System and method for three-dimensional reconstruction of a tubular organ
A technology for three-dimensional reconstruction of tubular organs, applied in the field of medical imaging systems for angiography, and can solve problems such as incorrect results, adequate support for coronary angiography, and trouble.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
[0083] graphic gathering
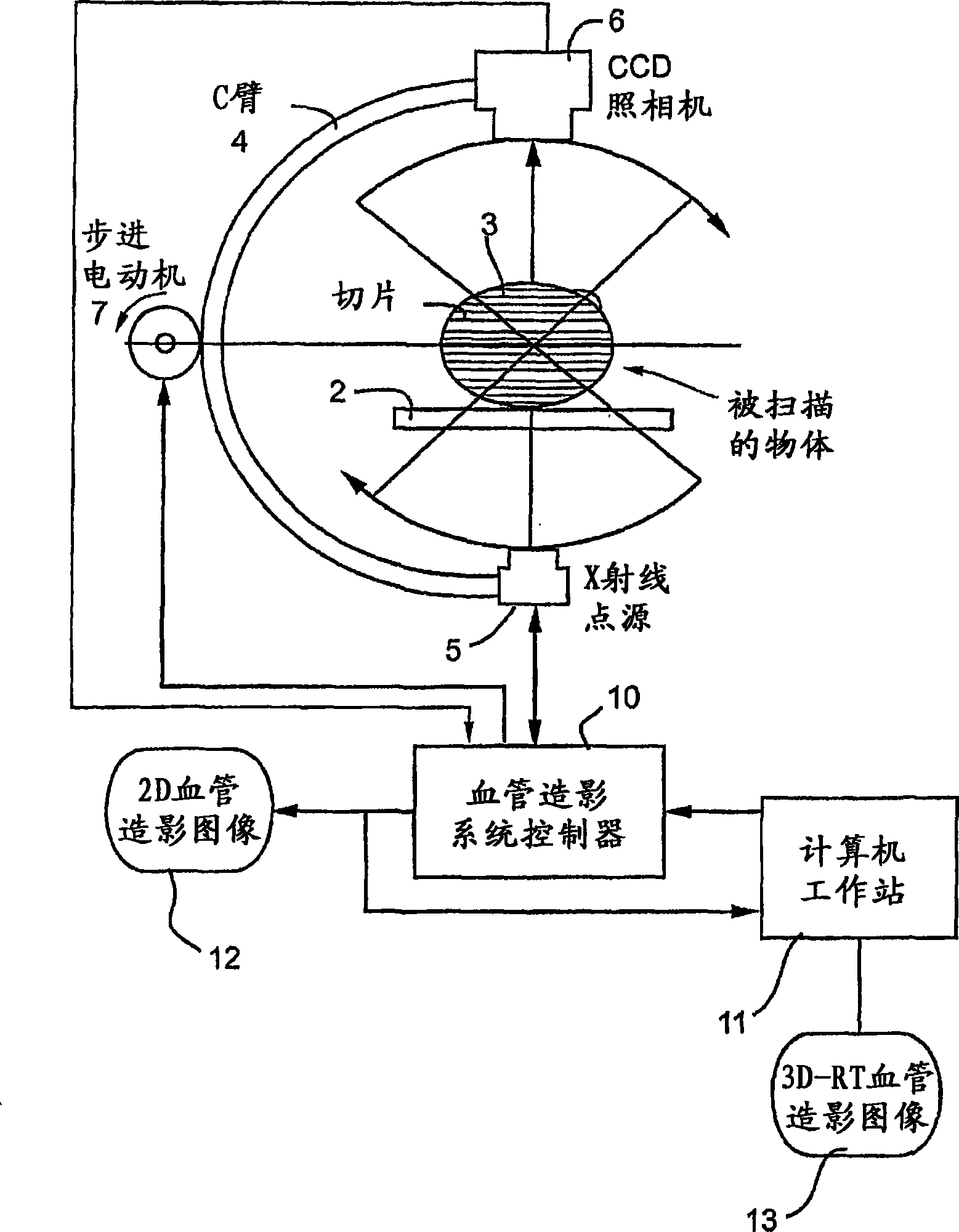
[0084] During catheterization of a patient, a plurality of angiographic cine-projected two-dimensional (2D) x-ray images are captured substantially in real time and displayed on a monitor. In addition to these images, C-arm angulation data and ECG data can also be acquired. With the ECG sensor, an ECG gating process can be used to render the optimal ("best") image (end-diastolic frame) from each captured angiographic cine-projected image.
[0085] Capture of the movie show can be done in an analog fashion (eg with a frame grabber) or via a standard DICOM connection (preferred). DICOM is an acronym for "Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine", and is a file format and digital communication protocol that allows medical equipment and software from different manufacturers to communicate with each other for easy sharing of medical data.
[0086] After image capture, the operator can perform catheter calibration on the image according to known me...
no. 2 example
[0174] It is an object of this group of embodiments of the invention to provide a method and system for three-dimensional reconstruction of tubular organs from angiographic projections. Specifically, the second group of embodiments improves the 3DR method of epipolar geometry conditions by providing additional considerations to the 3D reconstruction process, thereby providing precise correspondence between different projections, so that even in the presence of said geometric distortion and exopolar Accurate 3D models can also be provided under extremely problematic conditions.
[0175]According to a second set of embodiments, the proposed reconstruction method is based on the epipolar geometry enhanced by incorporating other considerations into the reconstruction process. These other considerations include, for example, parameters of the tubular organ derived from images along its centerline and local centerline directions, such as radius and densitometric (grayscale) values. ...
no. 3 example
[0244] It is an object of the third group of embodiments of the present invention to provide a method and system for three-dimensional organ reconstruction from more than two angiographic projections in an automated manner, i.e. without additional user interaction, i.e. Tubular organs are identified on radiographs.
[0245] Three-dimensional reconstruction of a tubular organ such as an artery from two projections can be achieved via methods known in the art. Typically, this requires user interaction to identify the organ of interest in the first two views. Once this reconstruction is available, a third group of embodiments provides a method for automatically updating based on two or more additional projections. When a 3D model reconstructed from two projections is available, it is projected onto an additional image plane according to the specific viewing geometry of this additional existing projection. This causes a large geometric distortion representing an unknown shift be...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com