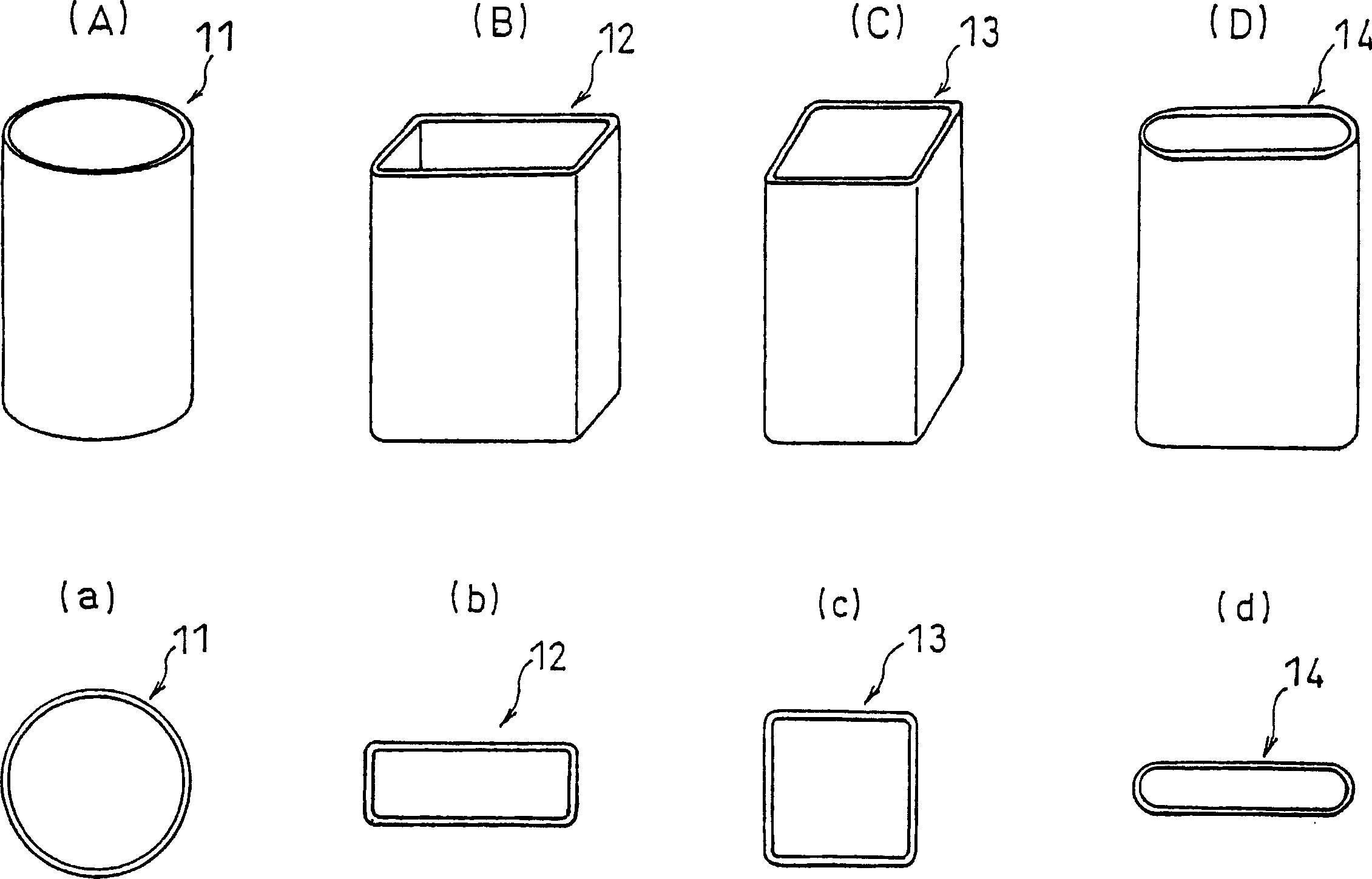
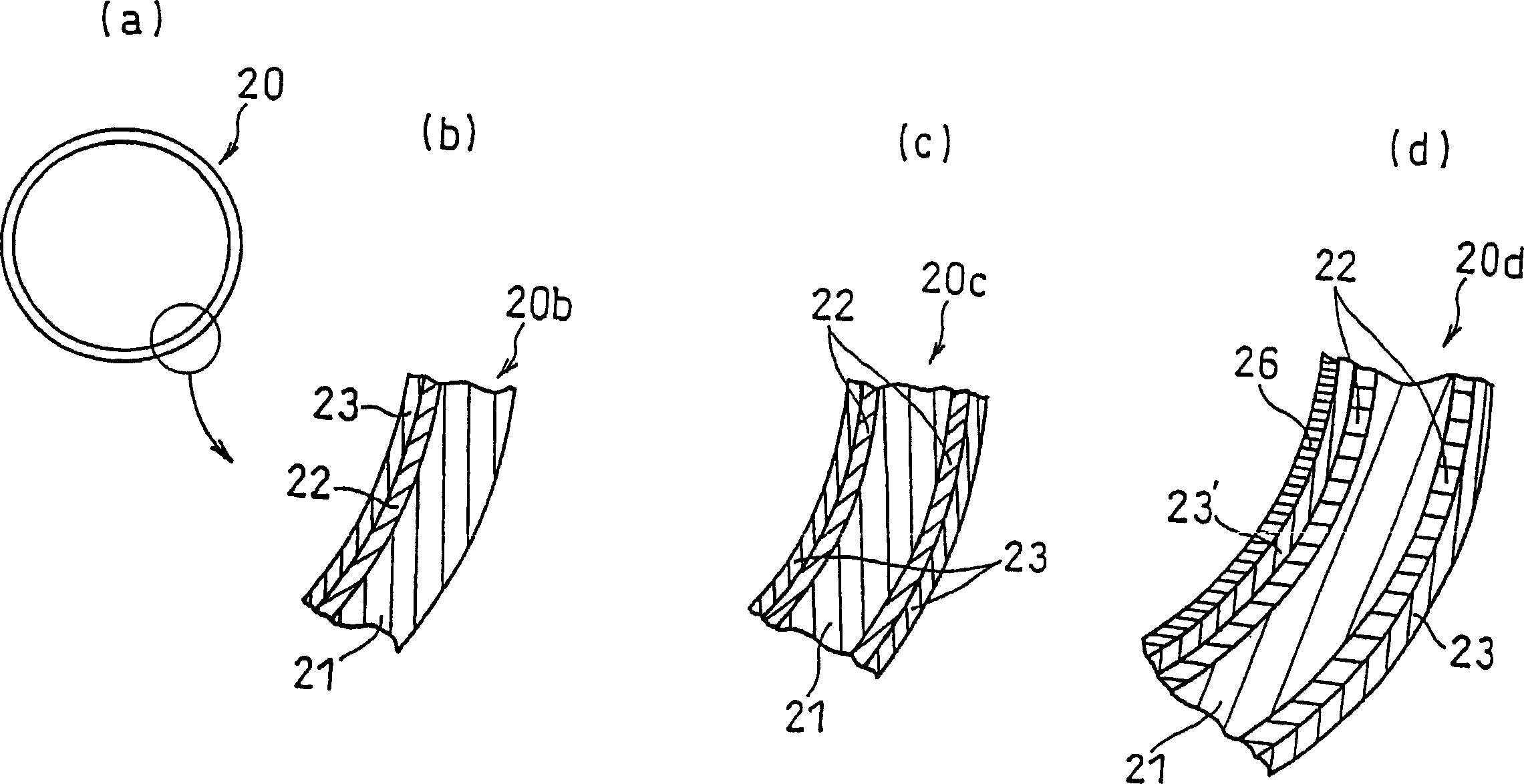
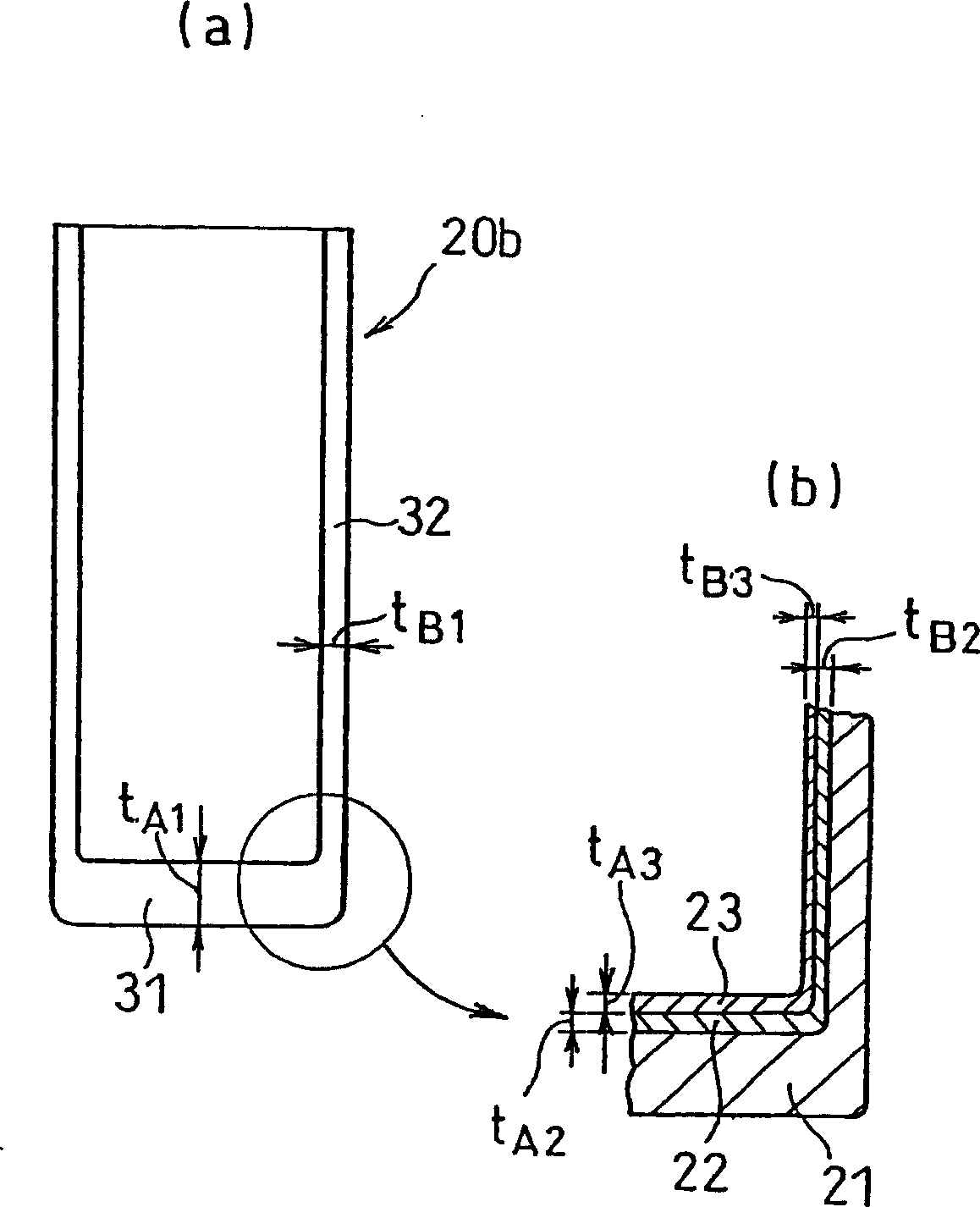
Battery can and manufacturing method thereof and battery using the same
A battery shell and electrolyte technology, applied to small-sized batteries/battery packs, dry batteries, secondary batteries, etc., can solve the problems of increased internal resistance of batteries, increased contact resistance, and insufficient corrosion resistance of battery shells, etc., to achieve low cost effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0060] (i) Ni plating treatment
[0061] Ring-shaped cold-rolled steel sheets (No. 1 to 19) having a thickness of 0.4 mm were prepared as battery case materials. These steel sheets contained components as listed in Table 1 in addition to Fe and impurities as main components. Each steel plate was plated with Ni on both sides thereof. The conditions of Ni plating are shown in Table 2.
[0062]
Steel plate number
Steel composition (% by weight)
C
mn
P
Si
Al
S
