Novel sodium channel blockers
A general formula, selected technology, applied in the preparation of organic compounds, medical preparations containing active ingredients, preparation of isocyanate derivatives, etc., can solve the problem of unclear intracellular mechanism of cancer cell morphology
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach
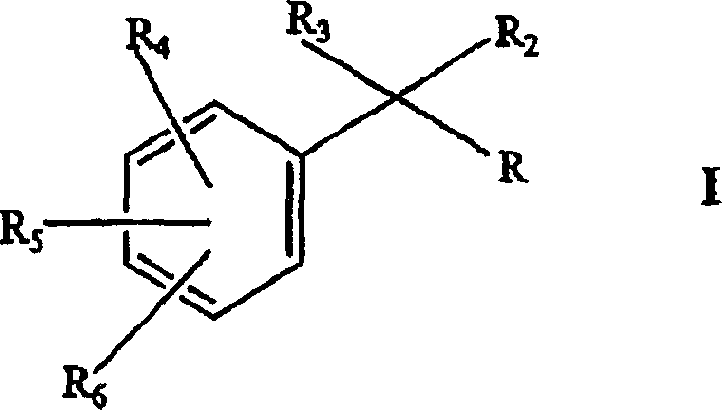
[0047] According to one embodiment, the present invention provides a sodium channel blocker, wherein the blocker has the general formula:
[0048] or
[0049] where R is selected from C 1 -C 12 Alkyl, C 2 -C 8 Alkenyl, C 2 -C 8 Alkynyl, -(CH 2 ) n C 3 -C 6 Cycloalkyl,
[0050]
[0051] and
[0052] where n is an integer from 0-4. R 2 is H or C 1 -C 4 Alkyl, R 4 and R 5 independently selected from H, halogen, C 1 -C 4 Alkyl, C 2 -C 4 Alkenyl, C 2 -C 4 Alkynyl, -COR 10 and (C 1 -C 4 ) alkoxy, and R 6 selected from H, halogen, C 1 -C 8 Alkyl, amino, hydroxyl, C 1 -C 8 alkoxy and
[0053] and
[0054] where R 7 and R 8 independently selected from H, C 1 -C 4 Alkyl, C 2 -C 4 Alkenyl and C 2 -C 4 Alkynyl, and R 9 is H, or R 8 and R 9 together with the atoms to which they are attached form an optionally substituted heterocyclic ring, and R 10 Choose from H, C 1 -C 4 Alkyl, NH 2 and OH.
[0055] In one embodiment, the pres...
Embodiment 1
[0116] Organic synthesis of the mentioned compounds
[0117] compound R 3 1 3-Cl2 4-Cl3 2-Cl4 4-OCH35 H9 4-F1
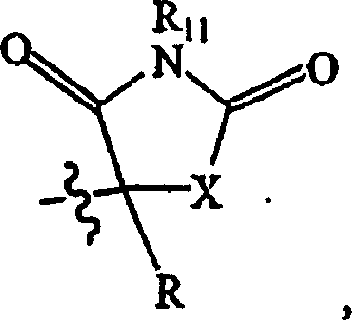
[0118] Hydroxyamide compounds 1-5 were synthesized according to literature procedures and as outlined in Scheme 1. Typically, the corresponding nitrile is converted to the ketone by Grignard addition, followed by conversion of the ketone to the TMS ether using TMSCN. TMS ethers were cleaved to cyanohydrins with 1% HCl, followed by hydrolysis of the corresponding cyanohydrins to the final products using concentrated HCl / HCl gas. Hydantoin analogs 44 and 66 were prepared from commercially available ketones by Bucherer-Berg reactions.
[0119] Process I
[0120]
[0121] Enantioselective synthesis of hydroxyamides using a Sharpless dihydroxylation strategy.
[0122] Since most existing compounds are chiral, it would be expected that it would be desirable to prepare several grams of each enantiomer of the active analog. To this end,...
