Polymer fibre web mfg. device and method
A polymer fiber and manufacturing device technology, which is applied in the field of polymer fiber net manufacturing device and polymer fiber net manufacturing, and can solve the problems that the technology for high-speed manufacturing of polymer fiber net has not yet been developed.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0070] After mixing 80g of dimethylacetamide (aimethylacetamide) in a stirrer, put polyvinylidene fluoride (polyvinylidene fluoride) copolymer (Atochem, Kynar761) into it and stir at 70°C for 24 hours to obtain a transparent polymer solution.
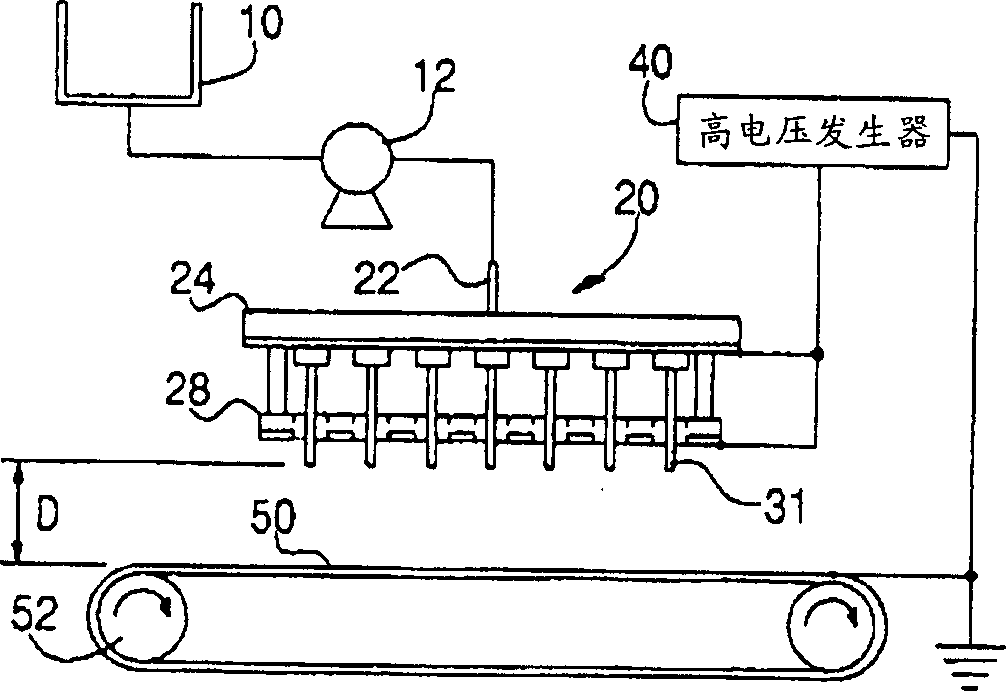
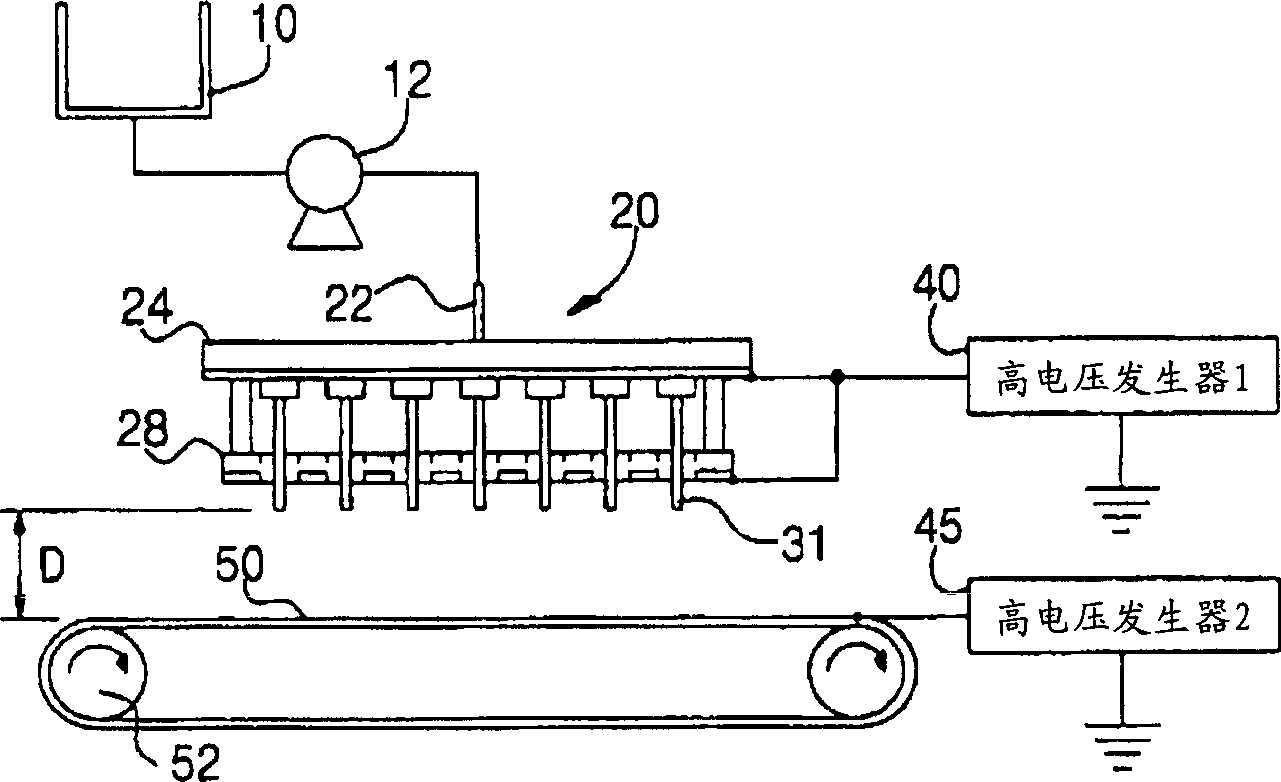
[0071] Put the polymer solution into the barrel 10, apply a voltage of 8-12KV to the conductive plate 30 having 42 single nozzles 32 with a needle 32a and the charge distribution plate 28, and the collector 50 is grounded.
[0072] The distance from the end of the needle 32a of the single nozzle 32 to the charge distribution plate 28 is 1.0 cm, and the height D between the needle 32a and the collector 50 is set to 8 cm.
