Semiconductor test device
A test device and semiconductor technology, applied in the direction of single semiconductor device test, measurement device, semiconductor/solid-state device test/measurement, etc., can solve the problems of inability to accurately monitor the actual temperature, inability to accurately control the heating temperature, etc., to achieve accurate temperature Effects of adjustment and reliability improvement
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
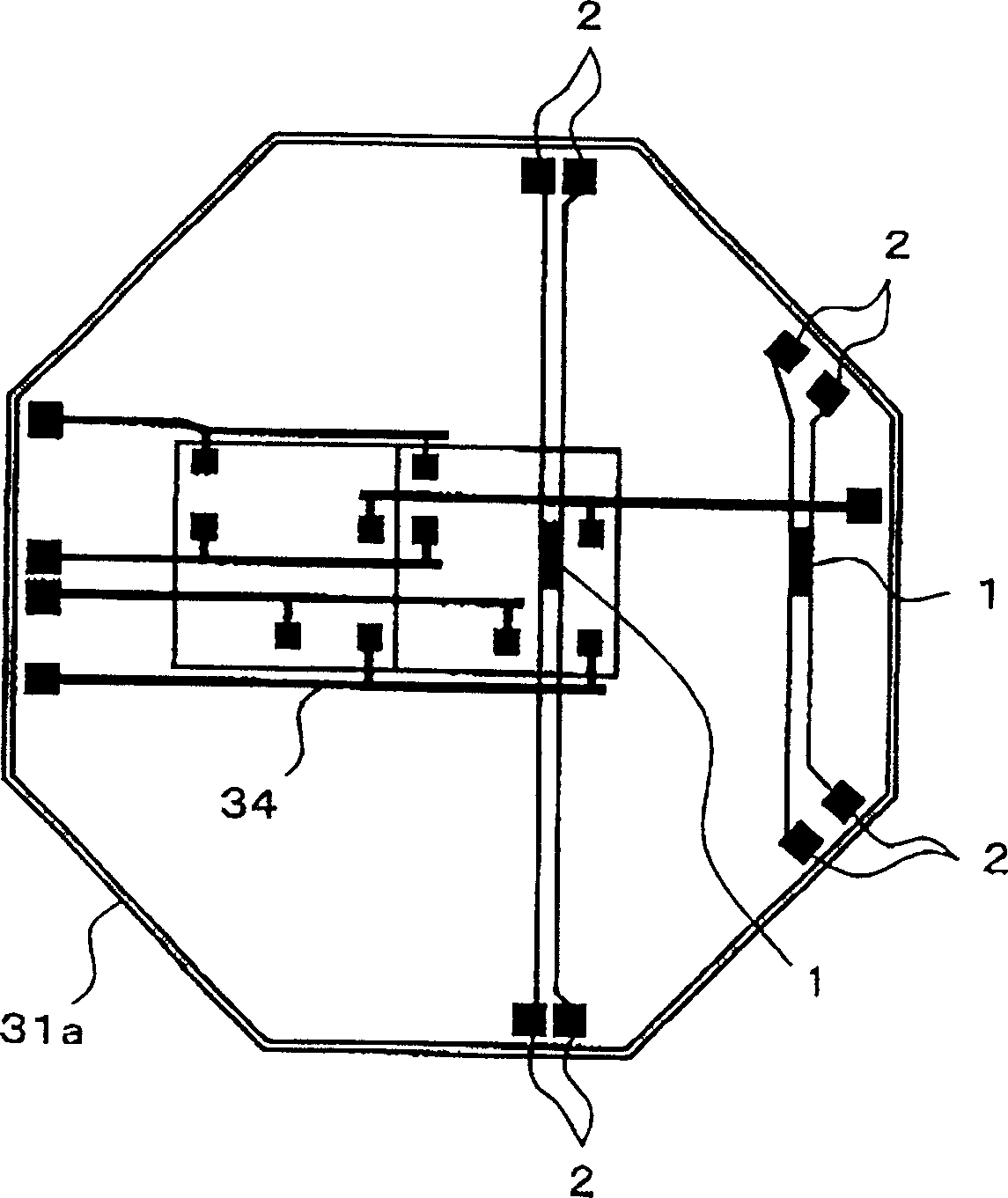
[0057] The preferred embodiment 1 of the present invention relates to the arrangement of temperature sensors. figure 1 This is a bottom view of the semiconductor testing device (detector) according to the preferred embodiment 1. in figure 1 Here, reference numeral 31a denotes a multilayer wiring board. The multilayer wiring substrate 31a corresponds to the multilayer wiring substrate 31 shown in the structure of FIG. 4. Reference numeral 34 denotes a wiring layer of the multilayer wiring substrate 31a. Reference numeral 1 denotes a temperature sensor, and reference numeral 2 denotes a terminal. In the temperature sensor 1, the measurement conditions are set from the outside through at least one of the terminals 2, and the output of the temperature sensor 1 is output to the outside through at least one of the terminals 2 and the output is monitored. The other parts of the structure are similar to the structure in FIG. 4 described above, and will not be described in detail here.
