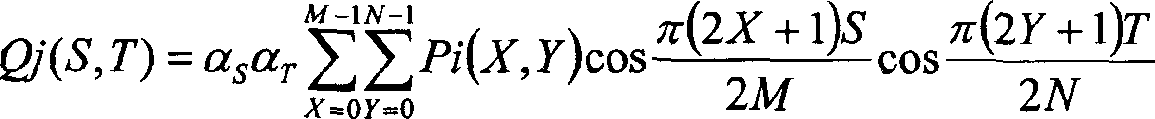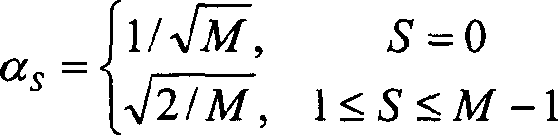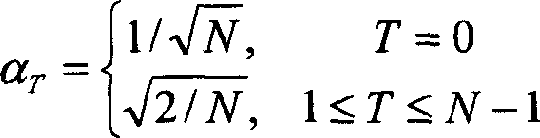Image processing method, image processing apparatus and image forming apparatus
An image processing device and image processing technology, applied in the direction of image communication, electrical components, etc., can solve the problems of texture and other problems, and achieve the effect of improving texture, reducing the number of tones, and maintaining good
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach 1
[0089] 3 is a block diagram showing a configuration example of an image processing device according to Embodiment 1 of the present invention. The image processing device is a device that generates and outputs image data Po(X, Y) in which the number of tones of image data Pi(X, Y) input to the image processing device is reduced. For example, the image processing device generates and outputs image data Po(X, Y) that quantizes image data Pi(X, Y) of 256 tones and reduces to, for example, 4 tones. Here, the image data Pi(X, Y) is the tone value of an image composed of pixels arranged in a two-dimensional matrix in X and Y directions perpendicular to each other, that is, horizontal rows and vertical rows. X represents the position on the horizontal line of the image, and Y represents the position on the vertical line of the image.
[0090] The image processing device includes an image data storage unit 11 for temporarily storing input image data Pi(X, Y). The image data Pi(X, Y) ...
Embodiment approach 2
[0130] 9 is a block diagram showing a configuration example of an image processing device according to Embodiment 2 of the present invention. The image processing apparatus of Embodiment 2 is the same as the image processing apparatus of Embodiment 1 shown in FIG. In addition to the addition unit 15 , the frequency inverse conversion unit 16 , and the threshold value processing unit 17 , a DC component determination unit 18 is also included. The configuration, function, and effect of the image processing device of Embodiment 2 other than the DC component determination unit 18 are the same as those of the image processing device of Embodiment 1, so the same reference numerals are assigned to the same components. and omit their detailed descriptions.
[0131] The DCT coefficient Qj(S, T) output from the frequency conversion unit 12 is input to the DC component determination unit 18 included in the image processing device according to the second embodiment. The DC component det...
Embodiment approach 3
[0136] 10 is a block diagram showing a configuration example of an image processing apparatus according to Embodiment 3 of the present invention. The image processing apparatus of Embodiment 3 is the same as the image processing apparatus of Embodiment 2 shown in FIG. In addition to the addition unit 15 , frequency inverse conversion unit 16 , threshold value processing unit 17 , and DC component determination unit 18 , it also includes a LUT (Look Up Table) unit 19 that stores DCT coefficients of blue noise used for noise addition. Furthermore, the LUT unit 19 is connected to the noise addition unit 15 . The structure, function, and effect of the image processing device of Embodiment 3 other than the LUT unit 19 are the same as those of the image processing device of Embodiment 2, so the same reference numerals are assigned to the same components and omitted. their detailed description.
[0137] The LUT unit 19 performs discrete cosine transform on the image data having blu...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com