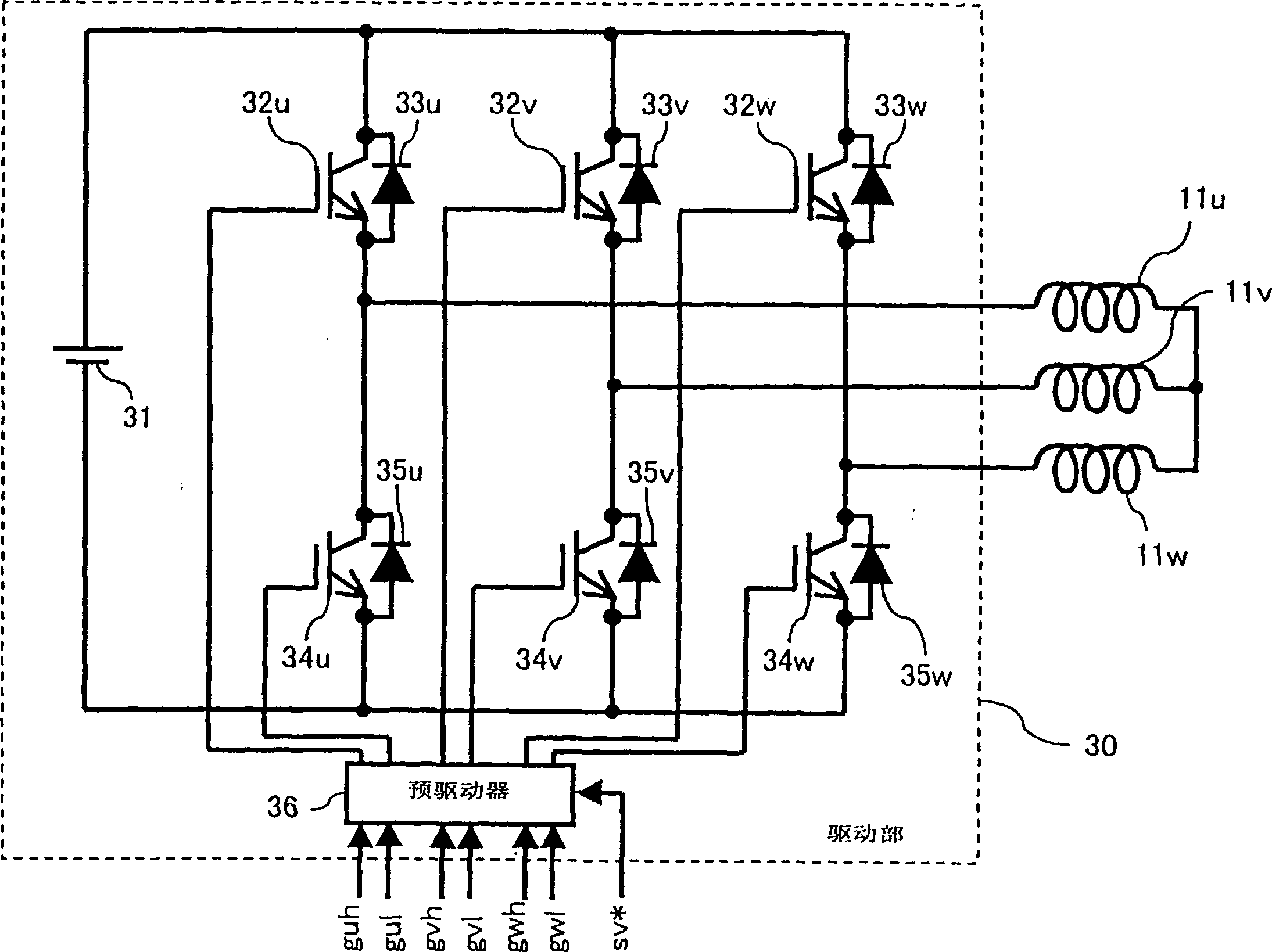
[0621] Next, a position sensorless motor control device according to Embodiment 2 of the present invention will be described. In the position sensorless motor control device of the first embodiment, the phase voltage values vu, vv, vw are generated from the phase voltage command values vu*, vv*, vw* generated by the current control unit 50 . In the position sensorless motor control device of Embodiment 2, a voltage sensor is added to directly detect the phase voltage. Therefore, high-precision angle estimation is realized with high resolution, angle estimation can be realized even when the phase voltage is saturated, and high-precision angle estimation can be realized even if the induced voltage constant changes.
