Use of biologically active HIV-1 Tat, fragments or derivatives thereof for preventing or therapeutic vaccination and/or treating other diseases
A biologically active, derivative technology for targeting and/or activating antigen-presenting cells in biologically active HIV-1 T at, fragments or derivatives thereof for prophylactic or therapeutic immunization and/or treatment of other diseases, and/or the area of use of the transported cargo molecules, able to resolve issues such as no claim for protection
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
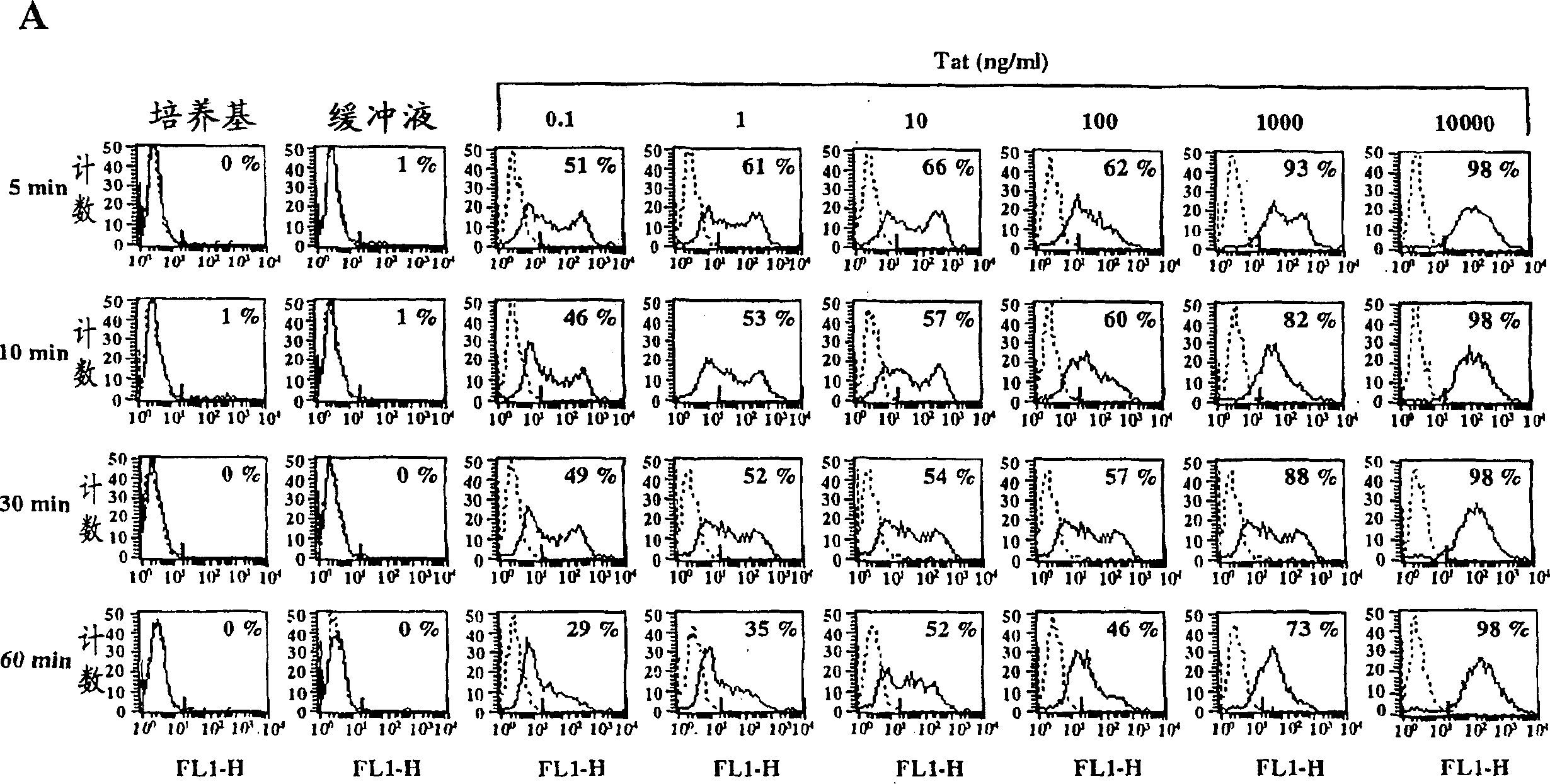
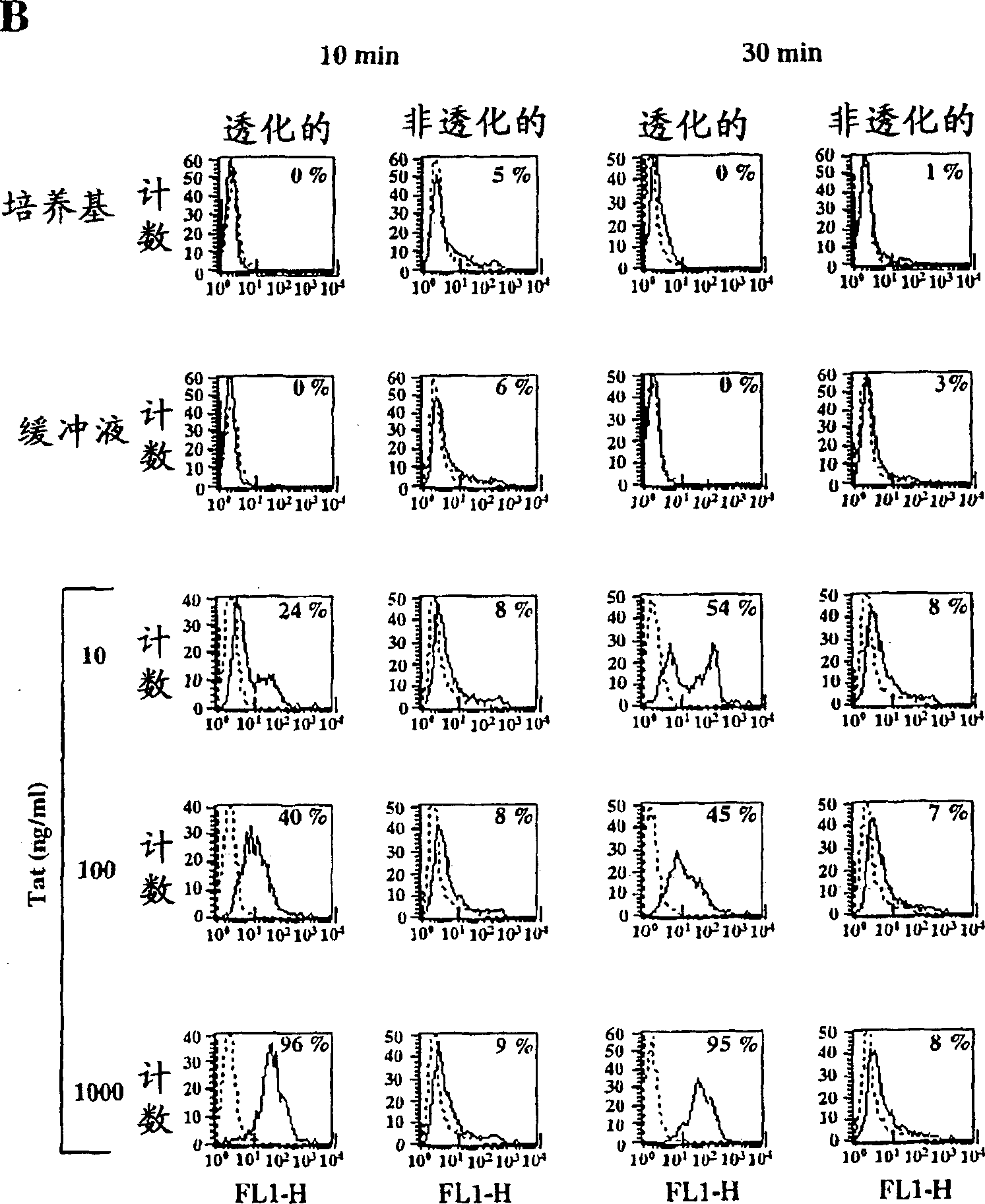
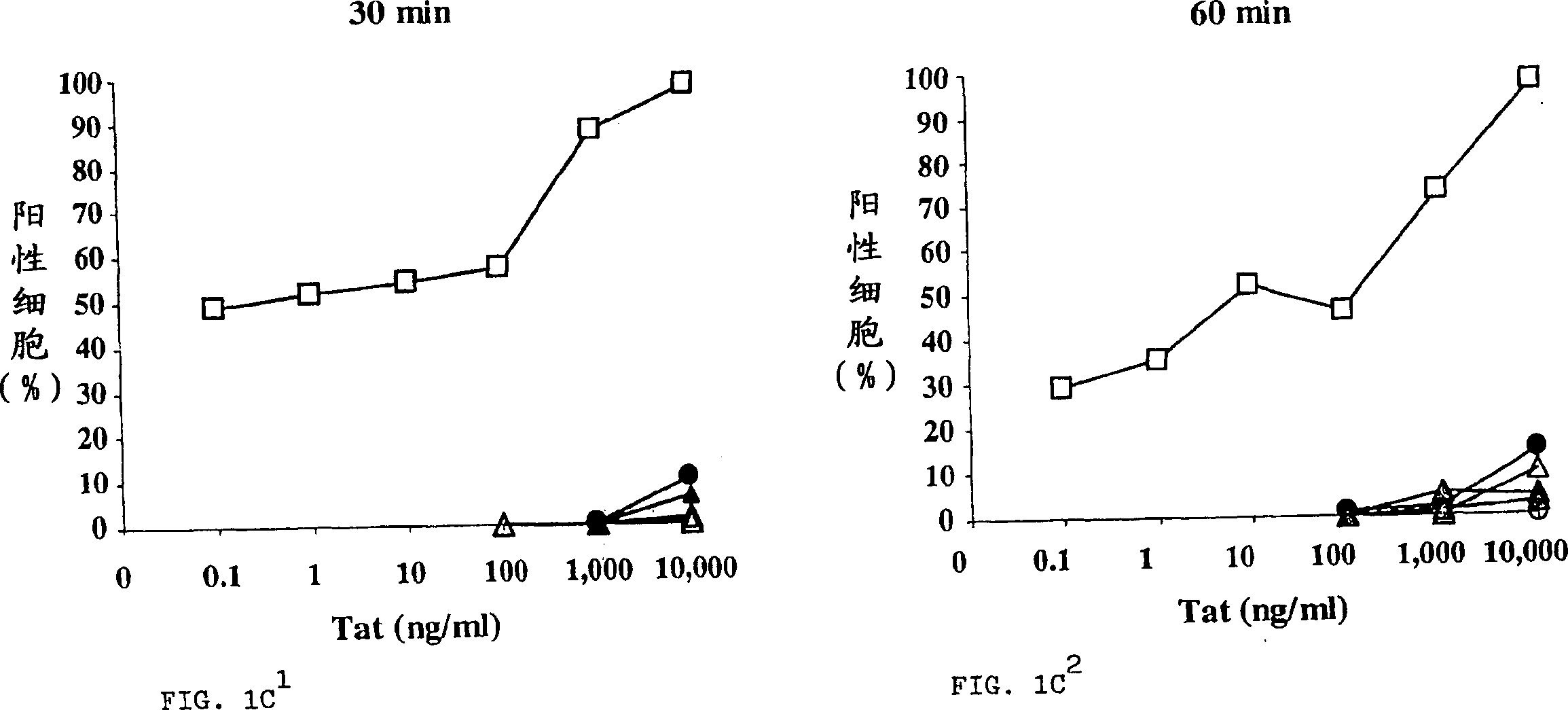
[0389] Active Tat is efficiently taken up by MDDCs but not TCBs and BLCLs
[0390] Uptake of active Tat by MDDCs, TCBs, and BLCLs was assessed by intracellular immunofluorescence in flow cytometry using specific affinity-purified polyclonal antibodies on permeabilized cells. Figure 1 shows the results for a representative donor whose Tat uptake level represents the median value obtained from the 14 donors tested. Tat uptake by MDDCs is highly efficient and occurs in a dose- and time-dependent manner (attached Figure 1A ). Uptake of Tat was already evident