Method for producing a complex nonwoven fabric and resulting novel fabric
a nonwoven fabric and complex technology, applied in the direction of needling machines, wood layered products, textiles and paper, etc., can solve the problems of forming rough products, and reducing the flexibility of complexes, so as to reduce achieve the effect of reducing the loss of cellulosic fibers, reducing the absorption of complexes, and increasing the cost of energy consumption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
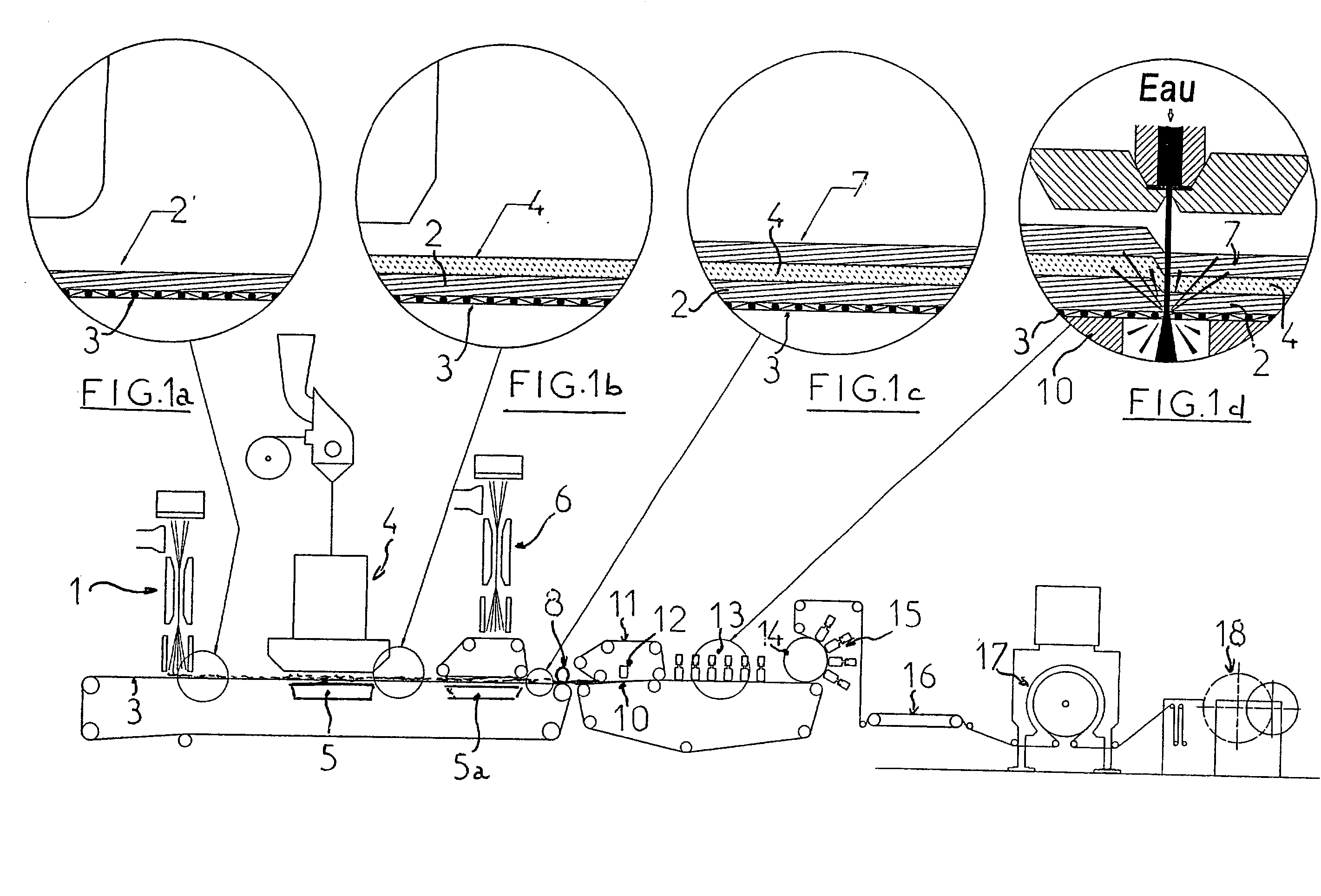
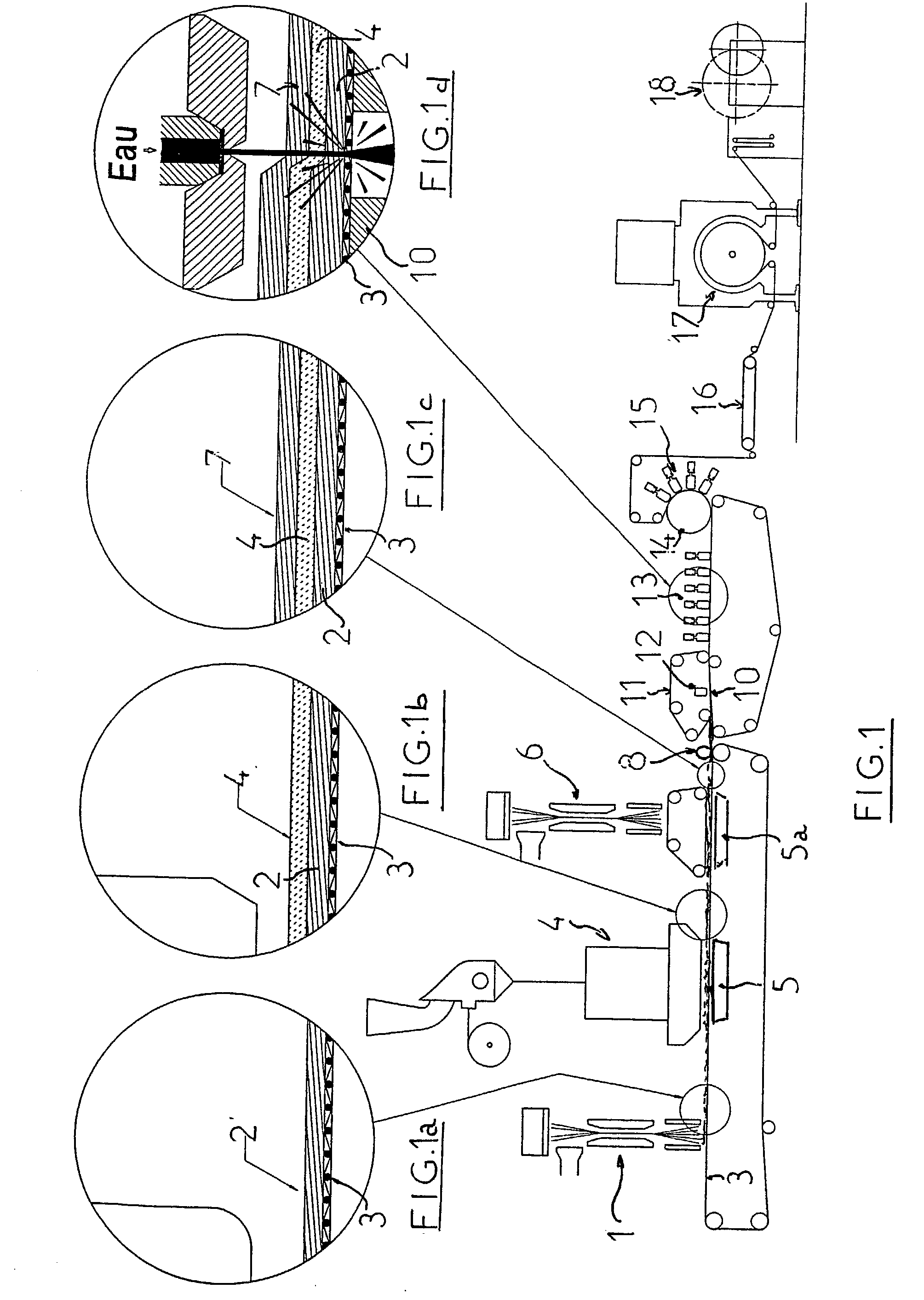
[0046] A product in accordance with the invention is produced in the following way.
[0047] A web (2) of continuous filaments, weighing 15 g / m.sup.2, is produced on a unit sold by the Applicant under the name "spunjet", which allows a nonwoven web to be produced by extrusion, drawing and distribution of continuous filaments.
[0048] In this embodiment, as polymer, polypropylene such as that sold by Amoco under the reference 100 ZA 35 is extruded.
[0049] The web formed consists of 7000 filaments per meter of width and is produced at a rate of 250 meters per minute. The diameter of the filaments after drawing is about 15 microns.
[0050] A suction unit placed opposite the drawing slit (20) allows precise control of the way in which the filament is deposited on the conveyor belt (3) and of its uniformity thereover.
[0051] Placed above the same conveyor (3) is a unit (4) for distributing, by the airlaid technique, discontinuous fibers over the web (2) formed beforehand.
[0052] Such a fiber-distr...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| velocity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com