[0622] First, the configuration of the position sensorless motor control device of the second embodiment will be described. Figure 11 It is a block diagram showing the configuration of the position sensorless motor control device according to the second embodi...
Embodiment 4
[0668] Next, a position sensorless motor control device in Embodiment 4 of the present invention will be described. The position sensorless motor control device of embodiment 1 uses the precise phase voltage equation to obtain the induced voltage value. On the other hand, the position sensorless motor control device of Embodiment 4 obtains the induced voltage value by using a simplified phase voltage equation, so the calculation time for angle estimation can be shortened.
[0669] ( Figure 15 illustrate)
[0670] First, a position sensorless motor control device according to Embodiment 4 will be described.
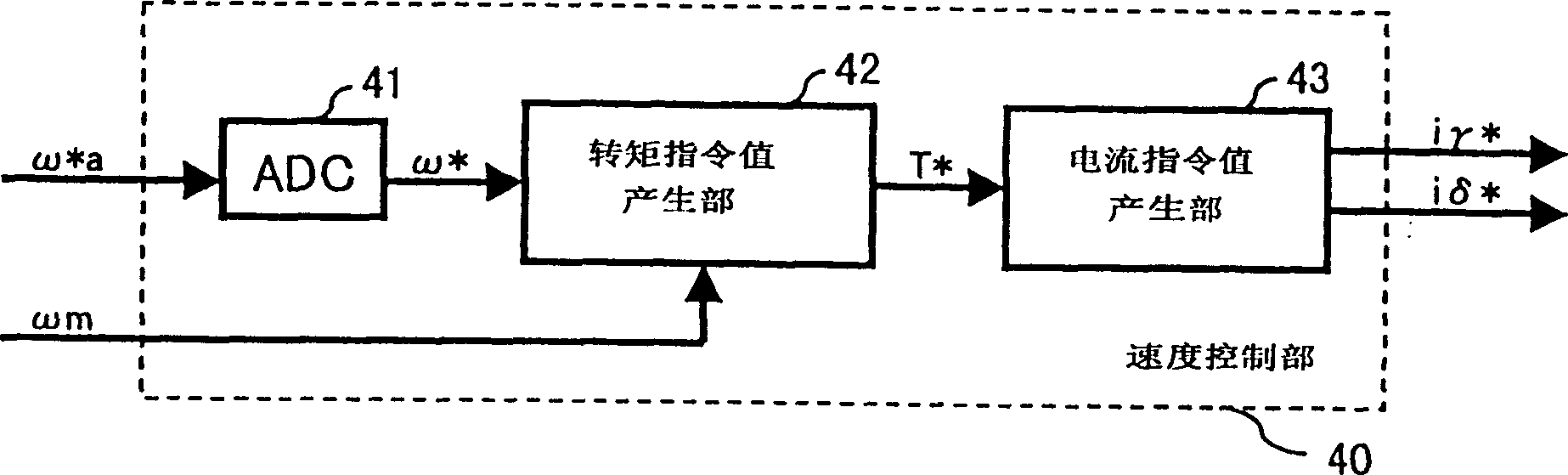
[0671] Figure 15 It is a block diagram showing the structure of the position sensorless motor control device in Embodiment 4, Figure 16 It is a block diagram showing the configuration of the angle estimation unit in the fourth embodiment. Only the microcomputer 422 is different from that of the first embodiment. The speed control unit 440, the current control unit...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com