1
0.001
0.020
0.010
0.020
0.040
0.010
2
0.002
0.020
0.010
0.020
0.040
0.010
3
0.004
0.020
0.010
0.020
0.040
0.010
4
0.005
0.020
0.010
0.020
0.040
0.010
5
0.008
0.020
0.010
0.020
0.040
0.010
6
0.020
0.020
0.010
...
example 2
[0100] Next, the effect of bright Ni plating will be described.
[0101] Using a steel sheet having the same composition as the steel sheet numbered 2 in Table 1, battery cases and batteries were fabricated in the same manner as in Example 1, except that bright Ni plating was not applied or by changing the thickness of the bright Ni layer. Cycle life tests were performed on these batteries. The results are shown in Table 6. The thickness of the bright Ni layer shown in Table 6 is its thickness on the bottom inner surface of the battery case. As is clear from Table 6, a bright Ni layer having a thickness of 0.5 µm or more gave good results.
[0102] Steel plate number
[0103] When a bright Ni layer exists in a corrosive environment, the uppermost bright Ni layer serves as an anode, and corrosion spreads in the lateral direction (direction perpendicular to the thickness direction of the bright Ni layer). However, since the Ni layer under the bright Ni layer serves ...
example 3
[0105] Next, explain t A1 / t B1 , t A2 / t B2 , and t A4 / t B4 value.
[0106] Use a steel plate with the same composition as the steel plate numbered 2 in Table 1, except by changing t A1 / t B1 , t A2 / t B2 , and t A4 / t B4 Except for the corresponding values of , a battery case and a battery were prepared in the same manner as in Example 1. Cycle life tests were performed on these batteries. The results are shown in Table 7. In order to achieve the t listed in Table 7 A1 / t B1 , t A2 / t B2 , and t A4 / t B4 The value of , changing the size and number of each mold and the size of the punching machine in the battery case forming process (ie, DI process).
[0107]
Steel plate number
battery case
Battery
t A1 / t B1
t A2 / t B2
t A4 / t B4
cycle life
cycle life
2
2
2
2
2 ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com