Solid-state imaging device, semiconductor wafer and camera module
A camera device, solid-state technology, applied in semiconductor devices, electric solid-state devices, radiation control devices, etc., to achieve the effect of reducing adverse effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach 1
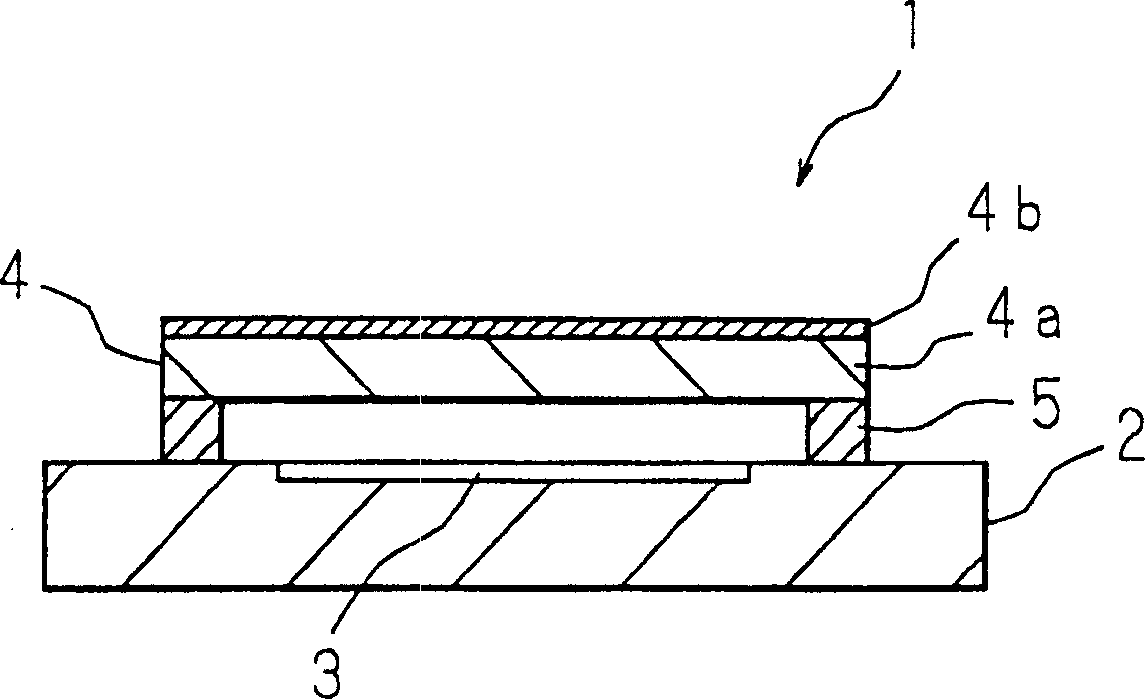
[0028] figure 1 is a cross-sectional view showing the configuration of the solid-state imaging device of the present invention. The solid-state imaging device 1 includes: a solid-state imaging element 2 formed in a rectangular shape in plan view on a semiconductor substrate; a light-receiving unit 3 formed on one surface of the solid-state imaging element 2; and on one side of the solid-state imaging device 2, a bonding portion 5 for bonding the light-transmitting cover portion 4 and the solid-state imaging device 2 is formed in a region except the light receiving portion 3. The solid-state imaging device 1 takes in light from the outside through the translucent cover portion 4 , and receives the light through the light-receiving elements (effective pixels) arranged on the light-receiving portion 3 of the solid-state imaging device 2 . In addition, although not shown in the figure, microlenses are arranged on the surface of the light receiving unit 3 to converge incident ligh...
