Quantity-of-light adjusting device, optical system having the same, and photographing device
A light quantity adjustment, optical technology, applied in optics, optical components, apertures, etc., can solve problems such as the impact of optical performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
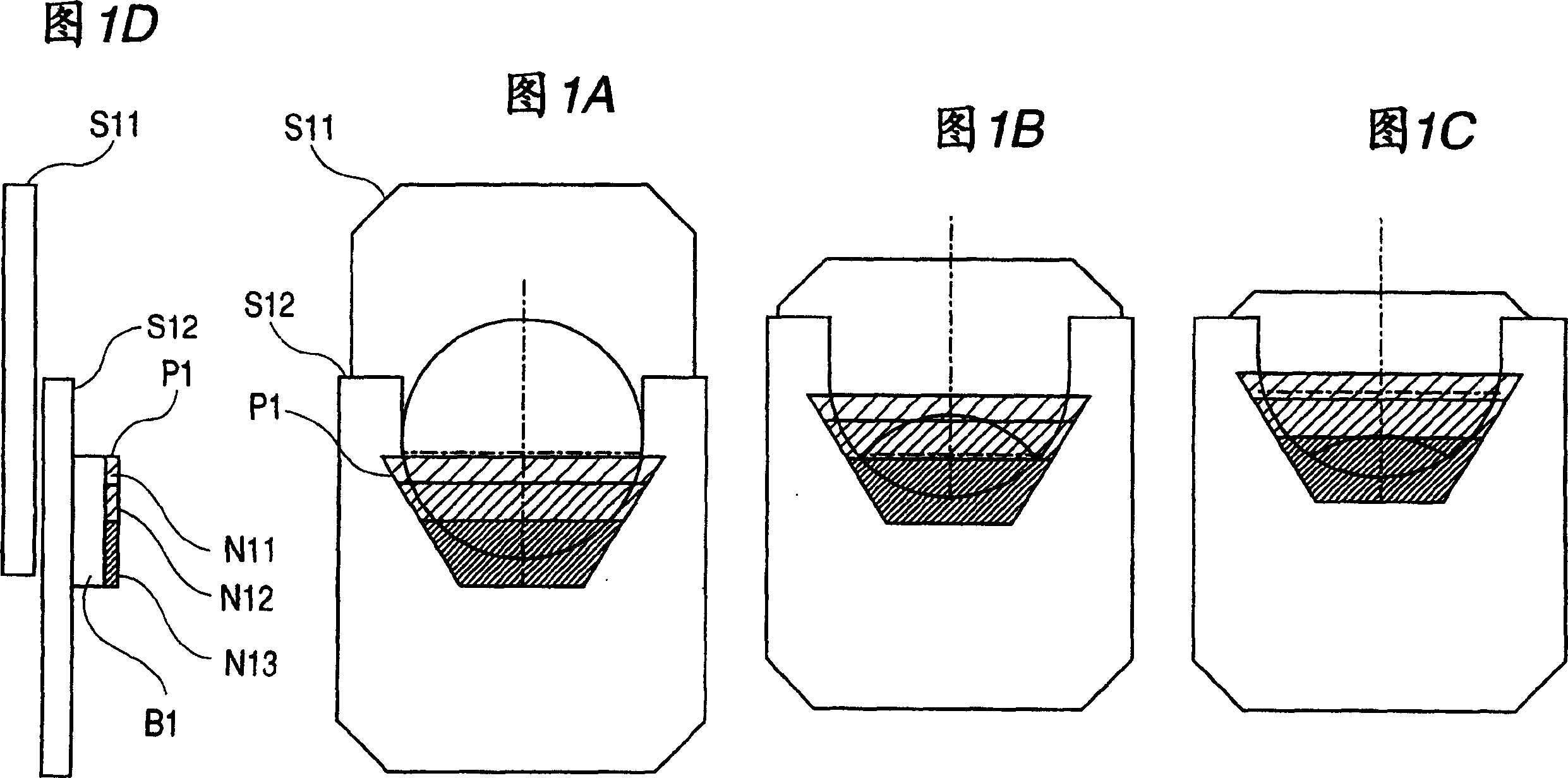
[0121] FIG. 1 shows Embodiment 1 of the present invention. Fig. 1A, Fig. 1B, Fig. 1C, and Fig. 1D are examples of a light quantity adjusting device (diaphragm device) to which the present invention is applied. FIG. 1A shows an open aperture state, FIG. 1B shows an intermediate aperture state, FIG. 1C shows a minimum aperture state, and FIG. 1D shows a side view of FIG. 1A .
