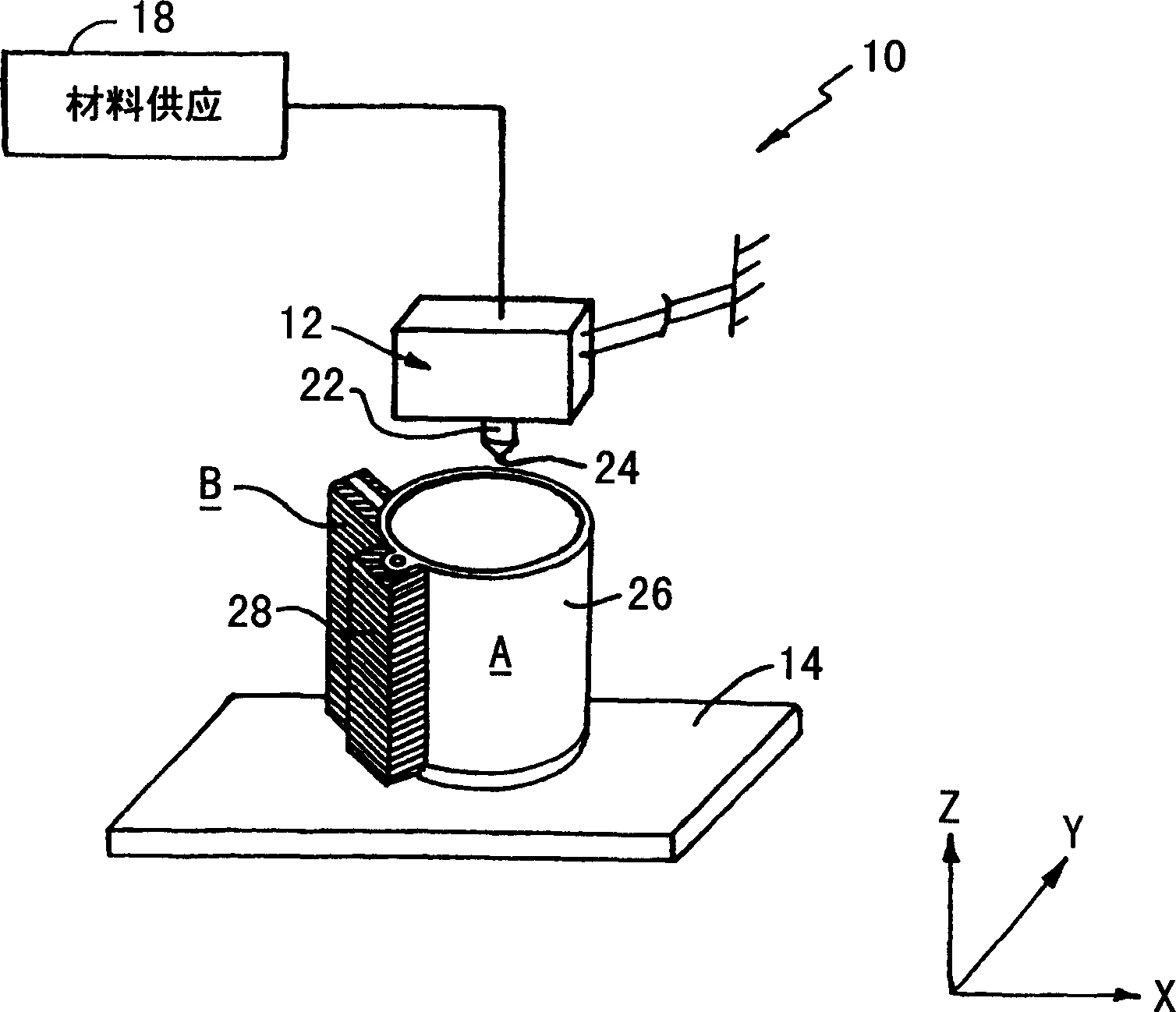
Material and method for three-dimensional modeling
A technology for modeling materials and three-dimensional objects, which is applied in the direction of liquid material additive processing, additive processing, processing and manufacturing, etc., and can solve the problems of not teaching support materials, not disclosing support materials, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0032] Modeling material : The molding material A is polycarbonate resin. A specific exemplary polycarbonate resin is Lexan(R) HF 1110 (available from General Electric Plastics). This resin has a heat deflection temperature of 156°C and a melt flow at 300°C under a load of 1.2kg in the range of 20-30 gms / 10min. Polycarbonate resin was successfully extruded from a liquefier at about 320°C into a build chamber at about 135°C.
[0033] support material : The support material B is a resin comprising a mixture of polyphenylene ether and polyolefin, such as high-impact polystyrene. The desired weight percent range is about 50-90% polyphenylene ether and about 10-50% polyolefin. A specific example of a resin is a mixture of 75 wt% Noryl(R) 731 polyphenylene ether and 25 wt% Noryl(R) N300X high impact polystyrene (each available from General Electric Plastics). This resin has a heat deflection temperature of 178°C and a melt flow similar to molding materials. Extruded from a l...
example 2
[0035] Modeling material : The molding material A is polycarbonate / acrylonitrile-butadiene-styrene resin. To provide the material with the enhanced strength and toughness of polycarbonate, the resin should contain at least about 50% by weight polycarbonate. A particularly preferred polycarbonate / acrylonitrile-butadiene-styrene resin is Cycoloy(R) C1110HF (available from General Electric Plastics). This resin has a heat deflection temperature of 143°C and a melt flow at 280°C under a load of 1.2kg in the range of 10-20 gms / 10min. The polycarbonate / acrylonitrile-butadiene-styrene resin was successfully extruded from a liquefier at about 320°C into a build chamber at about 110°C.
[0036] support material : The support material B is a resin comprising a mixture of polyphenylene ether and polyolefin, such as high-impact polystyrene. The desired weight percent range is about 40-80% polyphenylene ether and about 20-60% polyolefin. A specific example of a resin is Noryl(R) 731...
example 3
[0038] Modeling material : The molding material A is polyphenylsulfone resin. An example of a specific polyphenylsulfone resin is Radel(R) R 5600 NT (available from BP Amoco). This polyphenylsulfone resin has a heat deflection temperature of 236°C and a melt flow at 400°C under a load of 1.2kg in the range of 20-30 gms / 10min. Polyphenylsulfone resin was successfully extruded from a liquefier at about 400°C into a build chamber at about 200°C.
[0039] support material : The support material B is a resin comprising a mixture of polyphenylsulfone and amorphous polyamide. The material may further comprise polysulfone. The desired weight percent range is a mixture of about 60-90 wt % polyphenylsulfone and about 10-40 wt % amorphous polyamide, or about 60-90 wt % polyphenylsulfone, about 1-40 wt % polysulfone and about 10 wt % - 40% by weight of a mixture of amorphous polyamides. A specific exemplary resin is 50 wt% Radel® R 5600 NT polyphenylsulfone (available from BP Amoc...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Heat deflection temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Heat deflection temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com