Use of CD 23 antagonists for treatment of neoplastic disorders
An antagonist, tumor technology, applied in the direction of diseases, anti-tumor drugs, skin diseases, etc., can solve the problem of unsustainable remission
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0138] Expression of CD23 in B lymphoma and B-CLL cells
[0139] The expression of CD23 in several lymphoma cell lines was determined by flow cytometry. More specifically, CD23 expression was evaluated by flow cytometry using an anti-CD23 PE-labeled antibody (BD Biosciences, Cat. No: 33615X). Relative fluorescence intensity (RFI) of antibody binding was determined by comparing the mean fluorescence intensity of anti-CD23-PE antibody bound to cells with that of PE-labeled calibration beads (QuantiBrite). CD23 relative expression was calculated as RFI(sample)÷RFI of SKW cells.
[0140] B lymphoma cell lines expressing CD20 and B7 (SKW, SB, Daudi, Raji, Ramos and DHL-4 cells) were cultured in complete medium. The complete medium was RPMI 1640 medium (Irvine Scientific, Santa Ana, CA), supplemented with 10% heat-inactivated FBS (Hyclone), 2 mM 1-glutamine, 100 units / ml penicillin, and 100 ug / ml streptomycin . The SKW cell line is Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) positive and...
Embodiment 2
[0148] Expression of CD23 in CLL cells
[0149] To demonstrate the clinical utility of the present invention, CD23 expression was measured in whole blood on several different CLL samples (31 patients) by flow cytometry. Flow cytometric analysis was performed essentially as described in Example 1 using appropriate reagents. In this regard, in CD19 + The expression of CD20 and CD23 was measured on positive sorted cells. Specifically, PE-labeled anti-CD20 (BD Biosciences / Pharmingen, Cat # 555623) and anti-CD23 (BD Biosciences / Pharmingen, Cat # 33615X) monoclonal antibodies were used to detect CD20 and CD23 molecules, respectively.
[0150] In all patients, in CD19 + Both CD20 and CD23 antigens were detected in B cells, as shown in Table 2 below. Patients expressing high CD20 levels expressed varying degrees of CD23 antigen in their CLL samples. The expression level by CD19 + The percentage of cells and the mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) were determined. ...