Embodiment 2
[0149] Effects of synthesized compounds on the binding of 3H-BTX-B
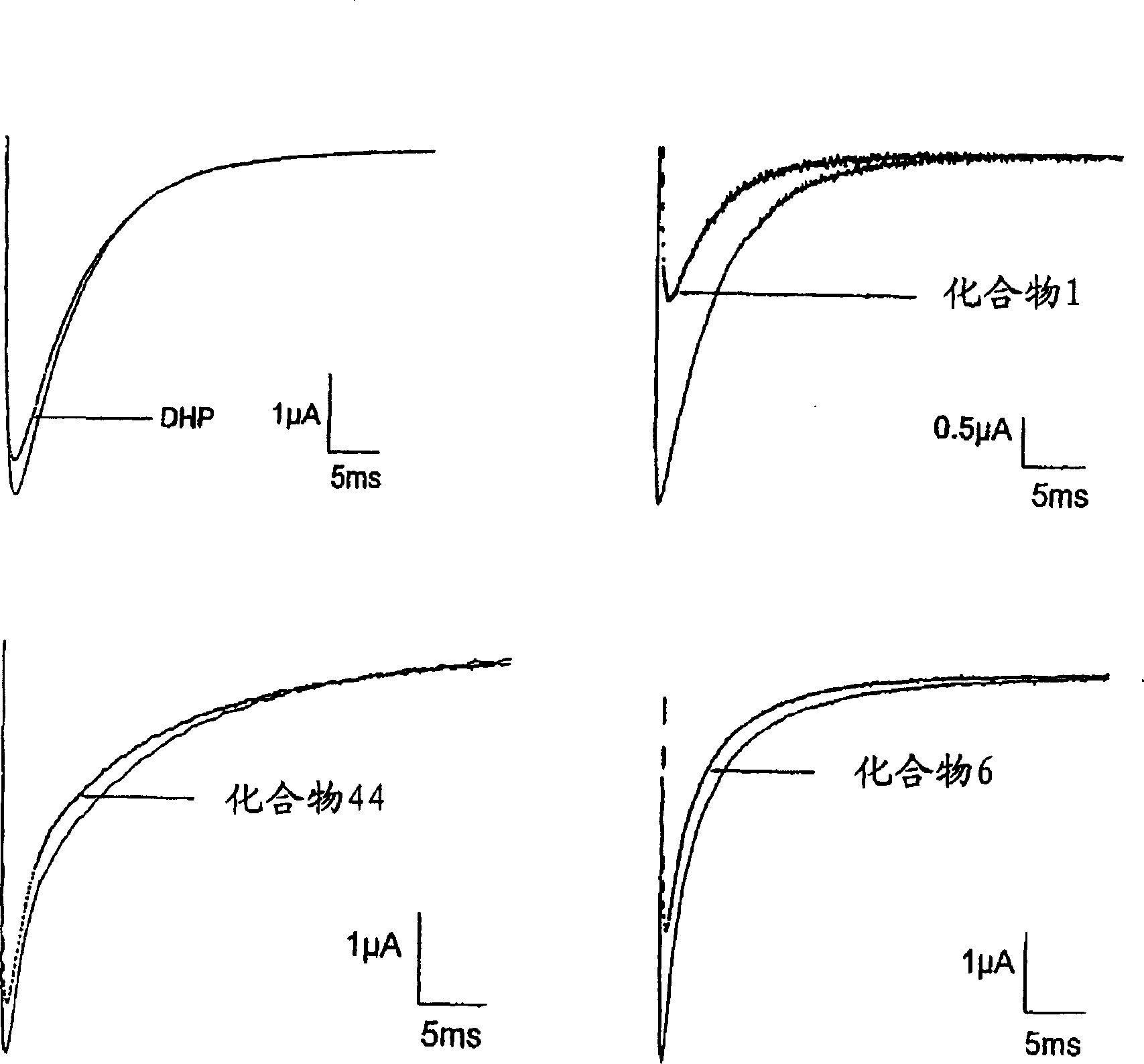
[0150] One assay for screening compounds that are modulators of sodium channel activity is based on the use of the radioligand 3[H]-BTX-B assay. BTX binds to position 2 on the channel protein, thus those compounds that can compete with or inhibit BTX binding to sodium channels are potential sodium channel inhibitors. This assay represents a flexible tool to pre-screen for sodium channel binding prior to more rigorous functional assays such as evaluating compounds by electrophysiology. Compounds 2 and 44 showed potent inhibition of 3H-BTX-B binding compared to phenytoin (see Table 1).
[0151] Table 1 3H-BTX-B inhibition data
[0152] Compound 3H-BTX-B(μM)
[0153] 5 9±2
[0154] 44 5±1
[0155] Phenytoin 40
[0156]
[0157] name
[0158] name
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com