Eco-friendly process for the preparation of chiral alcohols by asymmetric reduction of prochiral ketones
A chiral alcohol and prochiral technology, applied in biofuels, fermentation, organic chemistry, etc., can solve problems such as expensive cofactors and cumbersome recycling
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
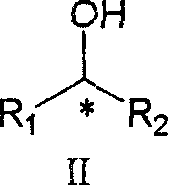
[0032] 50 g of washed Phaseolus aureus L (mung bean) was put into an Erlenmeyer flask and allowed to soak in deionized water (400 ml) for 24 hours. Add acetophenone I(a) (0.500 g; 0.004 mol) to Phaseolus aureus L (mung bean) soaked in the above water, seal and shake at 15-20° C. for 24 hours. The mung beans were then filtered off and washed with deionized water (3 x 100ml). The combined filtrates were extracted with chloroform (3 x 500ml). The chloroform layer was dried and a crude product (360 mg) was obtained. Pure 1-phenyl-(1S)-1-ethanol II(a) was obtained after silica gel column chromatography using chloroform as eluent.
[0033] Yield: 0.255g, 50%; ee: 84%; ([∝] 25 D = -37.8°, c = 1, methanol)
Embodiment 2
[0035] 50 g of washed Phaseolus aureus L (mung bean) was put into an Erlenmeyer flask and allowed to soak in deionized water (400 ml) for 24 hours. Add 4-chloroacetophenone I(b) (0.500 g; 0.0032 mol) to Phaseolus aureus L (mung bean) soaked in the above water, seal and shake at 15-20° C. for 24 hours. The mung beans were then filtered off and washed with deionized water (3 x 100ml). The combined filtrates were extracted with chloroform (3 x 500ml). The chloroform layer was dried to obtain a crude product (340 mg). After silica gel column chromatography using chloroform as eluent, pure 1-(4-chlorophenyl)-(1S)-1-ethanol II(b) was obtained.
[0036] Yield: 0.253g, 50%; ee: 89.76%; ([∝] 25 D = -38.6°, c = 1, chloroform)
Embodiment 3
[0038] 50 g of washed Phaseolus aureus L (mung bean) was put into an Erlenmeyer flask and allowed to soak in deionized water (400 ml) for 24 hours. Add 4-methylacetophenone I(c) (0.500 g; 0.0037 mol) to Phaseolus aureus L (mung bean) soaked in the above water, seal and shake at 15-20° C. for 24 hours. The mung beans were then filtered off and washed with deionized water (3 x 100ml). The combined filtrates were extracted with chloroform (3 x 500ml). The chloroform layer was dried to obtain a crude product (340 mg). Pure 1-(4-methylphenyl)-(1S)-1-ethanol II(c) was obtained after silica gel column chromatography using chloroform as the eluent.
[0039] Yield: 0.254g, 50%; ee: 94.54%; ([∝] 25 D = -48.5°, c = 1, chloroform)
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com