...
Embodiment 2
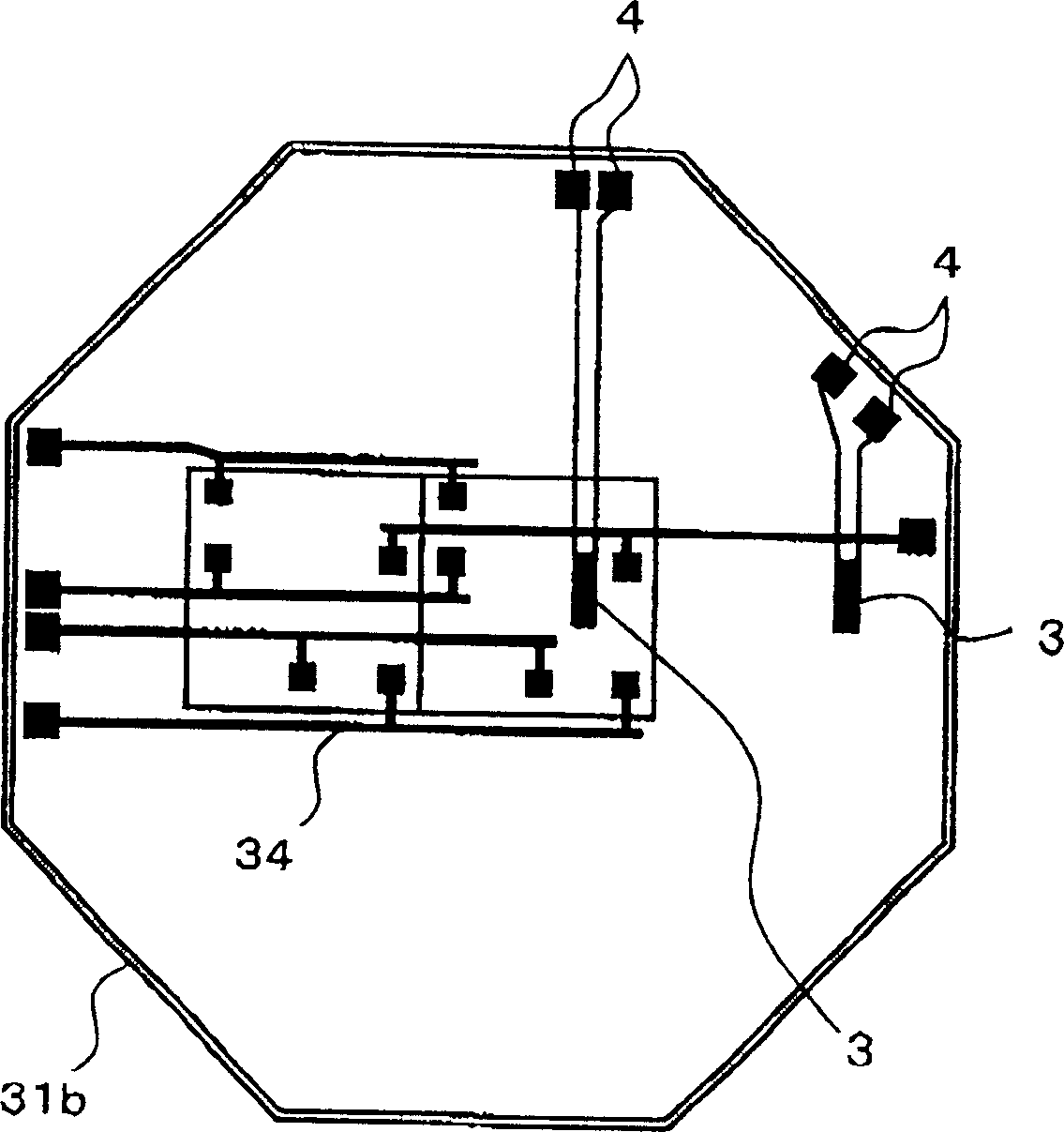
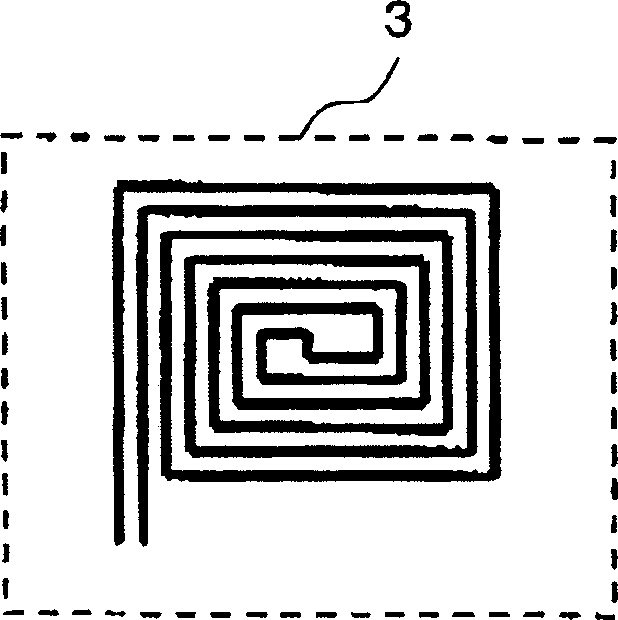
[0072] The preferred embodiment 2 of the present invention relates to the arrangement of the temperature regulator. Figure 2A It is a bottom view of the semiconductor test device according to the preferred embodiment 2. Figure 2B It is a specific example of the temperature regulator 3. Reference numeral 31b denotes a multilayer wiring substrate. The multilayer wiring substrate 31b corresponds to the multilayer wiring substrate 31 in the aforementioned structure of FIG. 4. Reference numeral 34 denotes a wiring layer of the multilayer wiring substrate 31b. Reference numeral 3 denotes a temperature regulator, and reference numeral 4 denotes a terminal. The other parts of the structure are similar to the structure in FIG. 4 described above, and will not be described in detail here.
[0073] The temperature regulator 3 is provided on the surface of the multilayer wiring substrate 31b facing the wafer. The temperature regulating surface of the temperature regulator 3 is flush with the s...
Embodiment 3
[0084] The preferred embodiment 3 of the present invention relates to the arrangement of temperature sensors and temperature regulators. image 3 It is a bottom view of a semiconductor test device combined with a temperature adjustment circuit according to the preferred embodiment 3. in image 3 Here, reference numeral 31c denotes a multilayer wiring board. The multilayer wiring board 31c corresponds to the multilayer wiring board 31 shown in FIG. 4 described above. Reference numeral 34 denotes a wiring layer of the multilayer wiring substrate 31c. Reference numeral 1 denotes a temperature sensor, and reference numeral 3 denotes a temperature regulator. Reference numerals 2 and 4 denote terminals. In the temperature sensor 1, the measurement condition is set from the outside through at least one of the terminals 2, and the output of the temperature sensor 1 is output to the outside through at least one of the terminals and the output is monitored. The temperature regulator 3 is co...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| temperature coefficient of resistance | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com