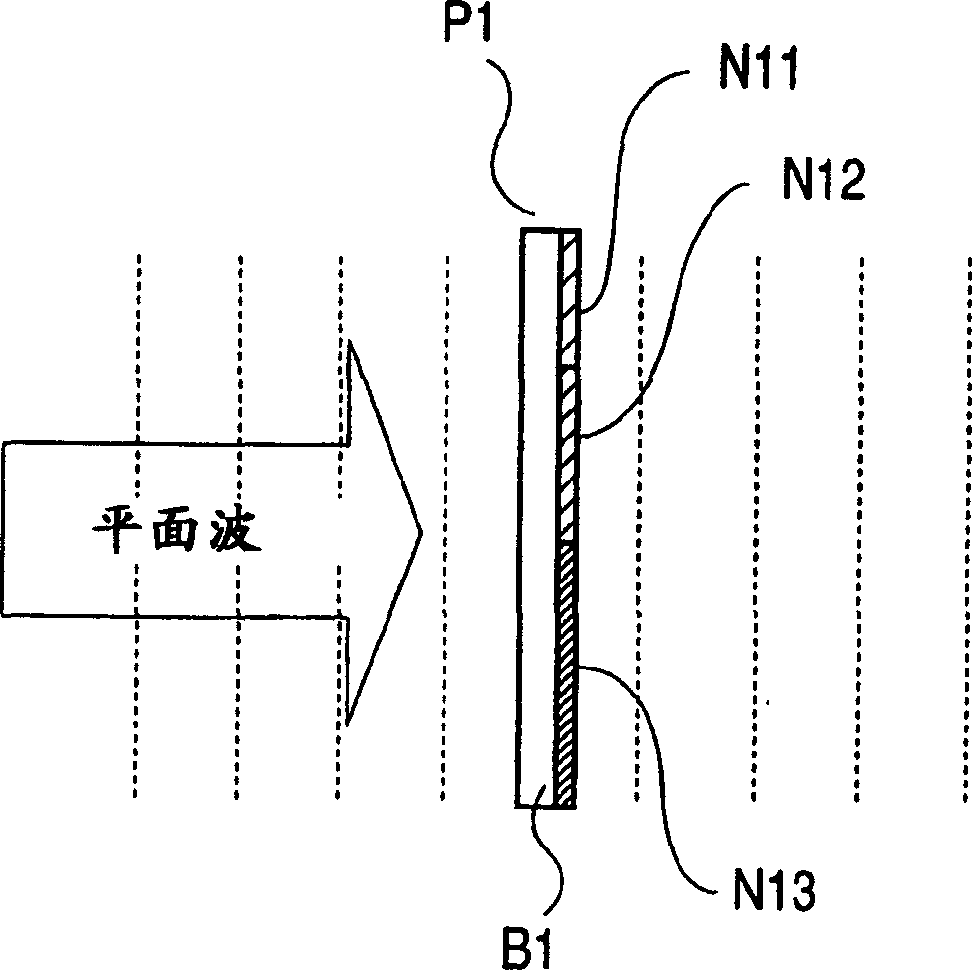
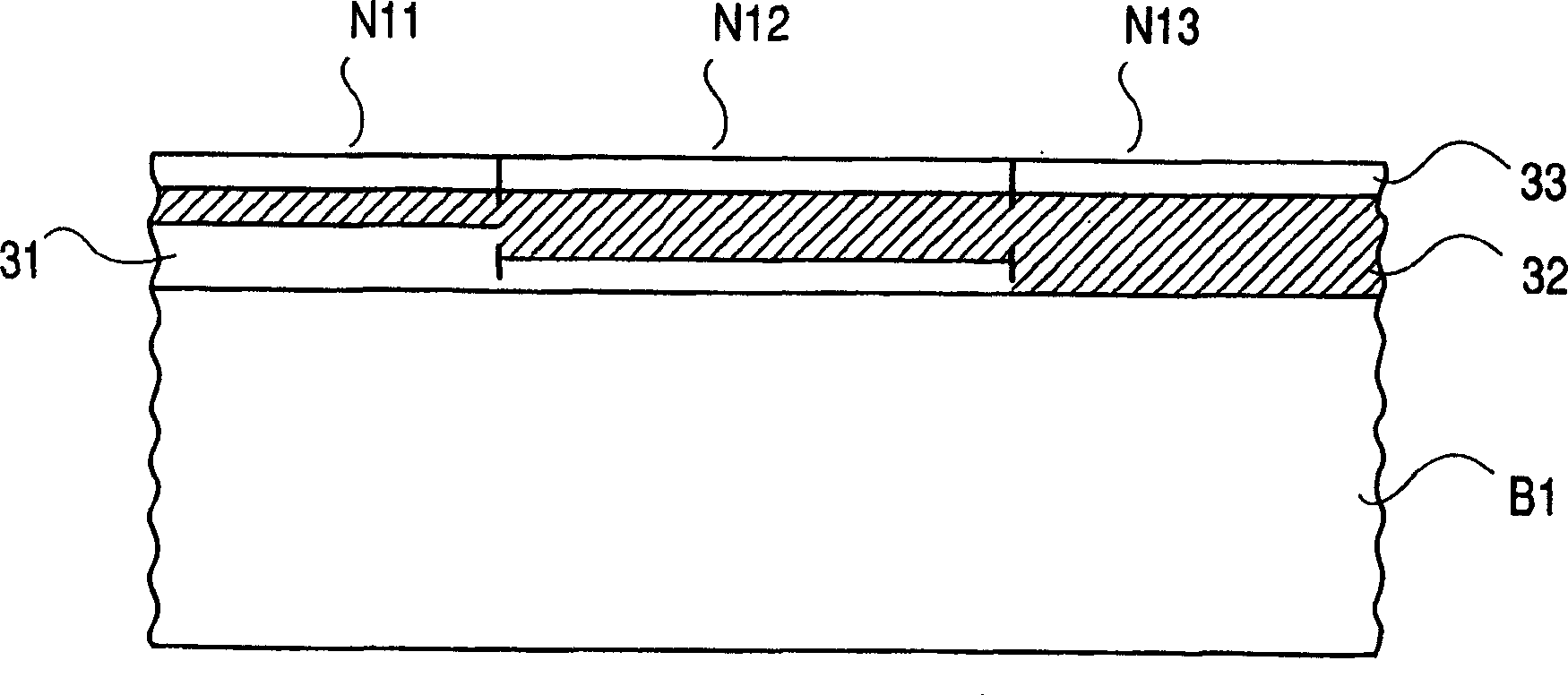
[0122] In the figure, S11 and S12 are diaphragm blades for forming the diaphragm opening, and the opening area can be changed by moving them relatively. P1 is an ND filter (filter member), pasted and fixed on the diaphragm blade S12. Therefore, as the diaphragm blades S11, S12 move relative to each other, the area where the ND filter P1 covers the opening changes. In addition, the ND filter P1 forms a region N13 with a small transmittance (concentration) on the substrate B1, a region N12 with the second smallest transmittance (medium transmittance), and a transmittance area N12 on the substrate B1 seque...
Embodiment 2
[0134]Embodiment 2 of the present invention is shown in FIG. 4A, FIG. 4B, FIG. 4C, and FIG. 4D. Fig. 4A, Fig. 4B, Fig. 4C, and Fig. 4D are embodiments in which the light quantity adjusting device (diaphragm device) of the present invention is applied in the same manner as in Embodiment 1, but different from Embodiment 1, the diaphragm blades and the ND are independently driven. Example of a filter, a device for adjusting the amount of light.
[0135] In the figure, S11 and S12 are diaphragm blades for forming the diaphragm opening, and the opening area can be changed by moving them relatively. P2 is an ND filter, and the diaphragm blades S11 and S12 can be driven independently. In this embodiment, from the open state shown in FIG. 4A to the predetermined narrowed state shown in FIG. 4B, the aperture is narrowed by the diaphragm blades S21 and S22 to adjust the amount of light, and then the aperture area is fixed, as shown in FIG. 4C. The ND filter P2 is inserted into the ope...
Embodiment 3
[0143] Embodiment 3 of the present invention is shown in Fig. 7A, Fig. 7B and Fig. 7C. 7A , 7B, and 7C are examples in which the light quantity adjustment device (diaphragm device) of the present invention is applied in the same manner as in the first embodiment. FIG. 7A shows an open aperture state, FIG. 7B shows an intermediate aperture state, FIG. 7C shows a minimum aperture state, and FIG. 7D shows a side view of FIG. 7A .
[0144] In the figure, S31 and S32 are diaphragm blades for forming the diaphragm opening, and the opening area can be changed by relatively moving them. P3 is an ND filter (filter member), pasted and fixed on the diaphragm blade S32. Therefore, as the diaphragm blades S31, S32 move relative to each other, the area where the ND filter P3 covers the opening changes.
[0145] Further, in the ND filter P3, a region N31 having a predetermined transmittance is formed on one surface of the substrate B3, and a region N32 having a different transmittance from...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com