with the lowest dose (0.1 ng / ml). Regardless of the Tat concentration tested, the level of staining always peaked after 5 min of incubation and diminished after 60 min, likely due to protein processing. However, high levels (98%) of Tat uptake remained at the highest Tat dose used (10 μg / ml) up to 60 minutes of incubation. No staining was observed for cells incubated with medium or reconstitution buffer alone (attached F...
Embodiment 2
[0394] The uptake of active Tat by MDDCs increases with cell maturation and is lost due to protein oxidation and inactivation.
[0395] Immature MDDCs take up antigens through phagocytosis and pinocytosis (Bankereau 1998; Bell 1999). Mature DCs lose these activities despite their acquisition of strong antigen-presenting capacity. To verify whether cell maturation affects the uptake of natural Tat, LPS was used to induce MDDC maturation. Compared with immature MDDC, mature MDDC expressed higher levels of surface markers HLA-DR, CD83 and CD86. Either immature or mature cells were subsequently used for uptake assays. Tat uptake was greatly enhanced by MDDC maturation at all protein concentrations tested (attached Figure 2A ). Indeed, culture of mature MDDCs with low Tat concentrations showed similar levels of intracellular staining as observed for immature cells at the highest Tat dose (attached Figure 1A and 2A ).
[0396] Tat contains seven cysteines and is extremely se...
Embodiment 3
[0408] Blockade of active Tat uptake by MDDCs with anti-α5β1 and anti-αvβ3 monoclonal antibodies or their natural ligands FN or VN.
[0409] To verify whether the uptake of Tat by MDDC is subject to the specific receptor-mediated endocytosis pathway, specific monoclonal antibodies or competitor ligands against integrin receptors α5β1 and αvβ3 were tested. These receptors are selected from several receptors that bind Tat on different cell types because they are highly expressed by activated endothelial cells and KS cells that proliferate, migrate and adhere in the presence of Tat and this is regulated by the TatRGD domain Mediated by binding to α5β1 and αvβ3 integrins. as attached Figure 3A , B, both anti-α5β1 and anti-αvβ3 mAbs inhibited the uptake of Tat by MDDCs, and this blockade was complete in the presence of both antibodies (attached Figure 3A , B). The natural ligands for these receptors, FN and VN, similarly block Tat uptake (attached Figure 4A , B). Thus, α5β1...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com