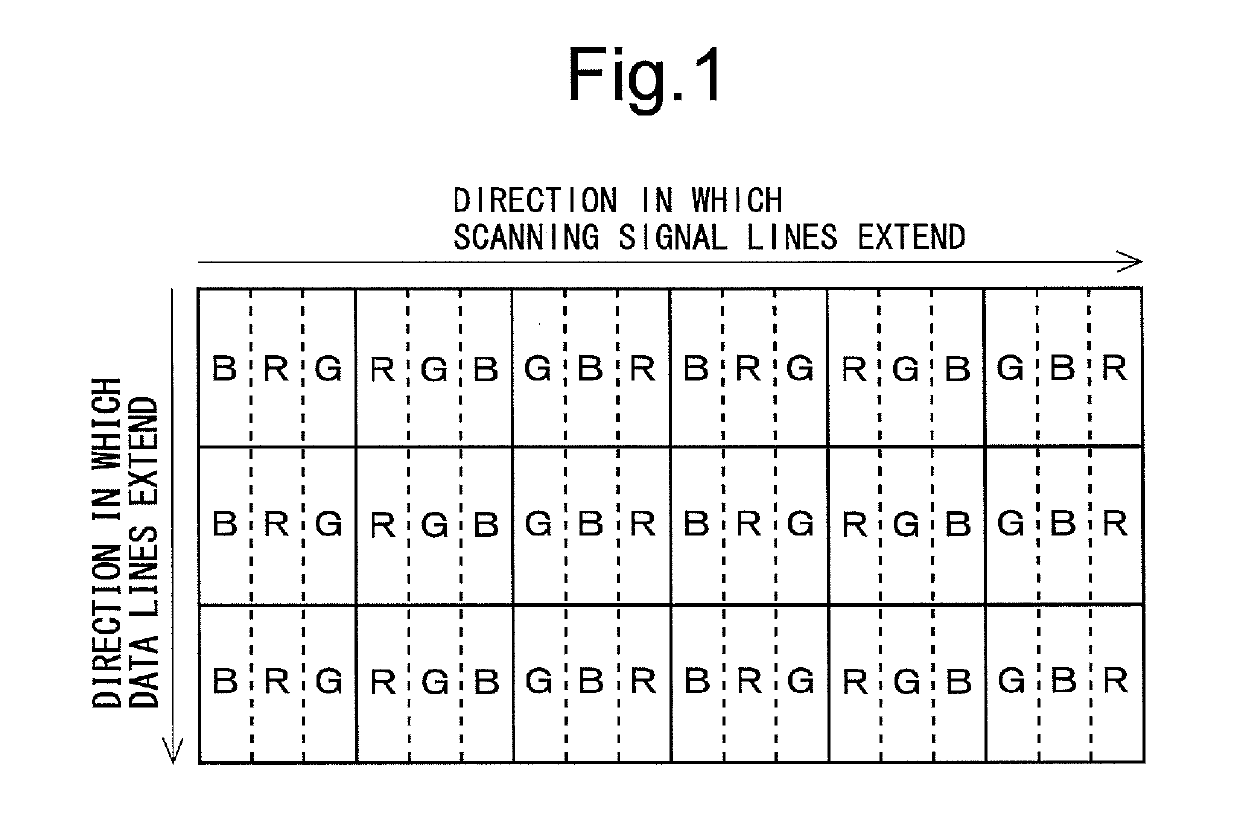
Display device and driving method therefor
a technology of a display device and a driving method, which is applied in the direction of static indicating devices, instruments, electroluminescent light sources, etc., can solve the problems of difficult to achieve size increase and definition improvement, difficult to achieve definition improvement, etc., to suppress display unevenness or vertical stripes, low resolution image, and low driving frequency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
1. First Embodiment
[0164]
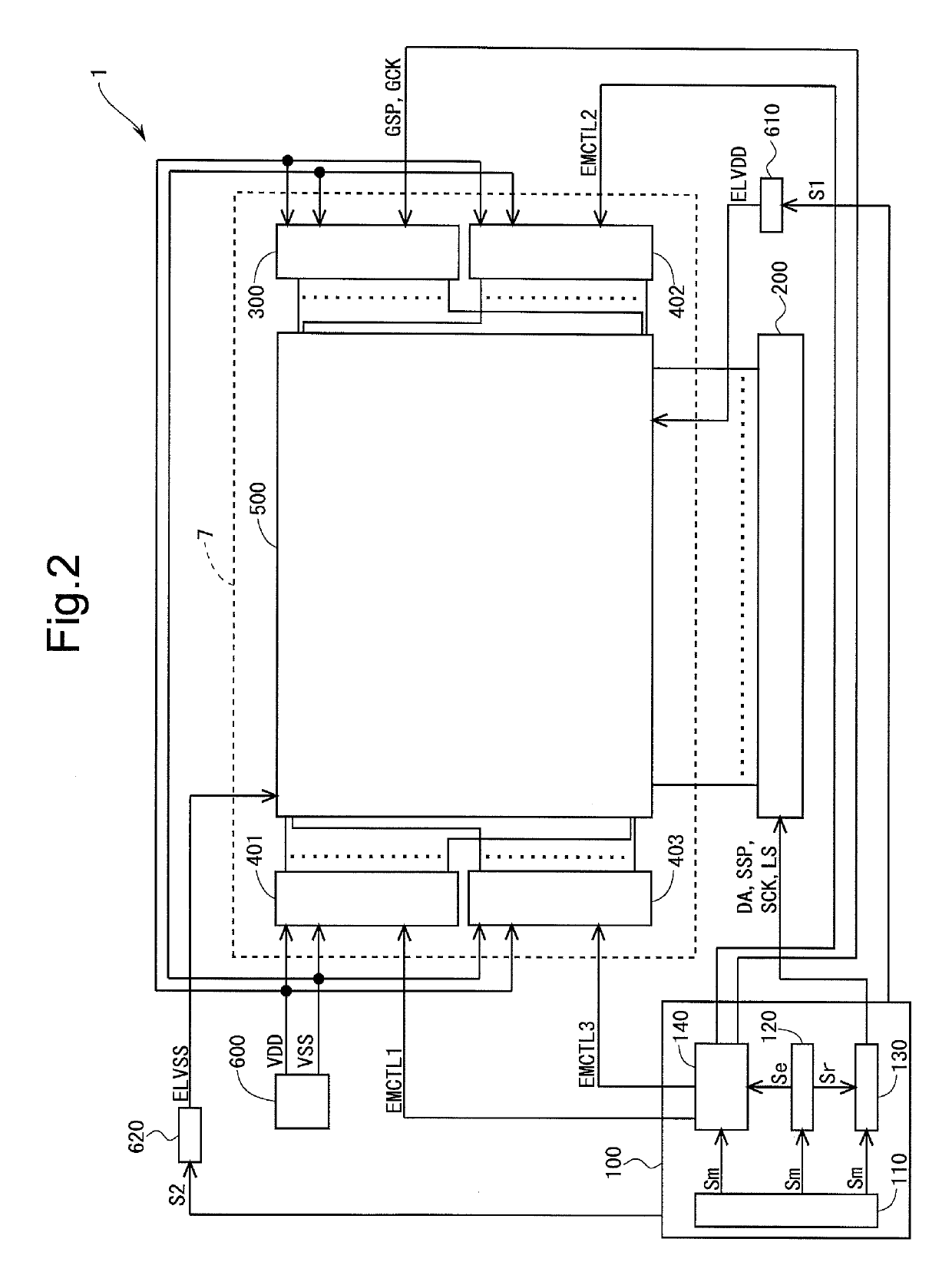
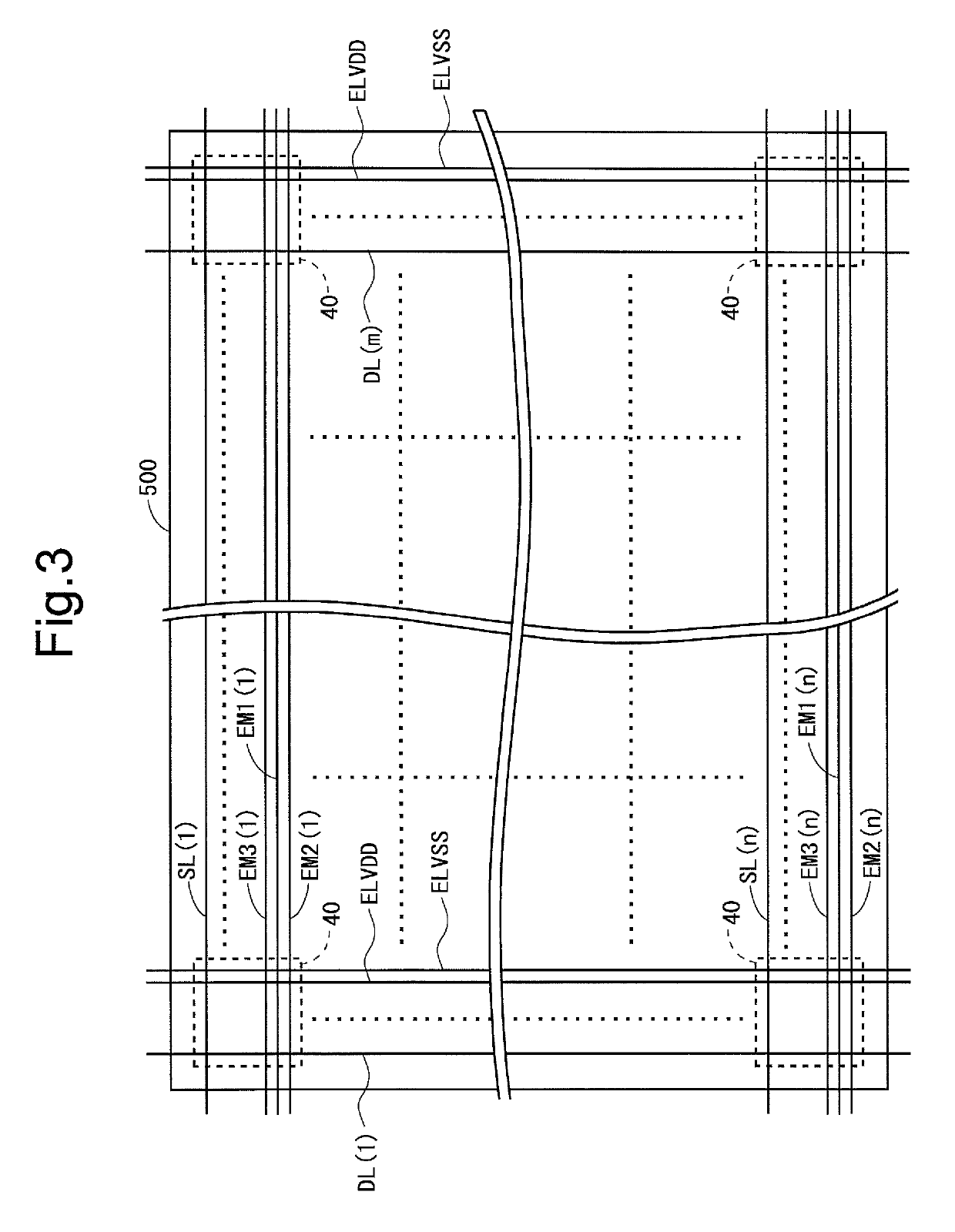
[0165]FIG. 2 is a block diagram showing an overall configuration of an active matrix-type organic EL display device 1 according to a first embodiment of the present invention. The organic EL display device 1 includes a display control circuit 