Magnetoresistance effect type magnetic head and its mfg. method
A magnetoresistance and magnetic head technology, which is applied in the manufacture of magnetic flux-sensitive magnetic heads, magnetic recording heads, magnetic recording, etc., can solve the problems of not disclosing the means of returning the reversed magnetic moment to the original direction, and not disclosing the specific method of damage, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0051] Although this embodiment can be widely used in detecting external magnetic fields (for example, as a sensor), it refers here to a read head that is particularly useful for information recording and reading systems. Information is recorded as a distribution of magnetic domains. As the magnetic recording medium, any kind of medium can be used, for example, a magnetic tape, a magnetic drum, one or more hard disks, and the like. The magnetic regions are usually arranged along the track, and the structure of the track can be circular, spiral, spiral, or indefinite in length.
[0052] Figure 13 An example of a typical information recording and reading device is shown. The electronic computer 1 accepts input information through an input device 2 having one or more interfaces between a network, a keyboard, a scanner, or their equivalents. In addition to being connected to one or more input devices 2 , the computer 1 can also output to one or more output devices 3 . As the ...
Embodiment 2
[0211] Figure 8 The specific structure of the readout sensor representing another embodiment of the present invention will be described in detail later, refer to Figure 8 In terms of its structure, the spin-valve film 18 has a first ferromagnetic layer (hereinafter referred to as a free layer, corresponding to, for example, the CoFe film 44 and the Permalloy film 45 ) that is relatively easy to respond to a magnetic field, and is difficult to respond to a magnetic field. The second ferromagnetic