Parallel transmission dispatching method for stream media data
A transmission scheduling and streaming media technology, applied in the field of parallel transmission scheduling of streaming media data, can solve problems such as high cost and high cost, achieve good adaptability, ensure transmission quality, and achieve the effect of timely and stable transmission
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
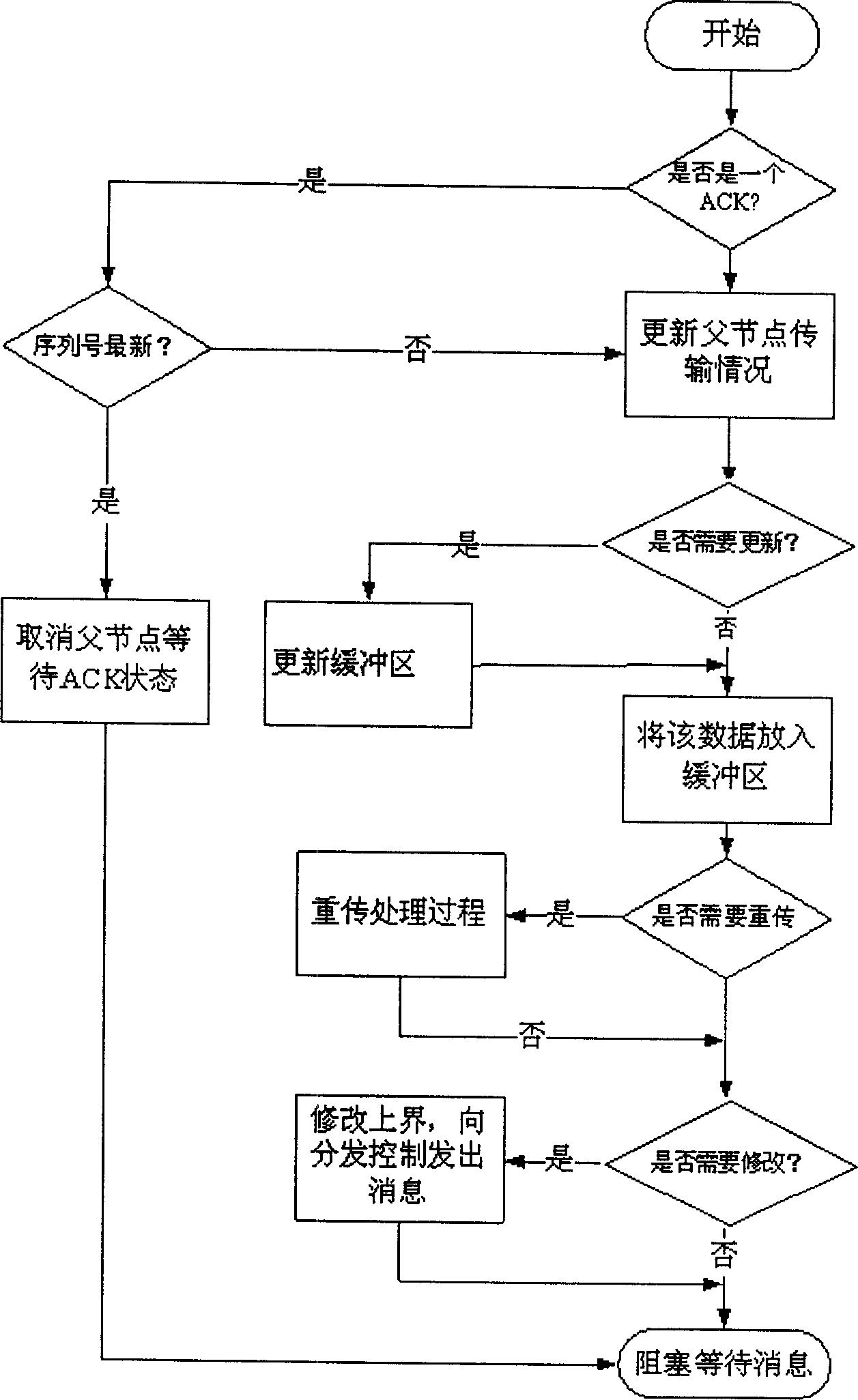
[0054]The streaming media server only needs to send data out, so it only needs to deploy the sending management module, while other nodes need to receive data and send data to downstream sub-nodes, so both the sending management module and the receiving management module need to be deployed. The receiving management module deployed on the child node acts as a scheduler, and sends a scheduling command to the sending management module deployed on the parent node, and coordinates each parent node to jointly provide streaming media data for the child node.
