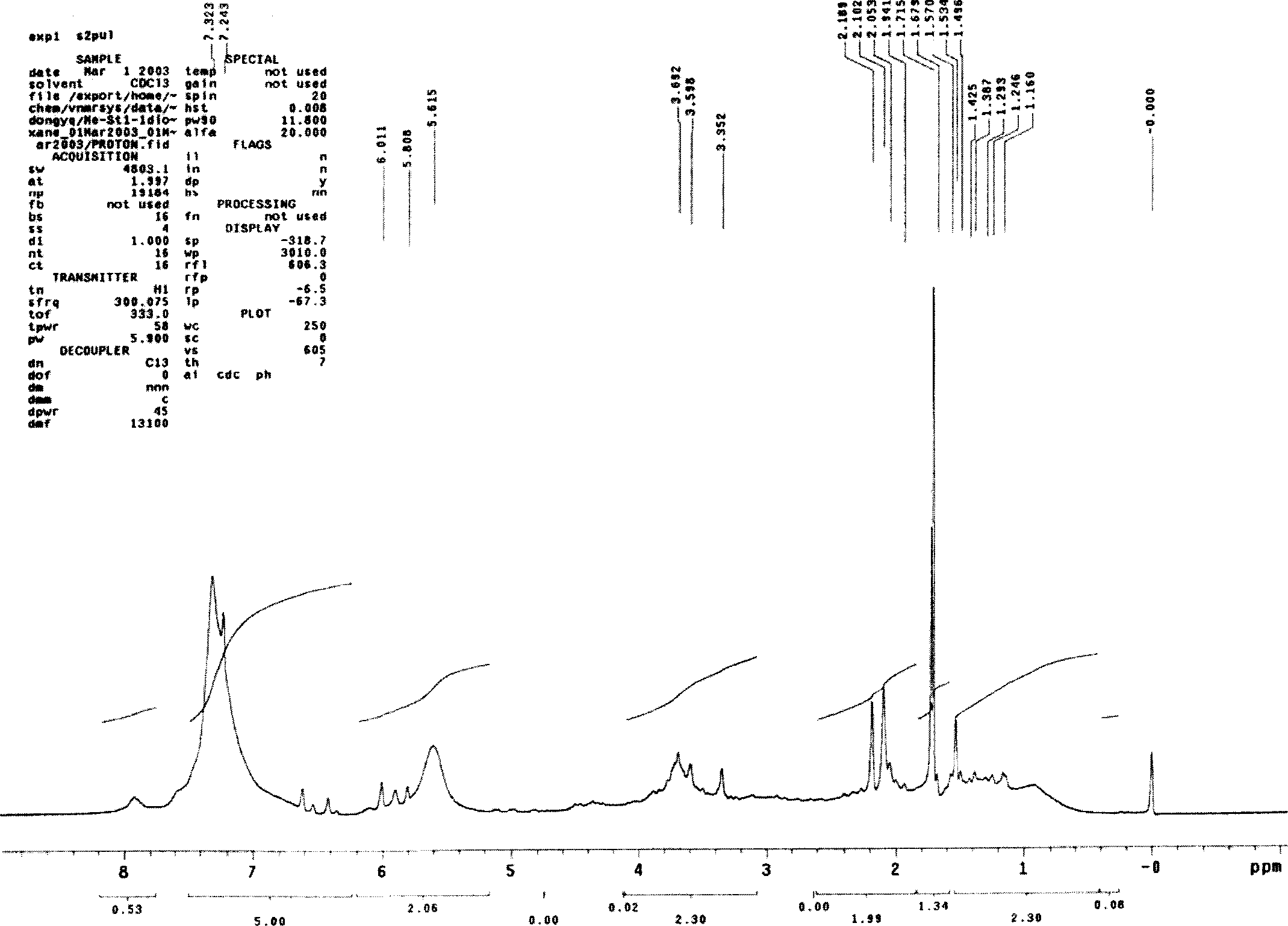
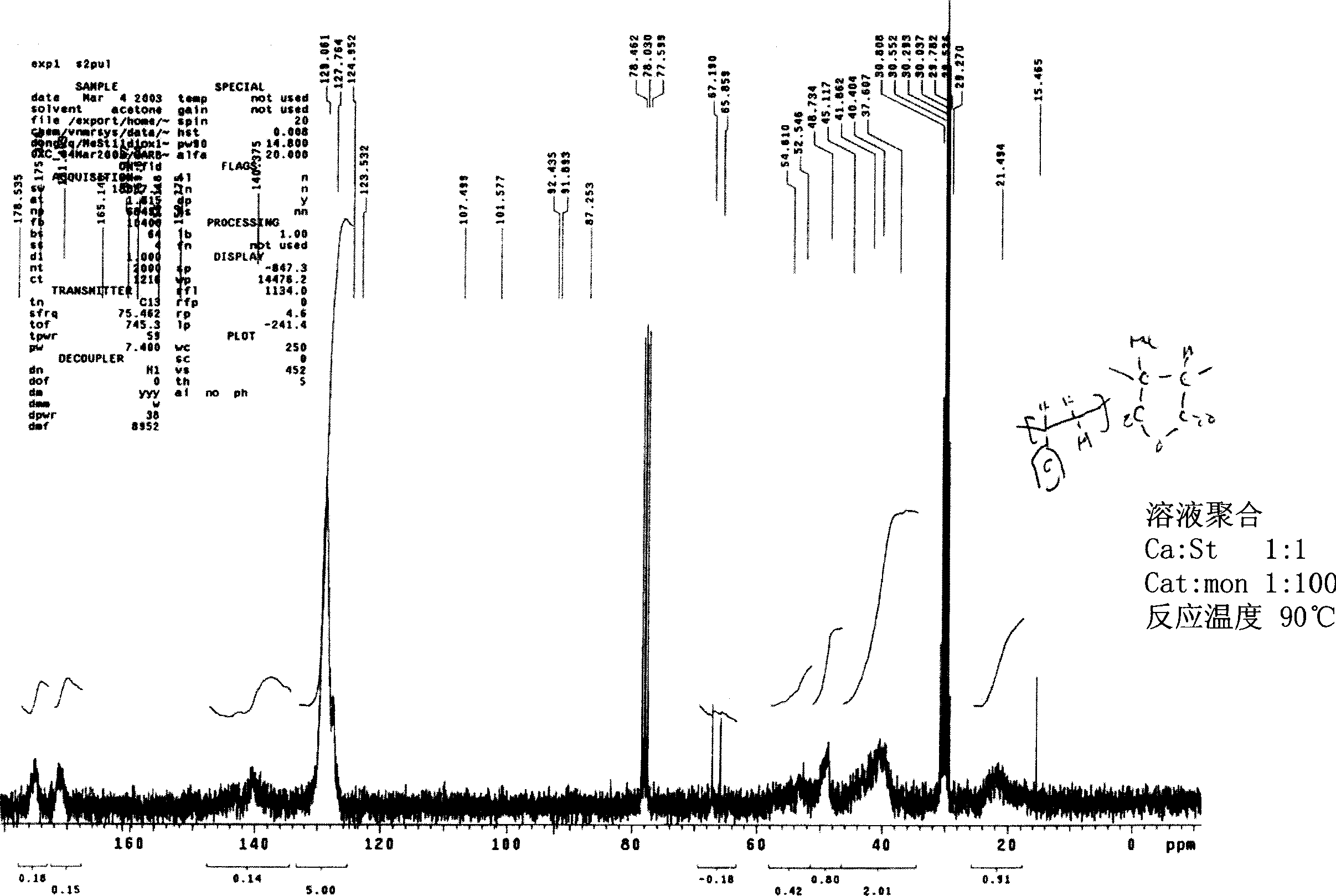
Anticreasing treating method for cotton fabrics with poly C (carboxylate acid) nano particles
A nanoparticle, cotton fabric technology, applied in fiber processing, textiles and papermaking, etc., can solve problems such as color enhancement, unsatisfactory performance, loss of fabric strength, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0055] emulsion polymerization
[0056] Polymerization is accomplished in an aqueous medium. In a typical implementation, at N 2 6 ml of deionized water, 0.02 g of SDS and 0.01 mol of monomer 1 were stirred under atmosphere for 30 min. After further stirring for 5 minutes at 60 °C, the initiator (0.0001 mol Na 2 S 2 o 8 ). in N 2 Polymerization was carried out at 60°C for 24 hours under air.
Embodiment 2
[0058] emulsion polymerization
[0059] except in N 2 0.01 mol of monomer 2 was stirred under gas for 30 minutes and the process of Example 1 was repeated. Add the initiator (0.003mol Na 2 S 2 o 8 ). in N 2 Polymerization was carried out at 90°C for 24 hours under air.
Embodiment 3
[0061] emulsion polymerization
[0062] except in N 2 0.01 mol of monomer 4 was stirred under gas for 30 minutes and the process of Example 1 was repeated. Add the initiator (0.004mol Na 2 S 2 o 8 ). in N 2 Polymerization was carried out at 80°C for 24 hours under air.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com