Safety writing method for flash memory
A flash memory and security technology, applied in the field of safe reading and writing of chip memory, to achieve good power-down protection, improve system performance, and improve service life.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
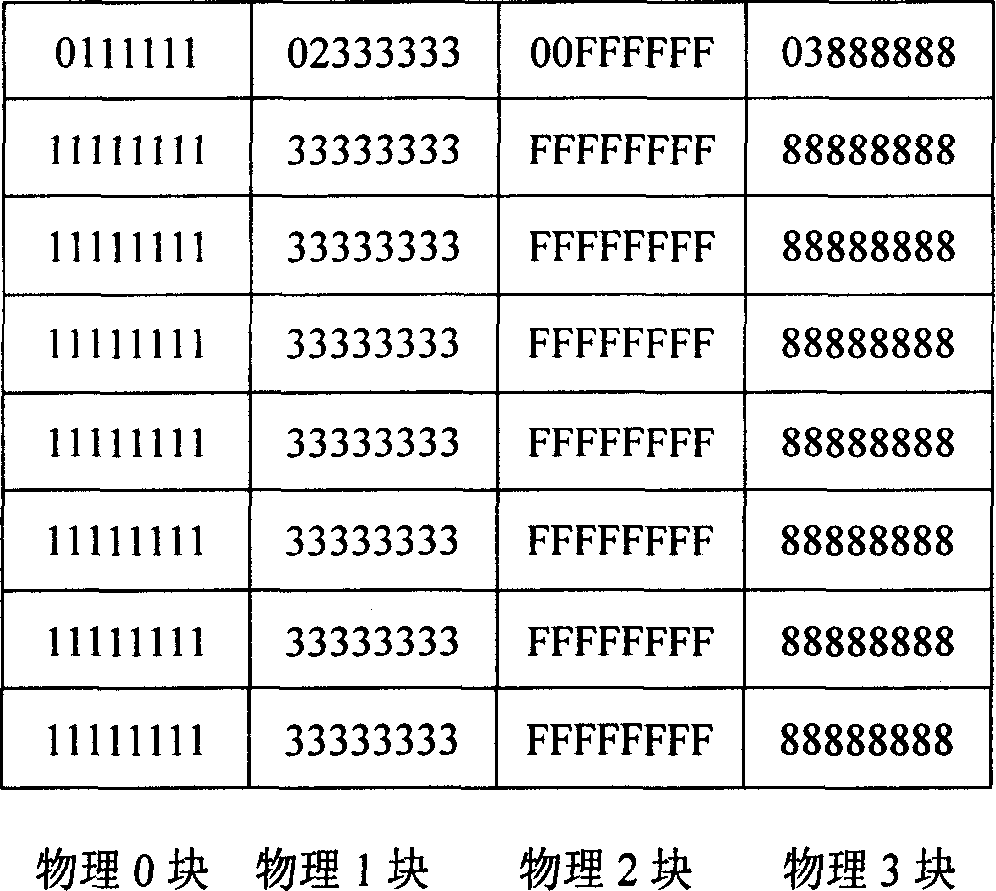
[0049]Embodiment 1, when the flash memory is initialized or formatted by the system, each physical erasing unit in the flash memory is corresponding to a logical block, and each logical block is numbered. In this embodiment, the first block of each logical block is occupied. The byte stores the logical block number, such as figure 1 As shown, the available capacity of each logical block actually becomes 63 bytes, and the size of the entire storage area is 252 bytes. Here we define the logic numbers of the four logic blocks as 00, 01, 02, and 03 respectively, among which the logic block with the logic number 00 is a reserved backup logic block, and it is an unused or erased logic block. for data transfer. At the same time, we set logical block No. 01 to correspond to physical block 0, logical block No. 02 to physical block 1, logical block No. 03 to physical block 3, logical block No. 00 to physical block 2, and the logical addresses to be logical block numbers from small to l...
Embodiment 2
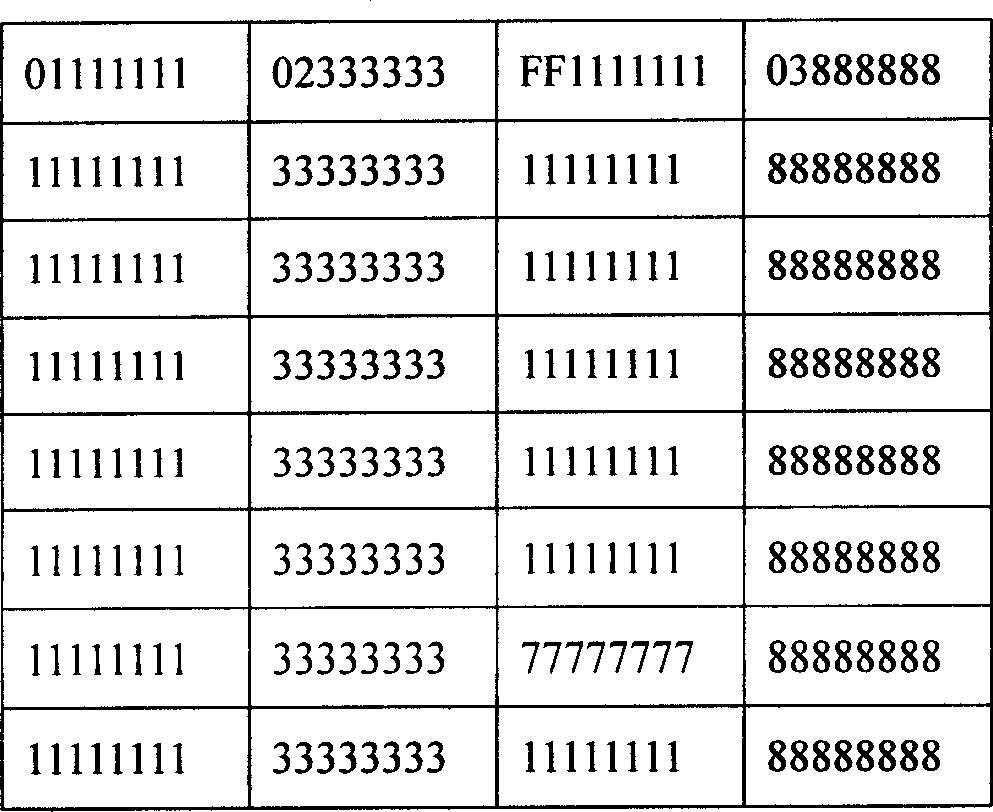
[0060] Embodiment 2, when the flash memory is initialized or formatted by the system, each physical erasing and writing unit in the flash memory is corresponding to a logical block, and each logical block is numbered. In this embodiment, the first one of each logical block is occupied. The byte stores the logical block number, such as Figure 6 As shown, the available capacity of each logical block actually becomes 63 bytes, and the size of the entire storage area is 252 bytes. Here we respectively define the logical numbers of the four logical blocks as 01, 02, 03, and FF, and the logical block with the logical block number of FF is a reserved backup logical block for data transfer. At the same time, we set logical block No. 01 to correspond to physical block 0, logical block No. 02 to physical block 1, logical block No. 03 to physical block 3, and logical block No. FF to physical block 2. The number of logical blocks is determined according to specific applications. Differe...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com