Embodiment approach 2
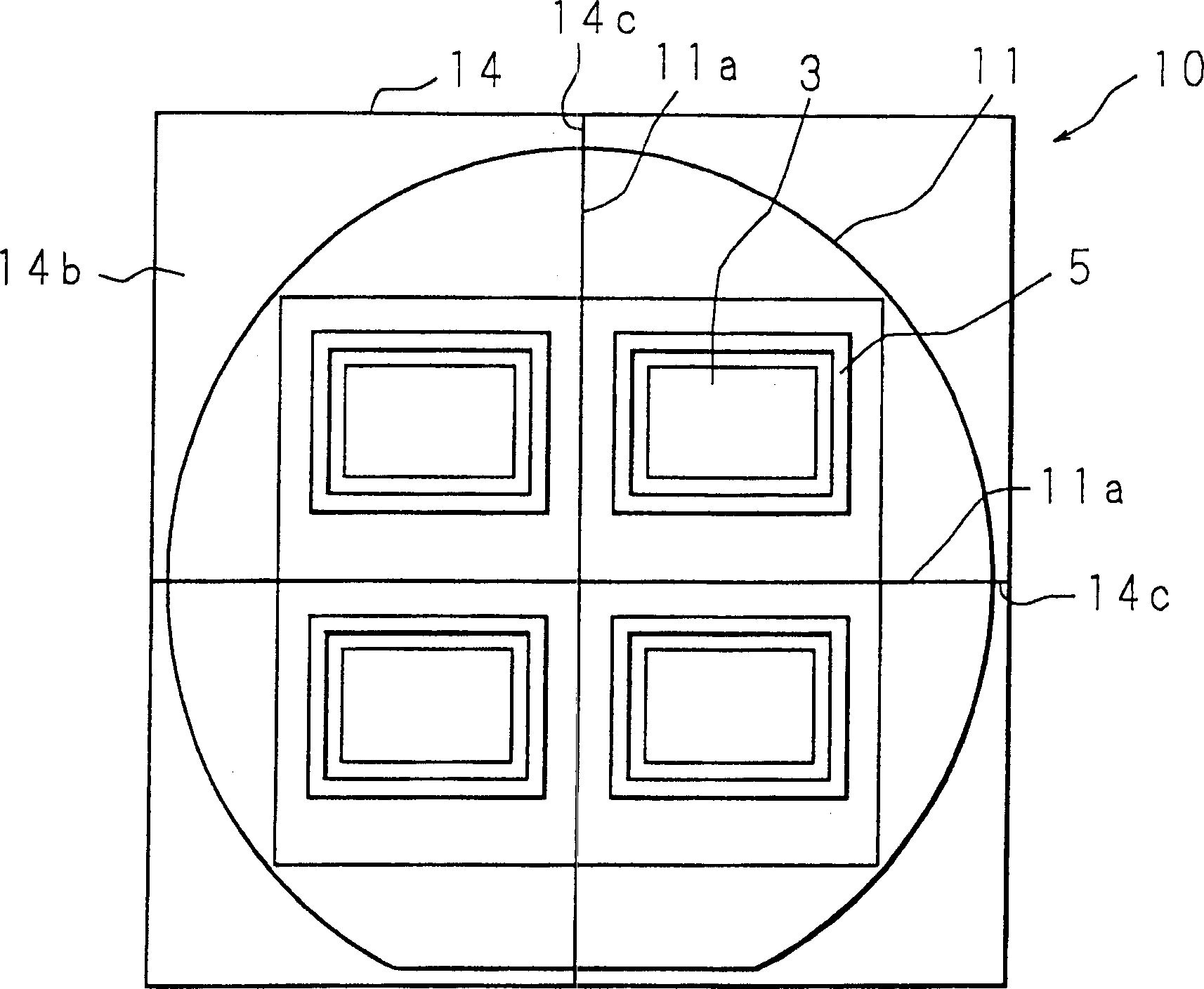
[0034] Figure 2A and 2B shows the structure of an example of the semiconductor wafer of the present invention, Figure 2A is its top view, Figure 2B is its cross-section. The semiconductor wafer 10 has a structure in which a light-transmitting plate 14 is bonded via an adhesive portion 5 to a semiconductor substrate 11 on which a plurality of light receiving portions 3 are patterned on one surface. In addition, although not shown in the figure, microlenses are arranged on the surface of the light receiving unit 3 to converge incident light on the light receiving element of each pixel.
[0035] The translucent plate 14 is made of a glass substrate 14a and an infrared shielding film 14b formed on one side of the glass substrate 14a, and the translucent plate 14 is arranged so that the one side of the translucent plate 14 (glass substrate 14a) on which the infrared shielding film 14b is formed It becomes the side opposite to the side of the semiconductor substrate 11 that f...