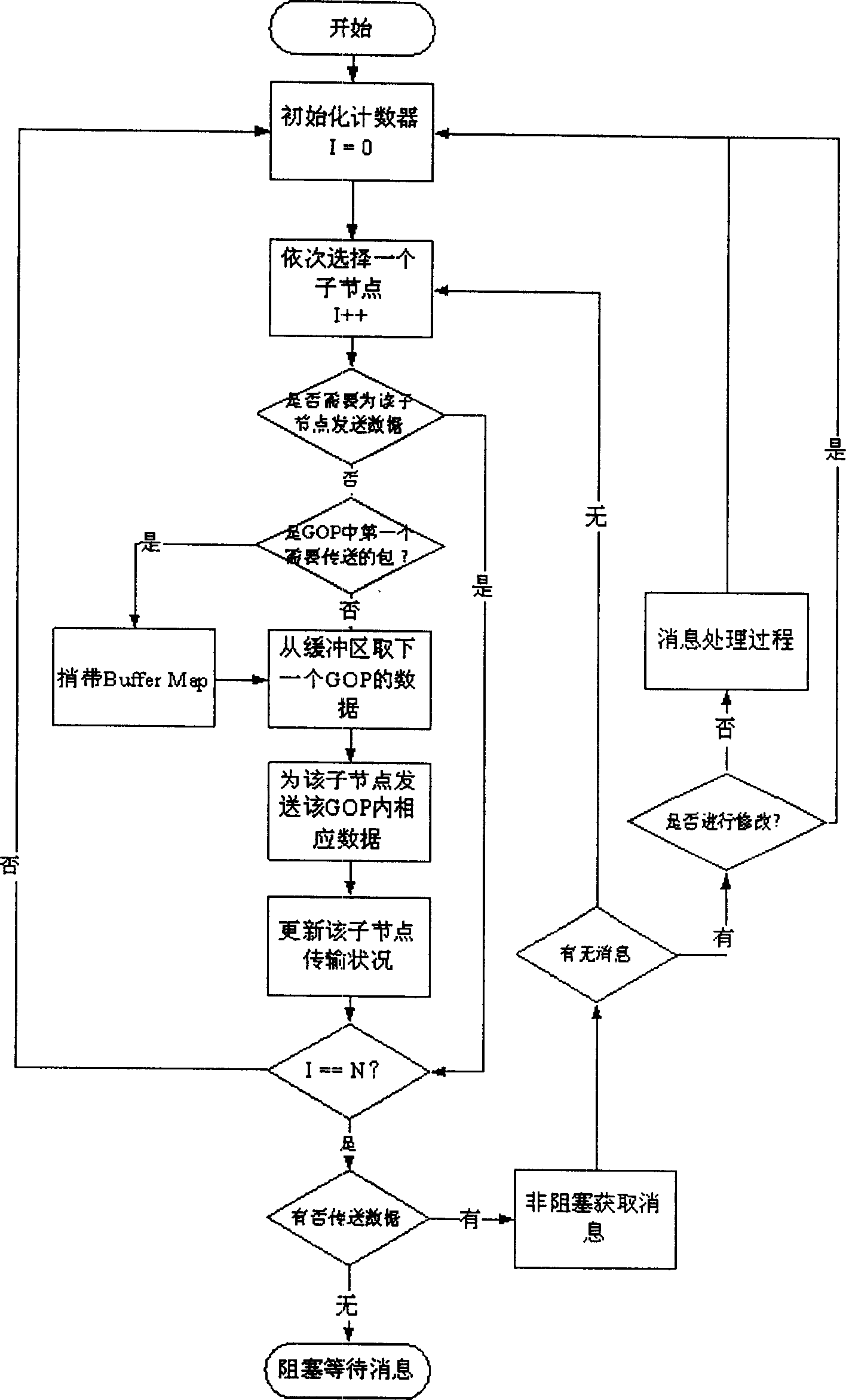
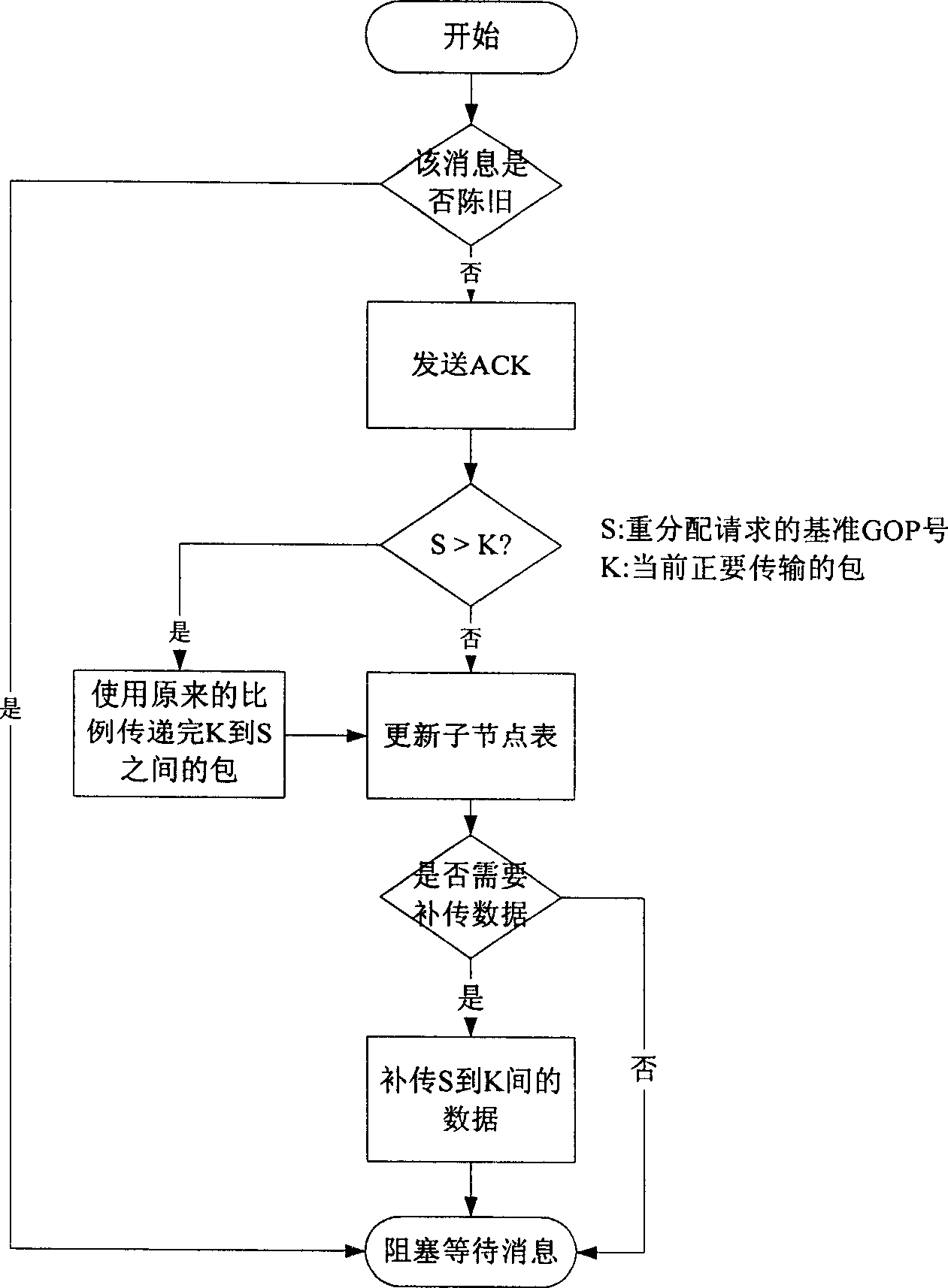
[0055] In each round, the sending management module sends the data assigned to it in a GOP for each child node in turn, and piggybacks the priority MAP and data possession status MAP in the first packet of each GOP. After sending a GOP data for each child node, receive whether there is a new message, these messages include "new child node join message", "exit channel message" and "reallocate transmission ratio message" and so o...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com