100, a source driver (a data line drive circuit) 200, a gate driver (a scanning signal line drive circuit) 300, first to third emission drivers (first to third light-emission control line drive circuits) 401 to 403, and a display unit 500. The first to third emission drivers 401 to 403 are hereinafter also collectively and simply referred to as “emission driver”. The emission driver is a drive circuit for wiring lines (emission lines which will be described later) for controlling the light emission of organic EL elements provided in the display unit 500. Note that in the present embodiment the gate driver 300 and the first to third emission drivers 401 to 403 are formed in an organic EL panel 7 including the display uni...
second embodiment
2. Second Embodiment
[0241]
[0242]A second embodiment of the present invention will be described. In recent years, in order to realize a reduction in power consumption in a display device, developments have been made in a driving method involving “providing a pause period during which a write operation of image data pauses by bringing all scanning signal lines into a non-scanning state, between a refresh period (a writing period) and a refresh period (a writing period)”. Such a driving is called, for example, “pause driving”. In a display device adopting the pause driving, since it can bring the operation of the peripheral drivers to a halt in the pause period, power consumption can be reduced. Also in the organic EL display device, the pause driving like this is being adopted. Therefore, an organic EL display device adopting the pause driving will be described as a second embodiment of the present invention. Note that an overall configuration (see FIG. 2), an arrangement of pixels (s...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com