Embodiment approach 3
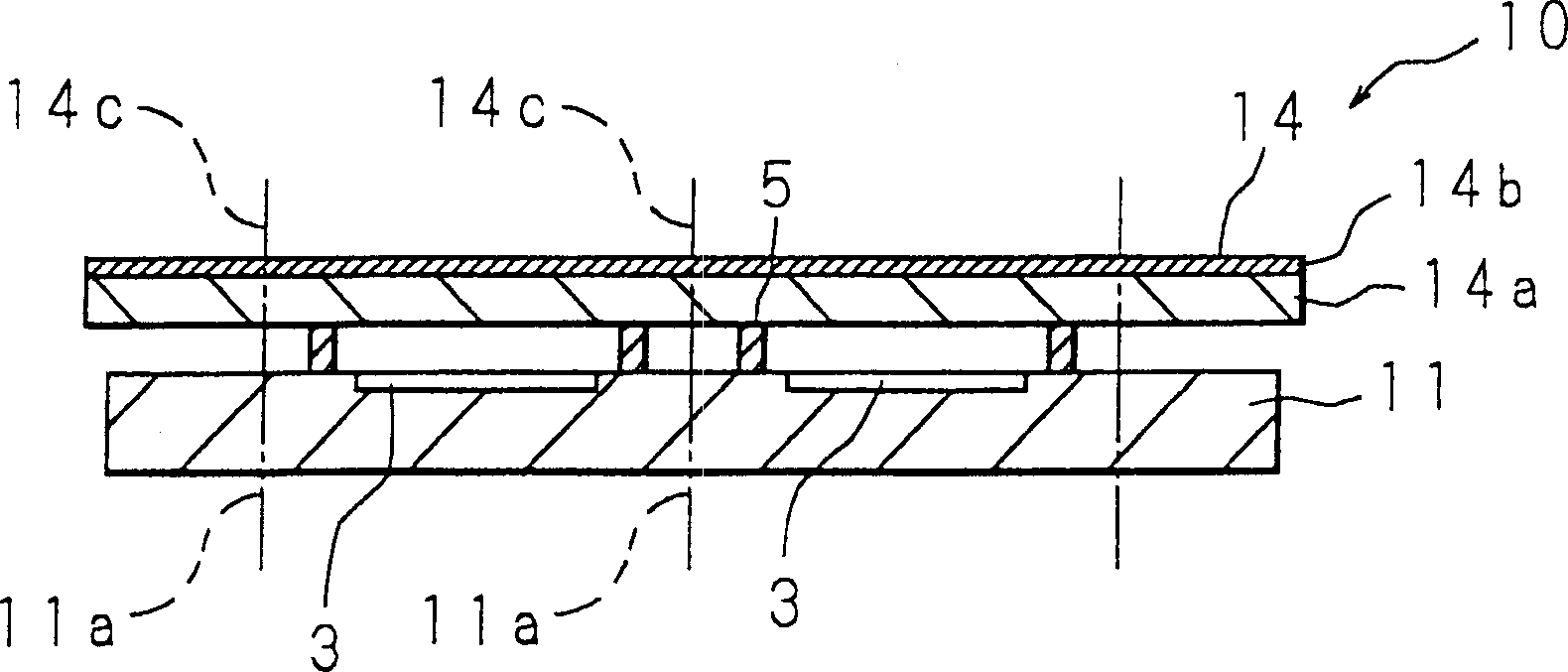
[0041] Figure 3A And 3B has shown the structure of other examples of the semiconductor wafer of the present invention, Figure 3A is its top view, Figure 3B is its cross-section. The semiconductor wafer 20 has a structure in which a plurality of singulated light-transmitting cover portions 4 are bonded by bonding portions 5 on a semiconductor substrate 11 on which a plurality of light receiving portions 3 are patterned on one surface. In addition, although not shown in the figure, microlenses are arranged on the surface of the light receiving unit 3 to converge incident light on the light receiving element of each pixel.
[0042] Each light-transmitting cover portion 4 is the same as the light-transmitting cover portion 4 of the first embodiment, and each light-transmitting cover portion 4 is arranged such that each light-transmitting cover portion 4 (each glass substrate 4 a ) on which an infrared shielding film 4 b is formed One side is the side opposite to the side fac...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com