Flame-resistant sheet with candle wick support
a flame-resistant sheet and wick technology, applied in the field of candles, can solve the problems of destroying the ability of the peripheral wall to contain the pool of liquid fuel, destroying the ability of the peripheral wall to absorb the liquid fuel, and wicks not falling over and ashes properly
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
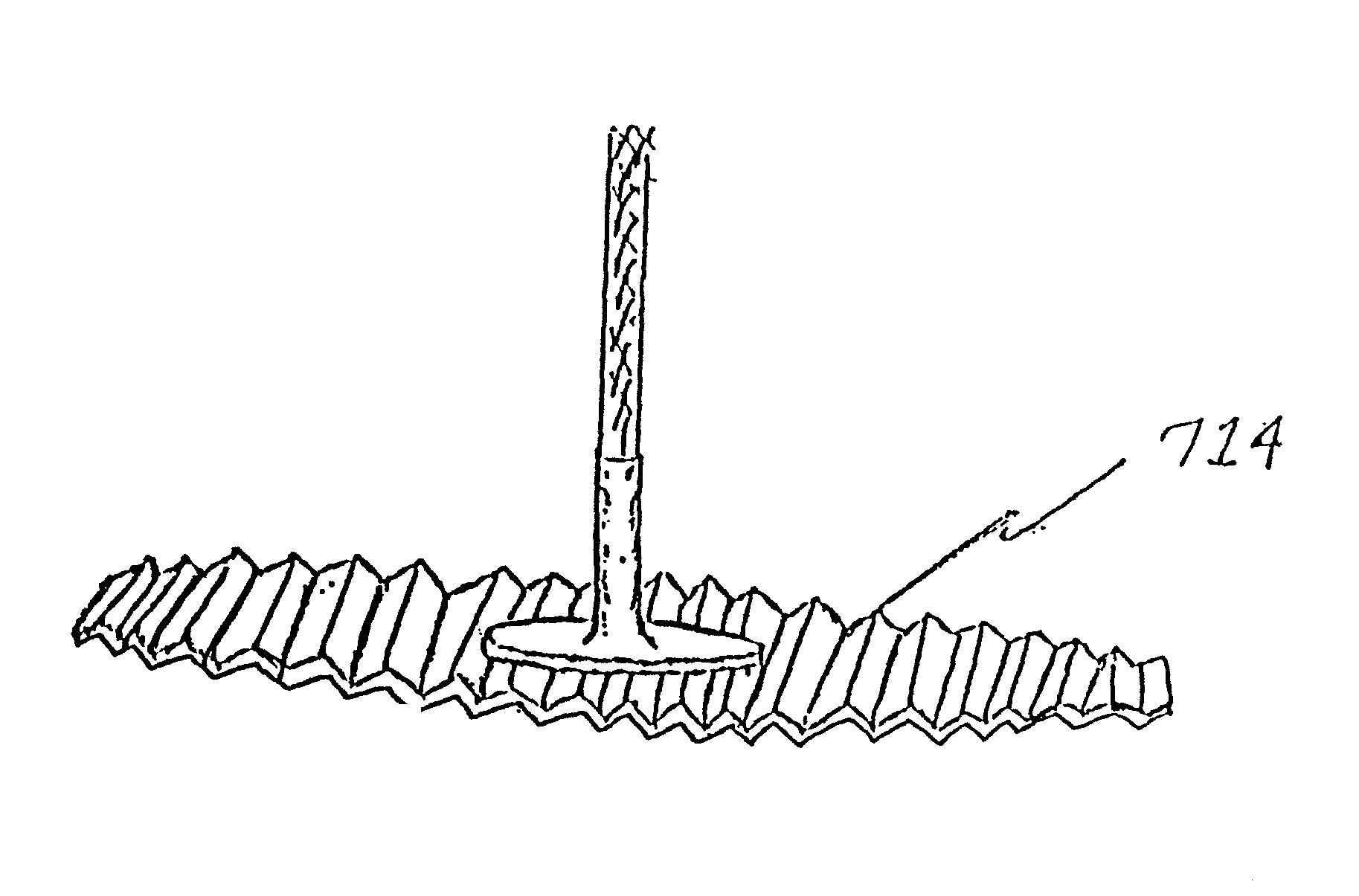
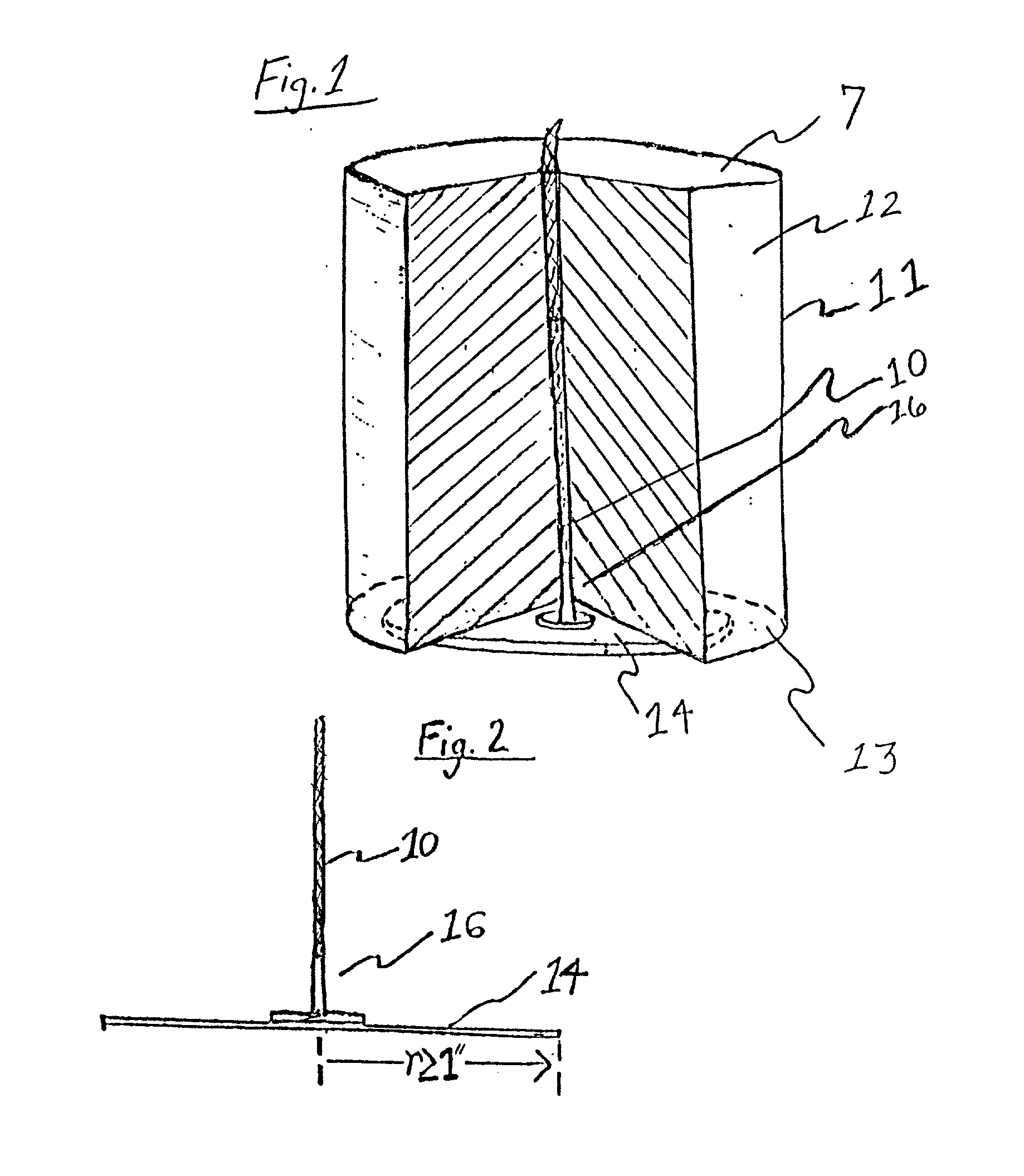
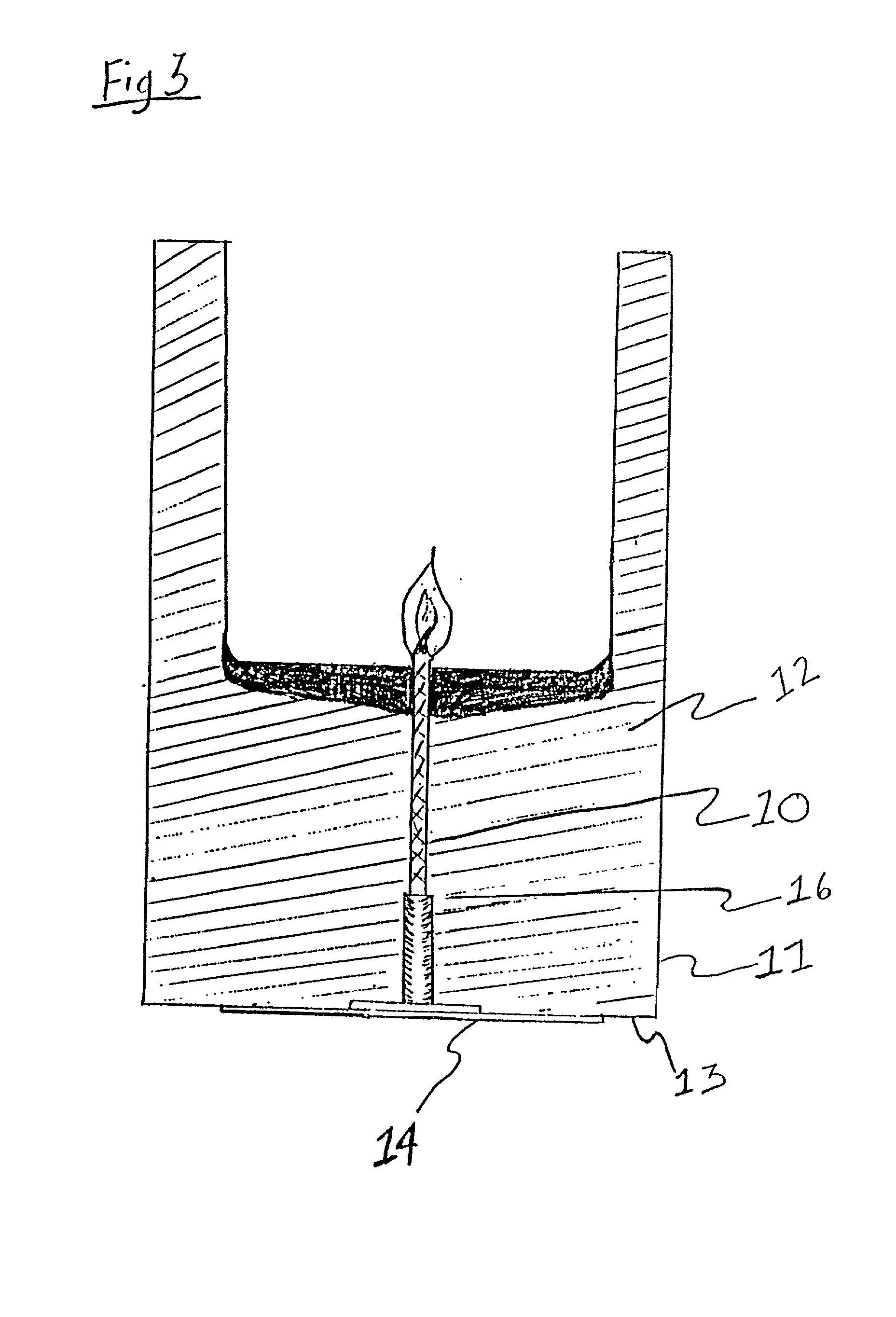
[0045] The utility of the invention is for a freestanding candle having a width of at least two inches, and structural elements of the preferred embodiment are shown in FIGS. 1-4. As depicted in FIG. 1, the freestanding candle is a fuel body 12 that has a top surface 7, a bottom surface 13, and an outer peripheral surface 11. The fuel body 12 supports a wick 10. A flame-resistant sheet 14 is joined to the fuel body 12, which has been cut away to show a wick support 16 contacting the sheet 14 and holding the wick 10.
[0046] The sheet 14 is flame-resistant, meaning that the sheet 14 will not ignite when exposed to the flame on the wick 10 and the heat from the flame. The sheet 14 is composed of a material such as metal or plastic, and the thickness of the sheet 14 may vary. The sheet 14 in FIG. 1 is shown circular by a hyphenated line, but the sheet 14 may have a different form, such as a square shape. Preferably the sheet 14 is the general shape of the pool of liquid fuel that accumul...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com