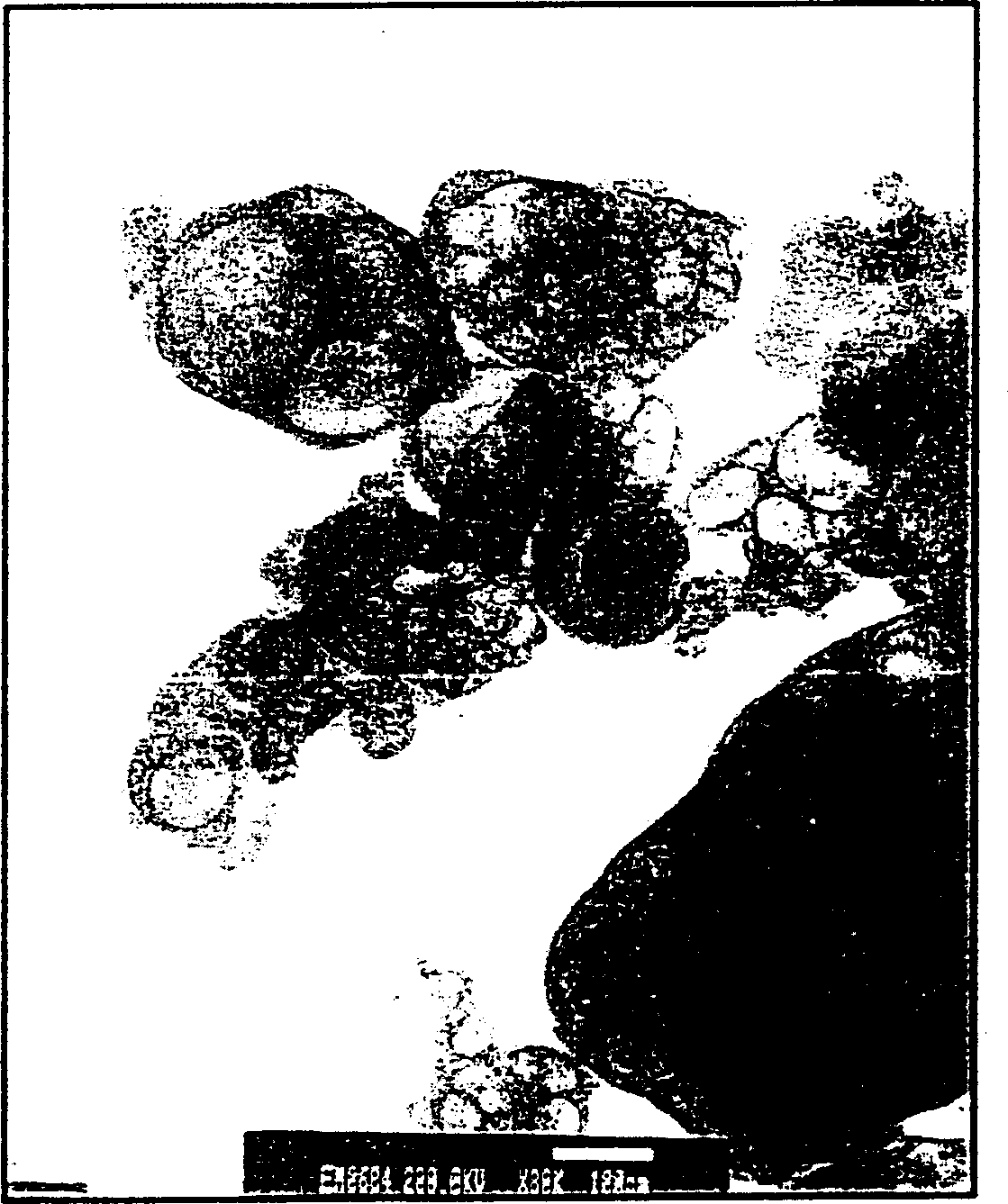
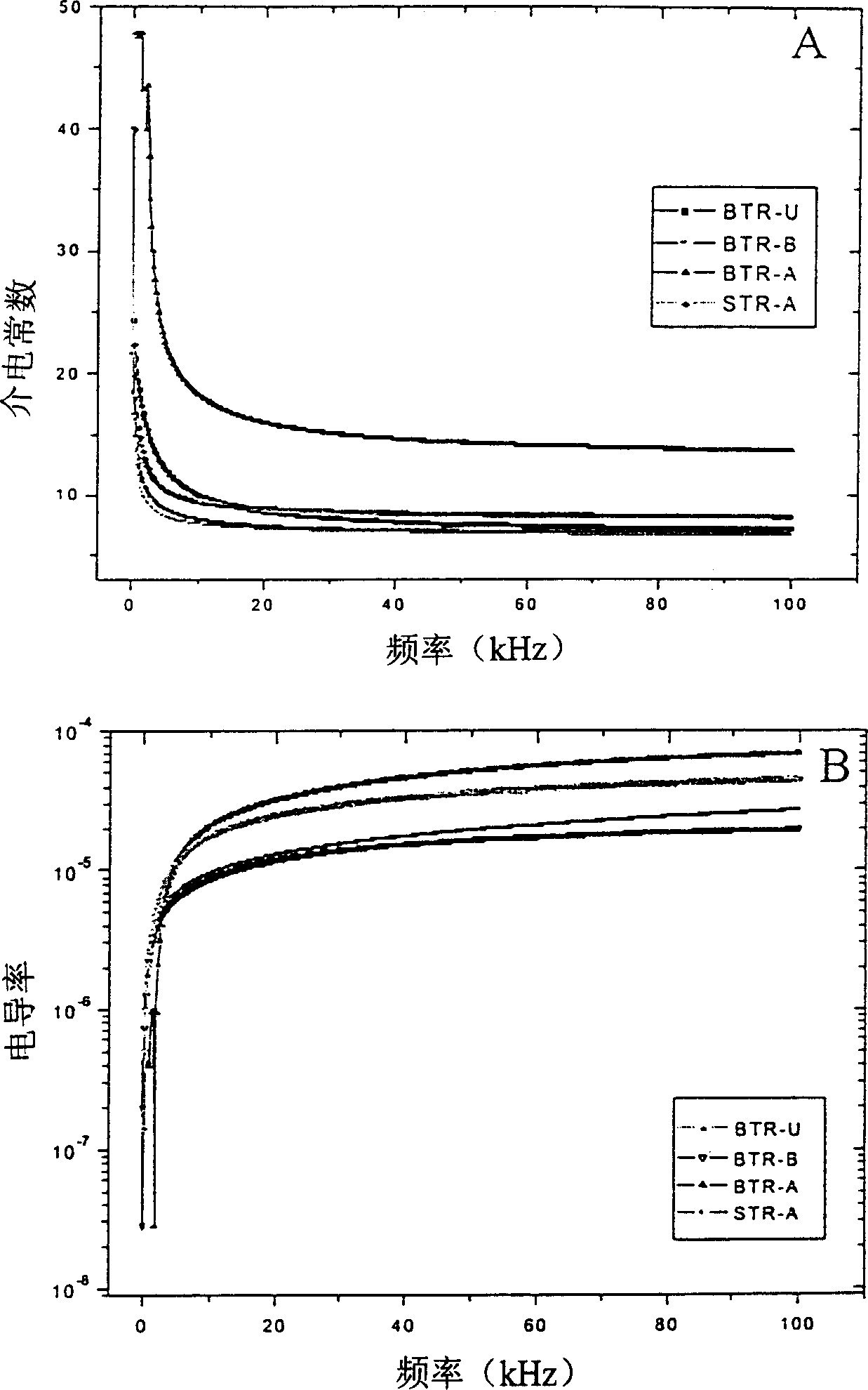
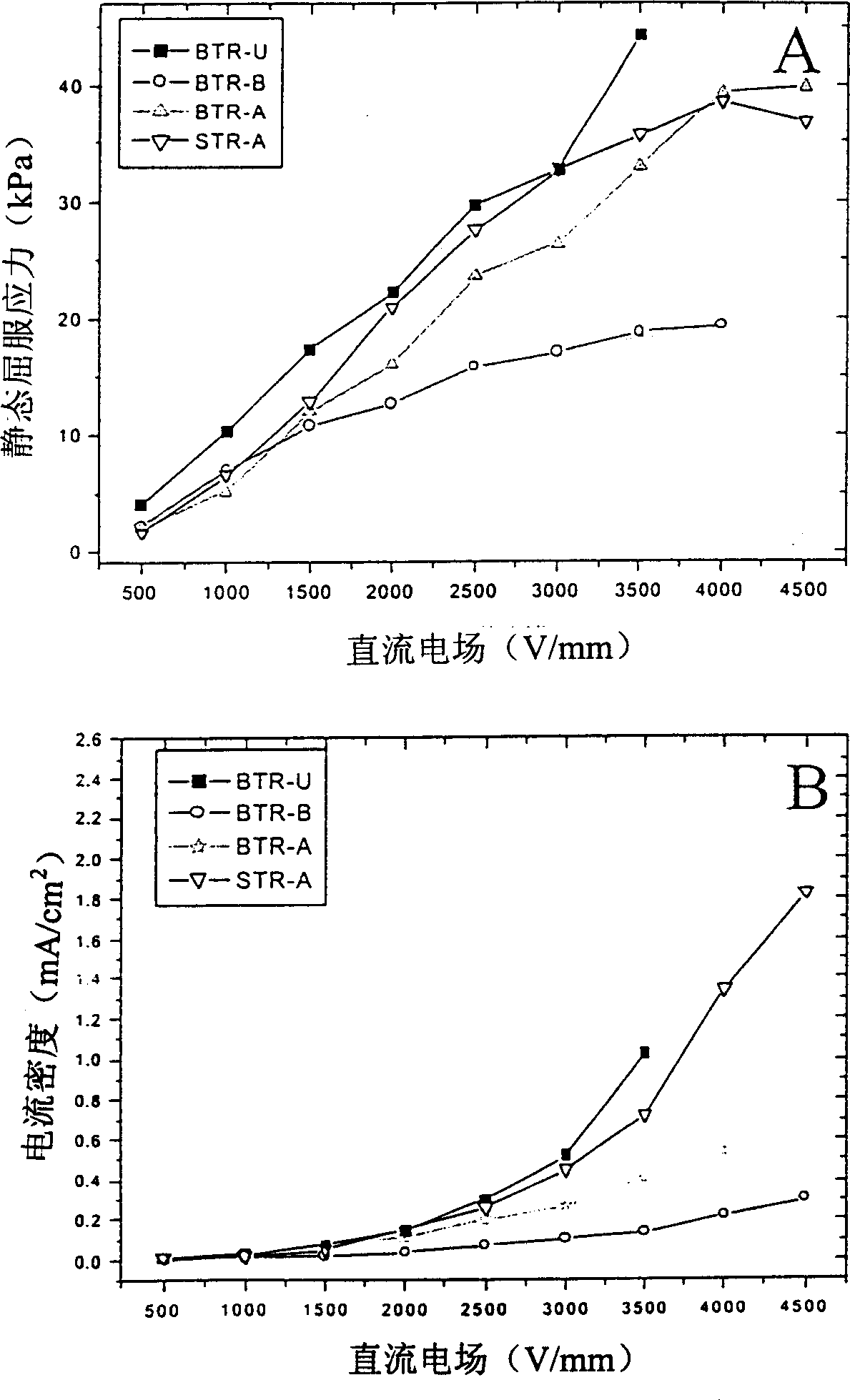
Electric rheological liquid
A technology for electrorheological fluids and liquids, used in the preparation of carboxylates, binders, additives, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0018] Example of Particle Manufacturing
[0019] The manufacture of particles useful in embodiments of the invention will now be described by way of example.
[0020] BTR (urea)
weight / g)
water (ml)
barium chloride
73.35
150
Rubidium Chloride
3.63
75
Titanium(IV) chloride
33
300
Oxalic acid 2-hydrate
94.56
750
Urea
45
165
[0021] First, rubidium chloride was dissolved in distilled water at room temperature, and barium chloride was dissolved in distilled water at a temperature ranging from 50°C to 70°C. Simultaneously, oxalic acid was dissolved in water under an ultrasonic tank at 65 °C. It may take 1 hour for the oxalic acid to completely dissolve. A solution was also prepared with titanium(IV) chloride. Because titanium(IV) chloride is very reactive in water, the liquid should be added slowly to the water using a disposable plastic dropper.
[0022] The solutions...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com