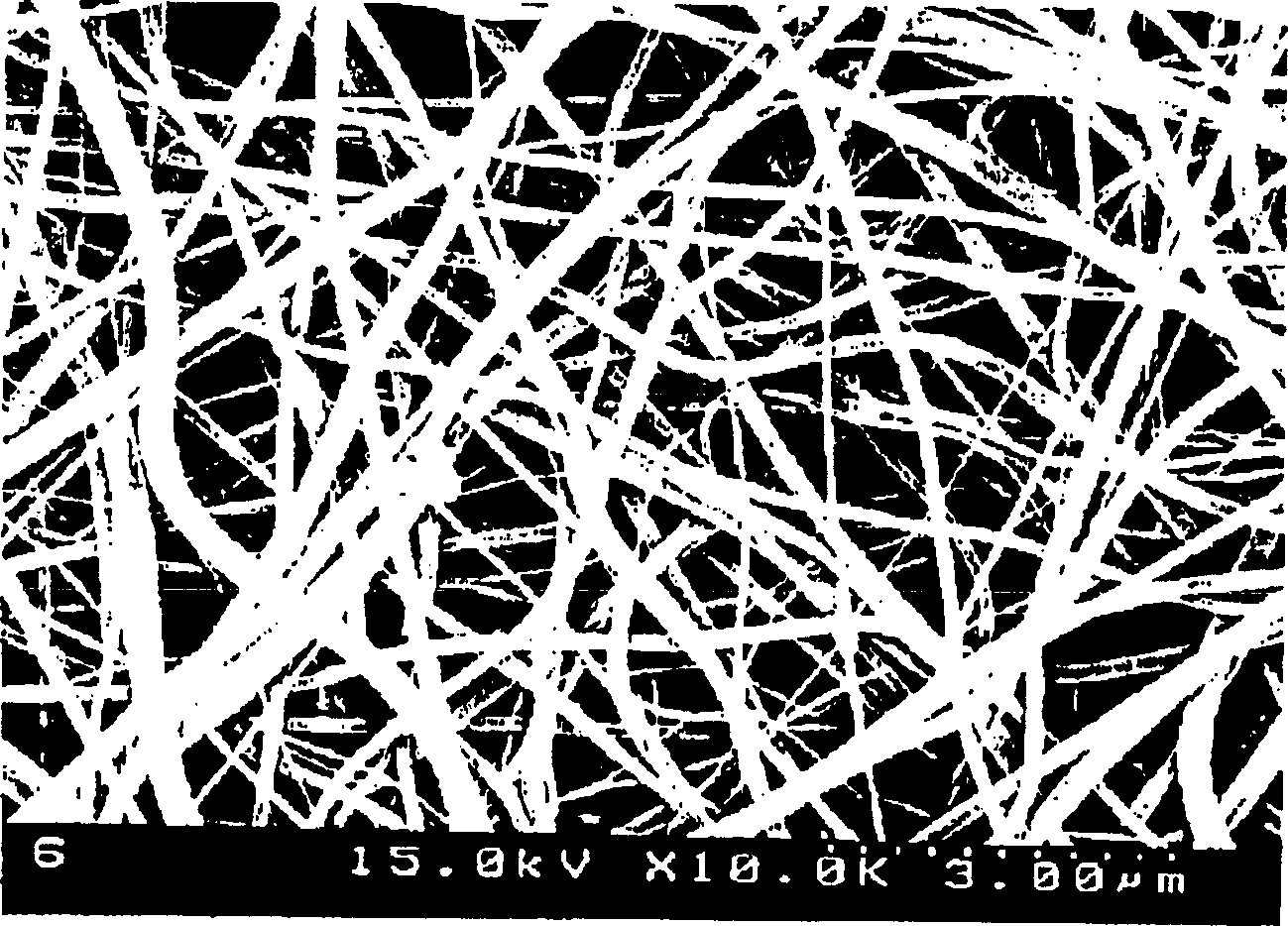
[0073] At this time, the collector 50 used a metal net (web), and the moving speed of the web was 10 m / min. The thickness of the produced porous polymer fiber web was measured with a micrometer, and the results are shown in Table 1.
[0074] Applicable voltage (kV)
Embodiment 2
[0076] After 80 g of acetone (aceton) was stirred and mixed in a stirrer, 20 g of polyvinylidene fluoride copolymer (Atochem, Kynar761) was put into it and stirred at 70° C. for 24 hours to obtain a transparent polymer solution.
[0077] The polymer solution is put into the barrel 10, and a voltage of 8-12KV is applied to the conductive plate 30 with 5 multi-nozzles 33 and the charge distribution plate 28 with 12 needles 32a, and the collector is grounded.
[0078] The distance from the end of the needle 32a of the multi-nozzle 33 to the charge distribution plate 28 was 1.2 cm, and the height D between the end of the needle of the multi-nozzle 33 and the collector 50 was set to 14 cm.
[0079] At this time, a metal net was used as the collector 50, and the moving speed of the net was 15 mm / min. The thickness of the produced porous polymer fiber web was measured with a micrometer, and the results are shown in Table 2.
[0080] Applicable voltage (kV)
Embodiment 3
[0082] 80 g of dimethylacetamide and 20 g of polyacrylonitrile polymer (PolyScience Co.) were put into a blender and stirred at 70° C. for 24 hours to obtain a transparent polymer solution.
[0083] Put the polymer solution into the bucket 10, apply a voltage of 8-16KV to the conductive plate 30 of the two multi-nozzles 33 with 4 needles 33a and the charge distribution plate 28, and the collector 50 is grounded.
[0084] The distance from the end of the needle 33a of the multi-nozzle 33 to the charge distribution plate 28 was 1.6 cm, and the height D between the end of the needle 33a of the multi-nozzle 33 and the collector 50 was set to 15 cm.
[0085] At this time, a metal plate was used as the collector 50, and the moving speed of the metal plate was 3 m / min. The thickness of the produced porous polymer fiber web was measured with a micrometer, and the results are shown in Table 3.
[0086] Applicable voltage (kV)
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com