Absorbent article including airlaid mixture material containing thermoplastic fibers treated with phosphate ester or sulfate ester
A thermoplastic fiber and absorbent product technology, applied in the field of absorbent products, can solve the problems of destroying the conformability of sanitary napkins, high hardness, leakage, etc., and achieve the effects of excellent fluid handling performance, improved conformability, and leakage prevention.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0096] 1. Preparation of sheep blood matrix test fluid
[0097] A number of fluids are known for simulating menstruation in laboratory tests. We have selected ingredients to simulate the highest viscosity of menses and prepared as follows.
[0098] 1) Prepare 1000 mL of a solution (Solution A) with 1.38 ± 0.005 g of monobasic sodium phosphate monohydrate and 8.50 ± 0.005 g of sodium chloride plus distilled water.
[0099] 2) Prepare 1000 mL of solution (solution B) with 1.42±0.005 g of anhydrous dibasic sodium phosphate and 8.50±0.005 g of sodium chloride plus distilled water.
[0100] 3) Add solution A to 450±10 mL of solution B while stirring slowly until the pH of the solution reaches 7.2±0.1 (solution C).
[0101] 4) Dissolve about 120 g of gastrin powder in 460±10 mL of solution C, stir with any propeller-type electric mixer, and stir for 2.5 hours at 70 ° C at a stirring speed that does not produce splashing. Gastrin powder can be purchased from, for example, the Unite...
Embodiment 1
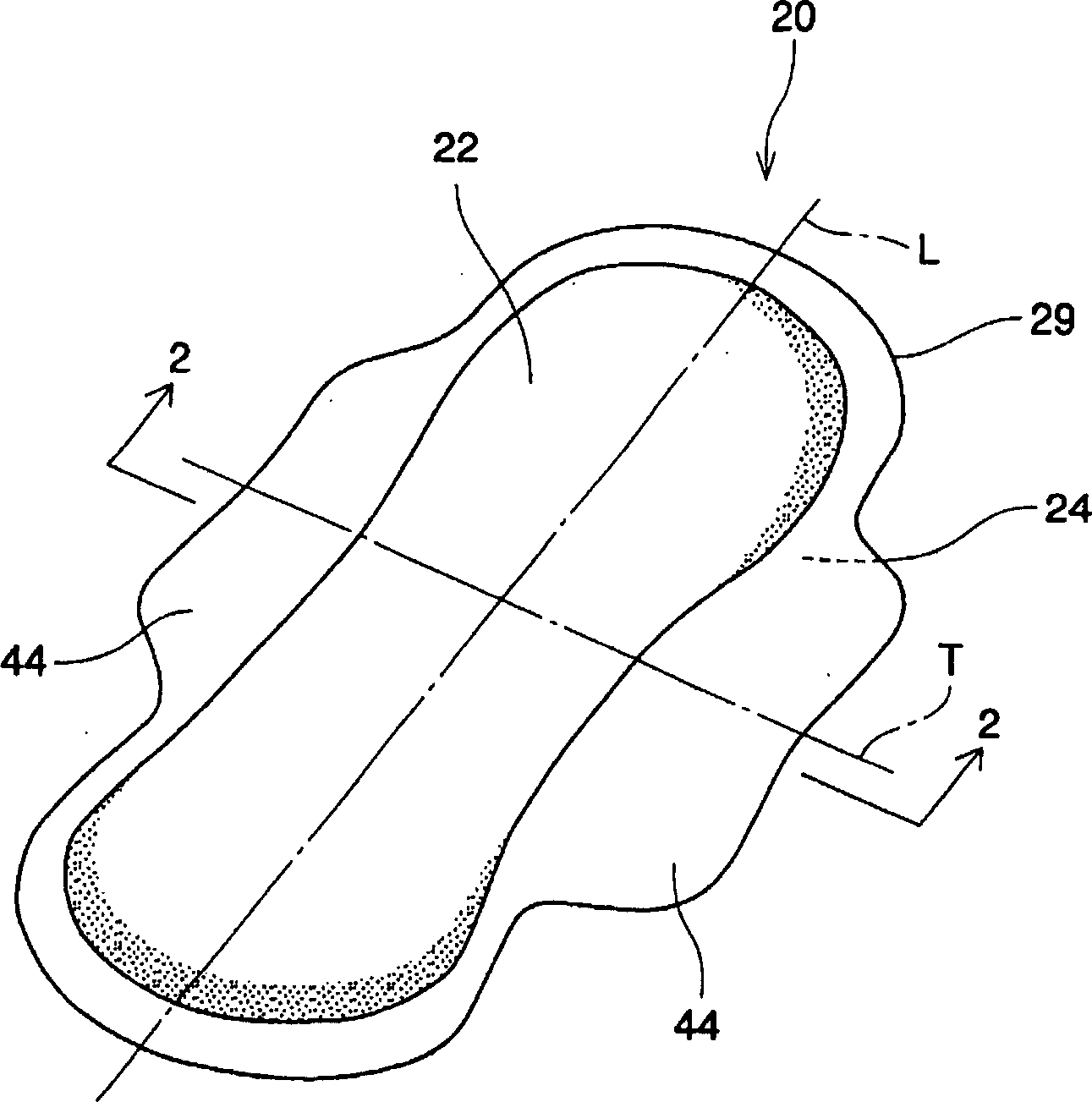
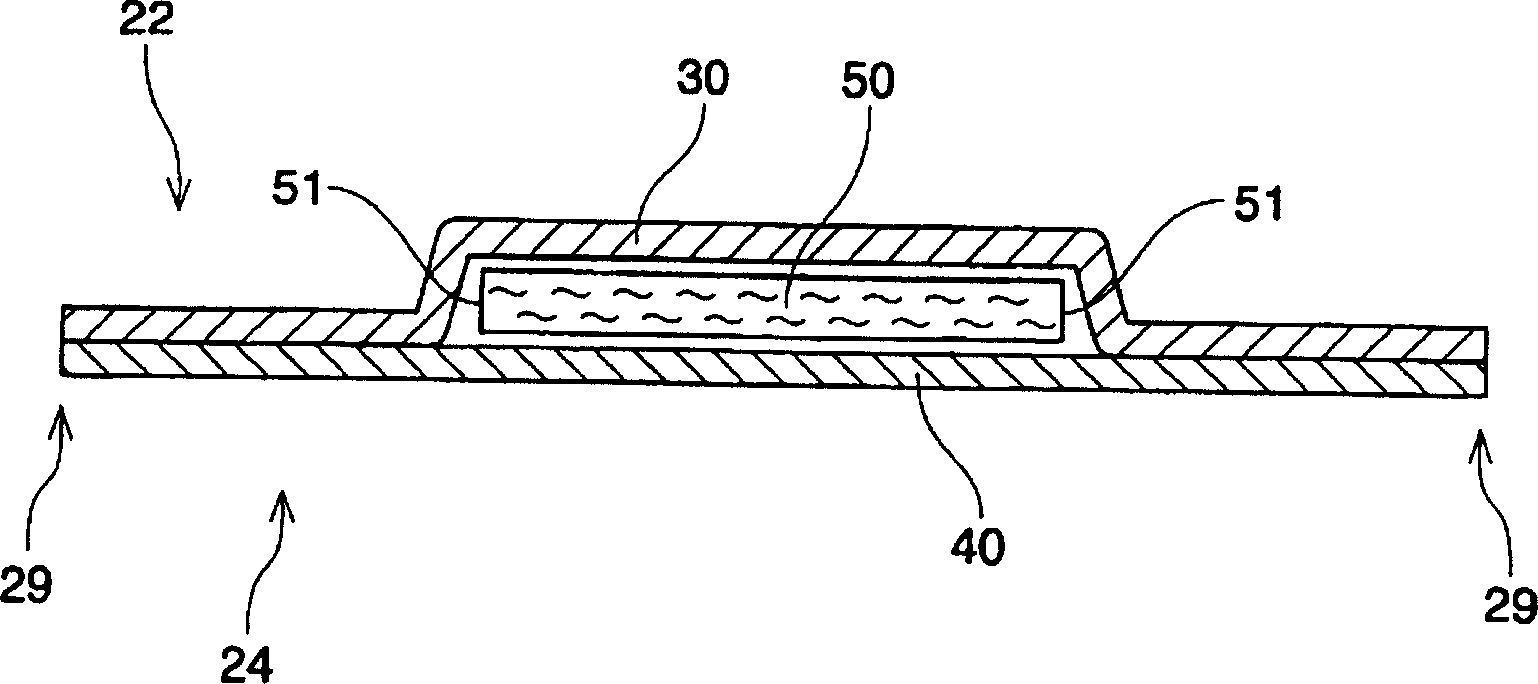
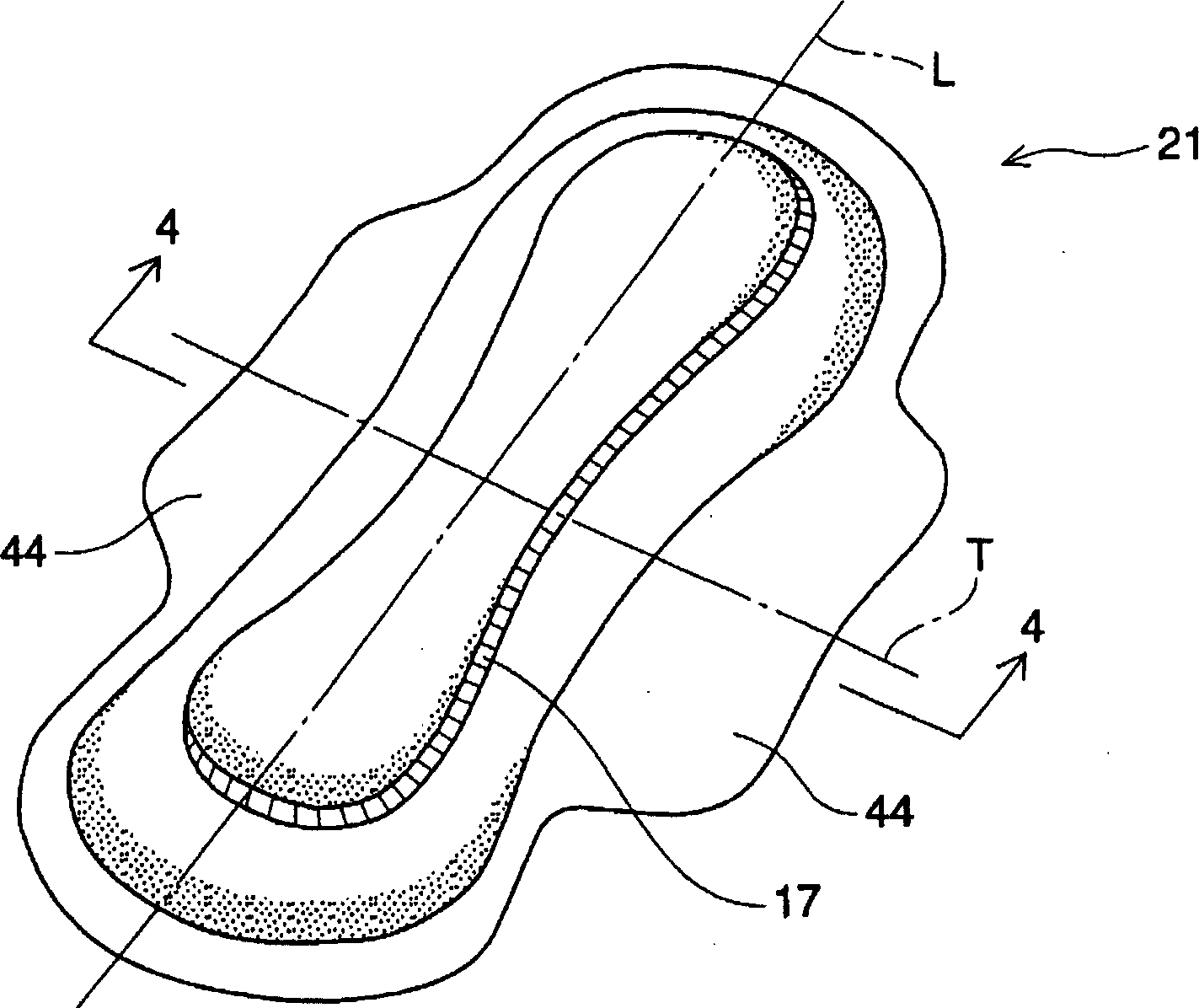
[0129] An 82% phosphate slurry available from Rayonier Inc., Georgia, USA under the trade name Rayfloc J-LD-E was used using an airlaid system ("Airlaid System") from M&J Fibretech A / S, Horsens, Denmark. Fibers ("pulp fibers") and 18% coated with a mixture of potassium N-dodecyl (C12) phosphate and potassium N-octyl (C8) phosphate available from Chisso Corporation in Osaka, Japan under the code XESC1015. % acid-modified polyethylene (in sheath) / polypropylene (in core) bicomponent fibers (1.7 dex, 5.0 mm long) (“bicomponent fibers”) to produce one layer of TBAM. Subsequent heat treatment is performed at about 142C. The material has a basis weight of 100g / m2 and a thickness of 20gf / cm 2 (ie, 0.050 g / cc) under pressure is about 2.0 mm. The TBAM layer is preferably used as figure 1 with 2 Absorbent core 50 in the illustrated embodiment.
Embodiment 2
[0131] A layer was produced using an air-laid system and subsequent heat treatment at 153C with 65% pulp fibers, 18% bicomponent fibers and 17% particulate AGM with an absorption rate of 7.3 g / g for the mentioned test fluid TBAM. The material has a basis weight of approximately 100g / m 2 And the thickness is 20gf / cm 2 (ie, 0.050 g / cc) under pressure is about 2.0 mm. The TBAM layer is preferably used as figure 1 with 2 Absorbent core 50 in the illustrated embodiment.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Dry density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com