layer (hereinafter referred to as a pinned layer, corresponding to the stacked pinned layer 50), and a conductive nonmagnetic spacer layer (for example, corresponding to the Cu film 43) between them. In addition, under the fixed layer, there is a substrate layer 42 for adjusting the crystal morphology and for increasing the resistance change. Furthermore, a capping layer (for example, corresponding to the Ta capping layer 46 ) is formed on the free layer composed of 44 and 45 .
[...
Embodiment 3
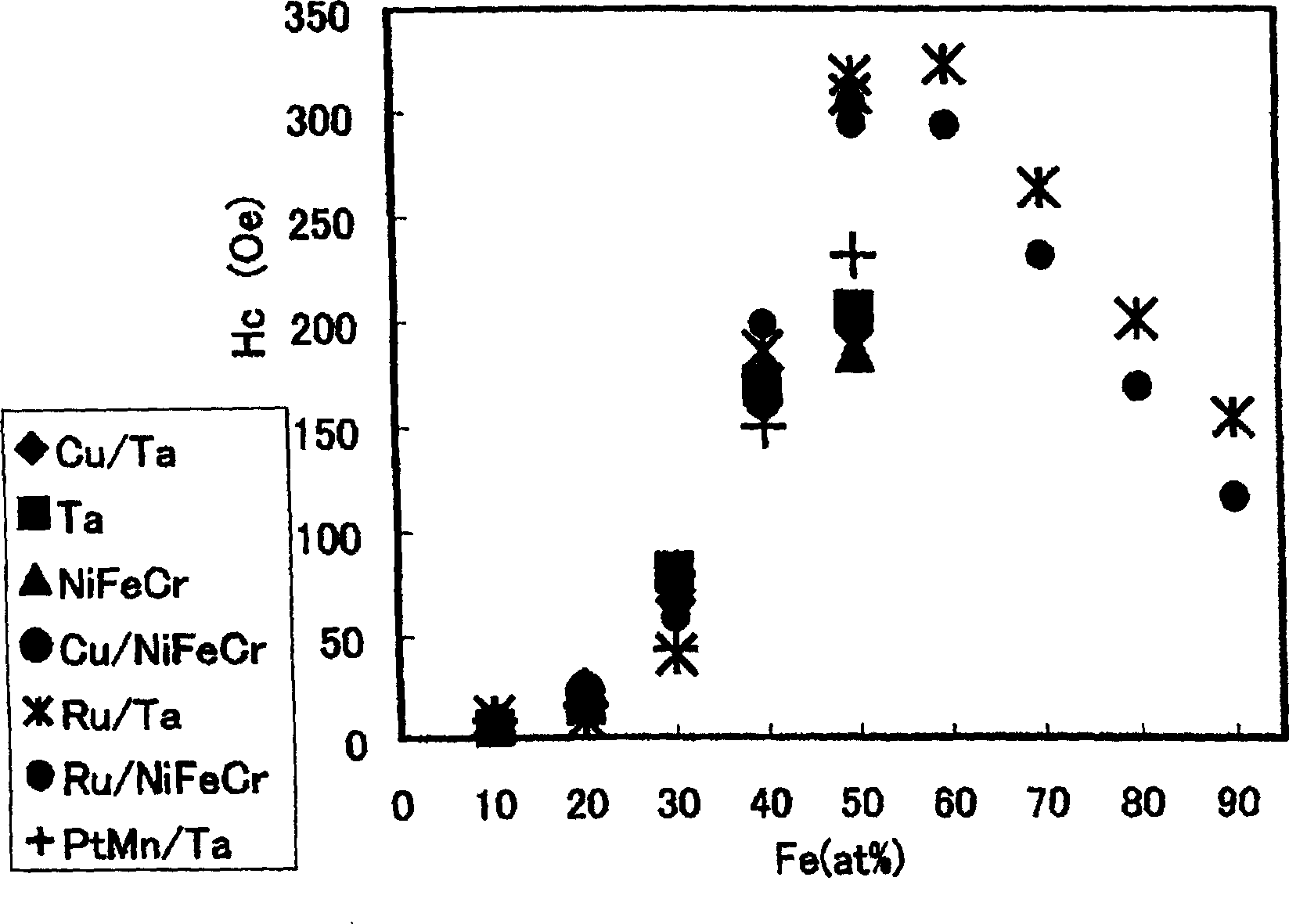
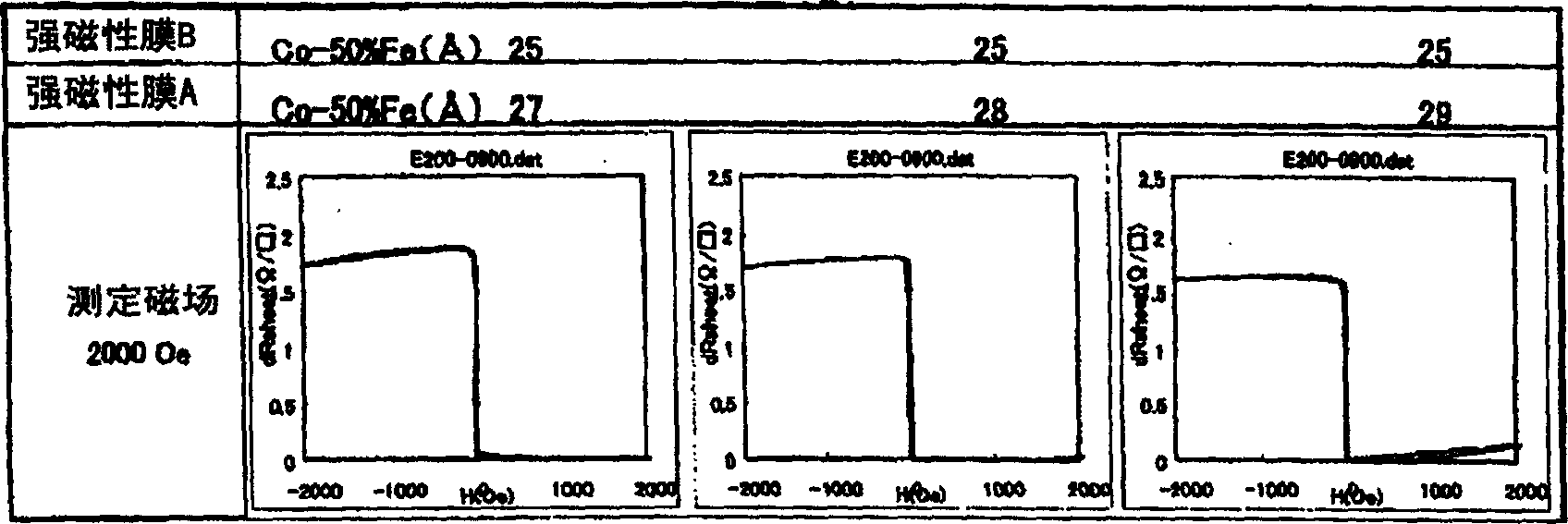
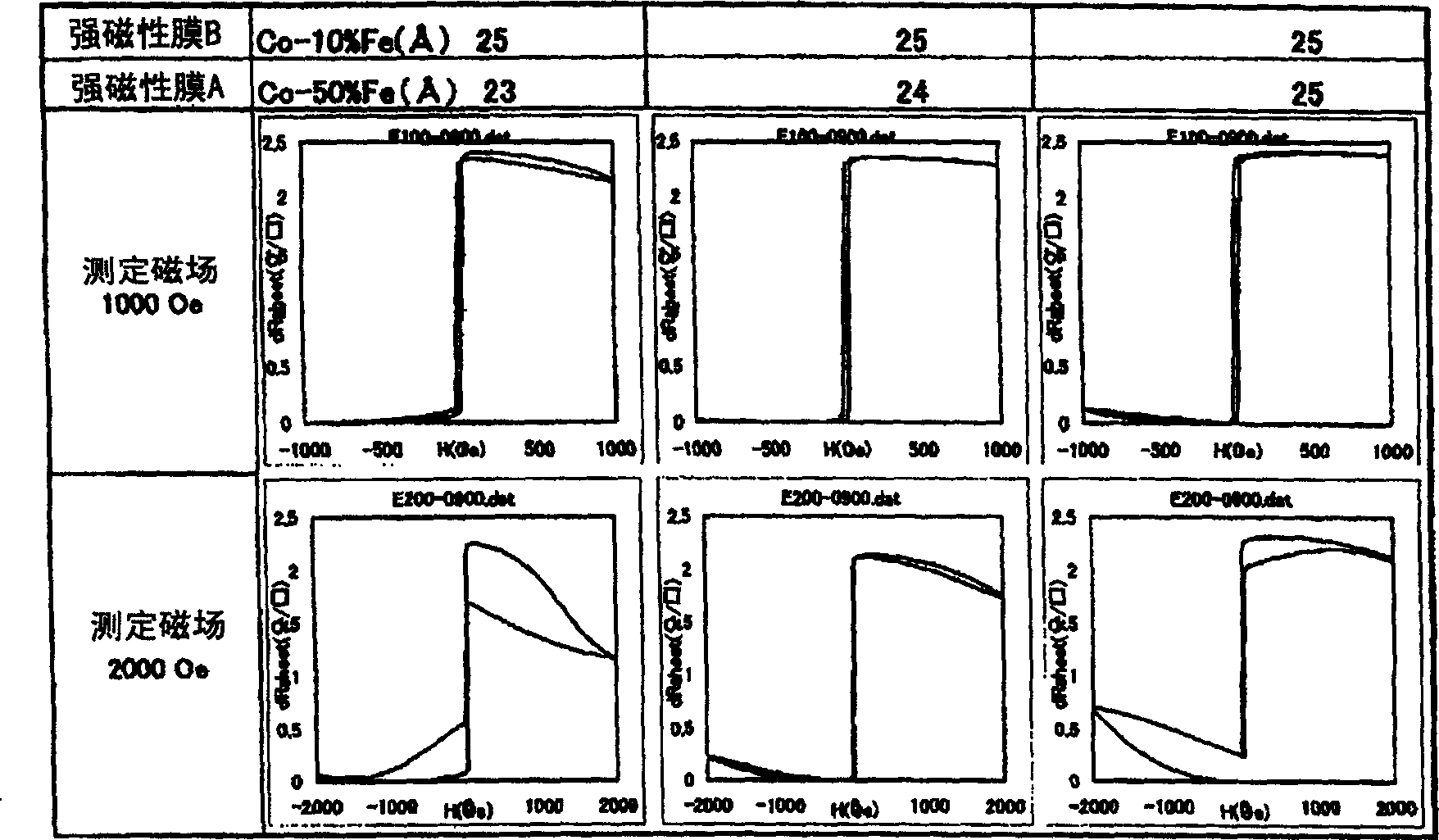
[0254] In Example 1 and Example 2, in order to increase the coercive force of the ferromagnetic film and make the composition of CoFe within an appropriate range, as another method, there is a method of adding additional elements to Co or CoFe. Elements to be added include elements such as Cr and V.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com