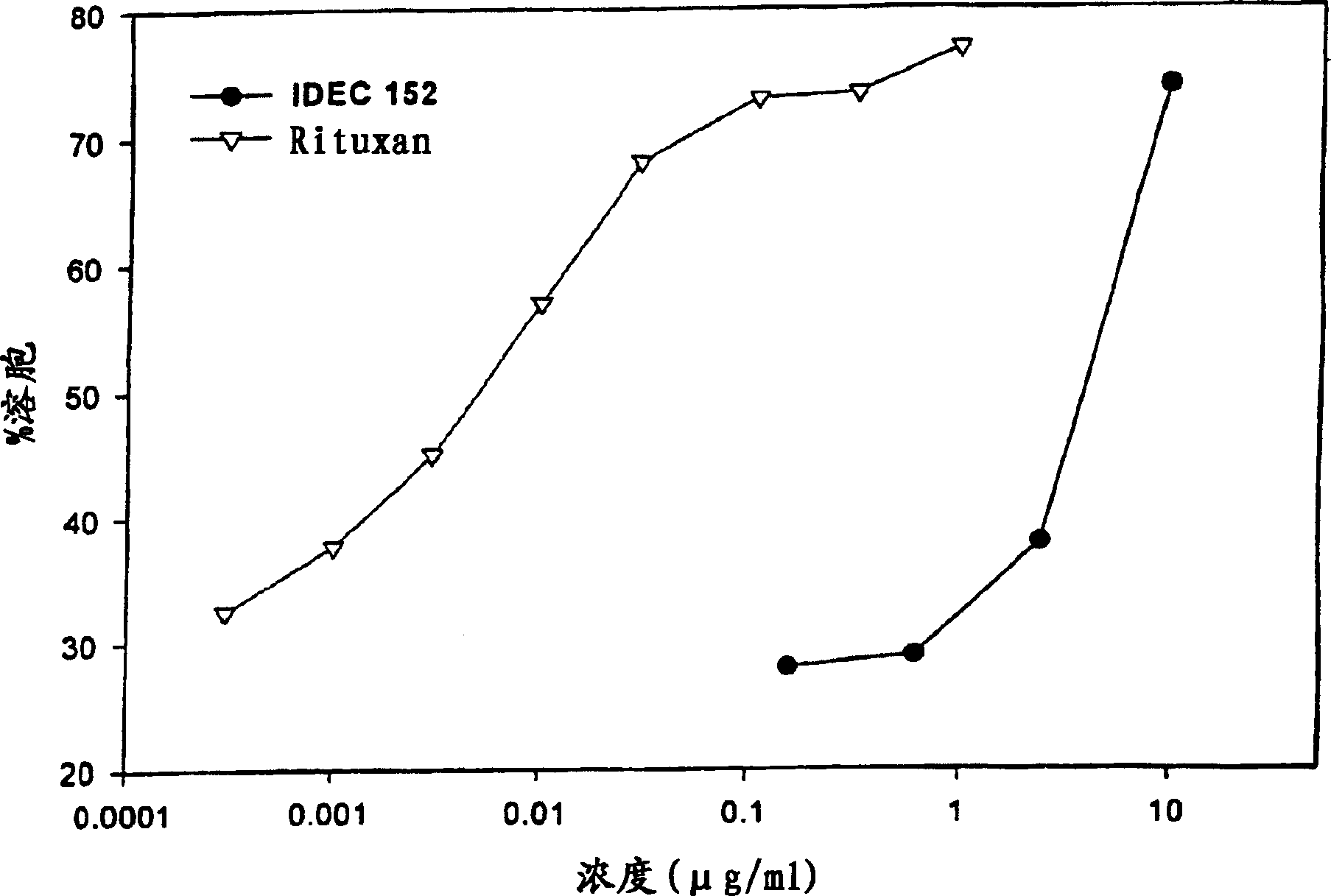
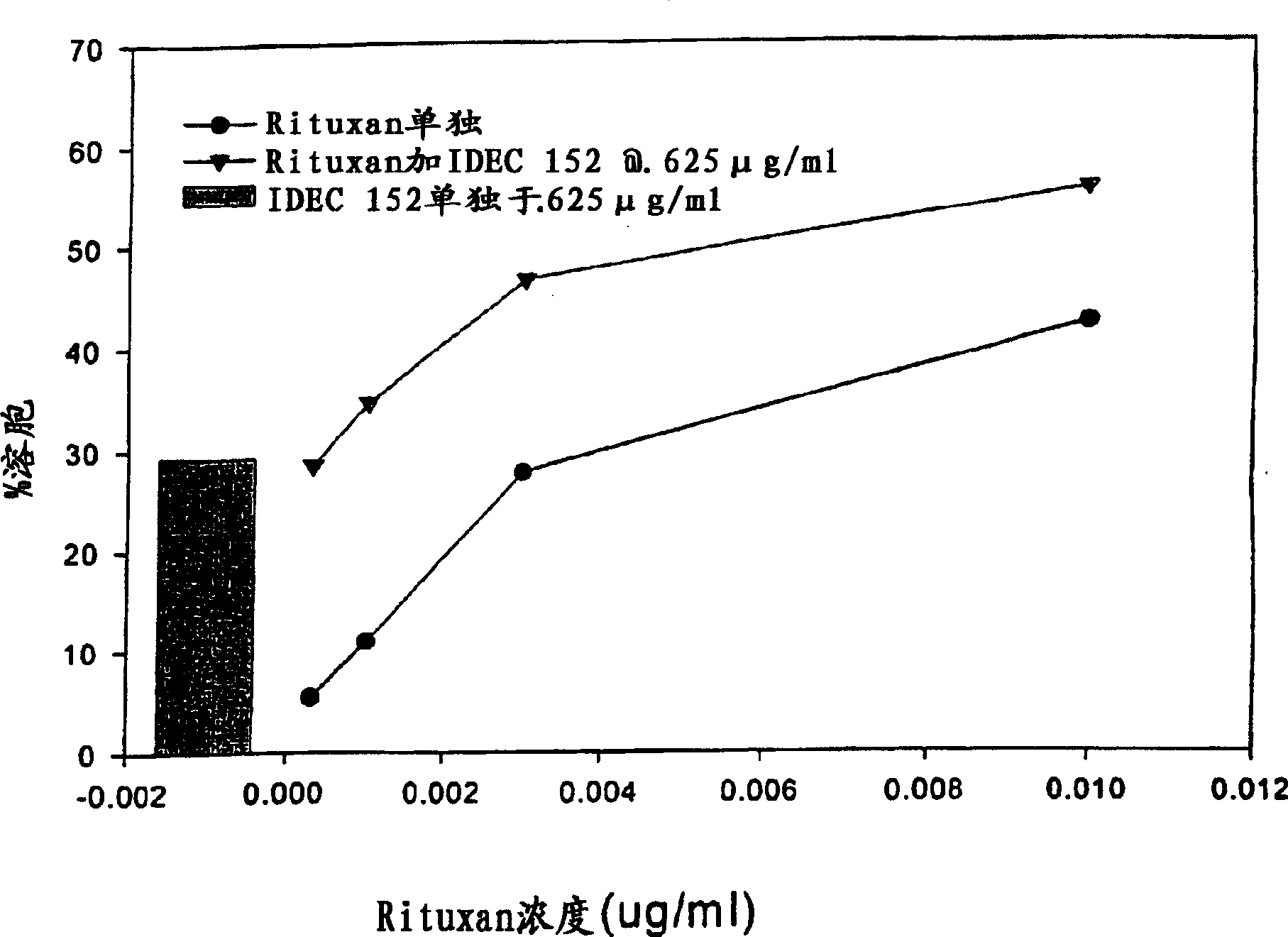
Embodiment 3
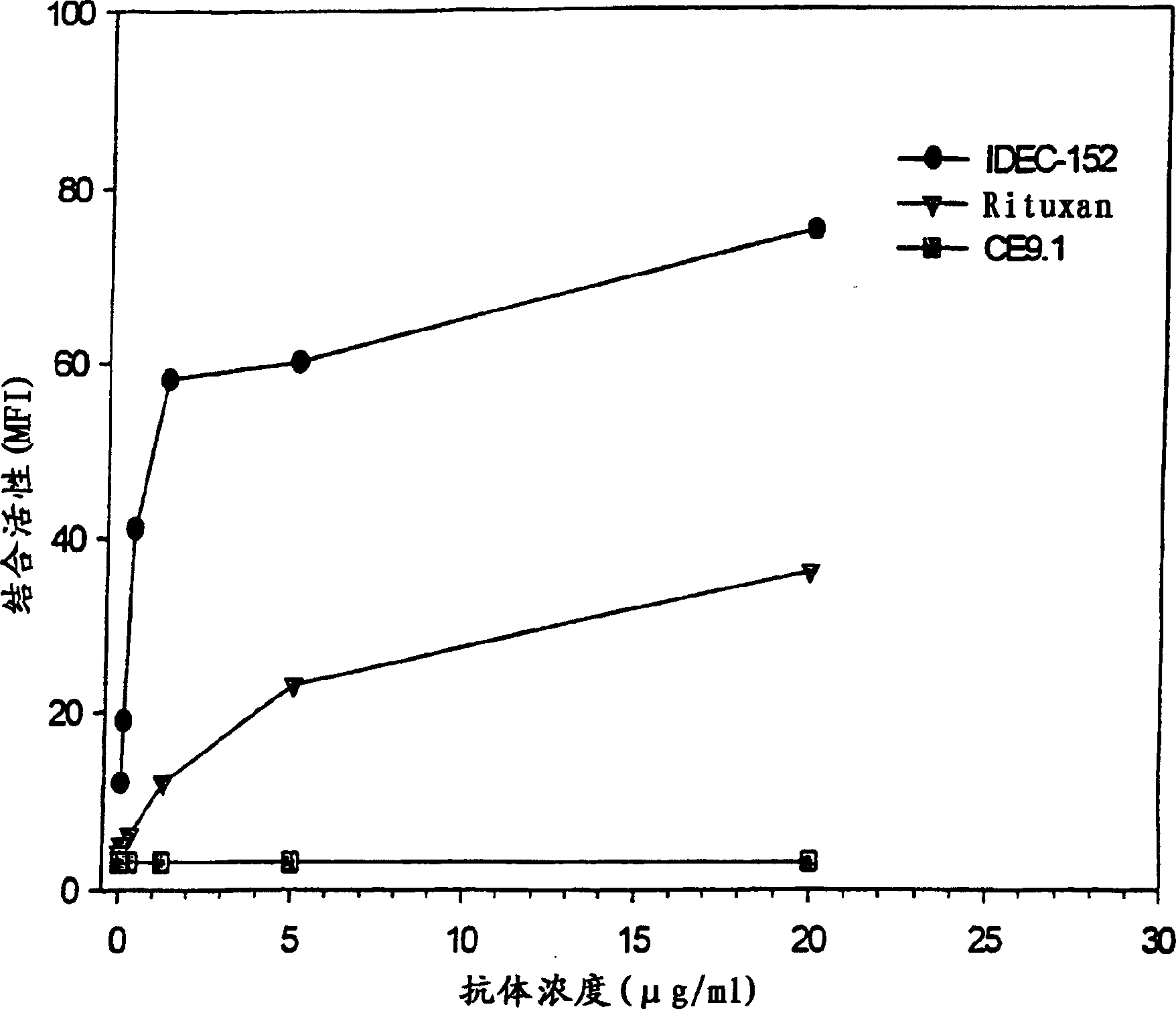
[0154] IDEC-152 and CD23 + cell binding
[0155] In order to further confirm the advantages of the present invention, as described in the previous examples, the binding activity of IDEC-152 to CD23 on SKW lymphoma cells was measured by flow cytometry. As noted above, SKW cells can be used to provide a clinically relevant model of CD23+ malignancies including CLL. See the test results figure 1 , which showed the specific binding of Rituxan and IDEC-152 to SKW cells in a concentration-dependent manner. Binding activity was measured using mean fluorescence intensity, which showed that SKW cells bound substantially higher levels of anti-CD23 antibody than anti-CD20 antibody. This suggests that in certain cell lines and tumors, CD23 may present a higher epitope density than other markers such as CD20. As expected, an isotype-matched control antibody of irrelevant specificity (CE9.1, directed against CD4) did not bind SKW. This example, and in figure 1 The correspon...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com