Headset for measuring physiological parameters
a technology for measuring headsets and physiological parameters, applied in the field of headsets for measuring physiological parameters, can solve problems such as increasing time delay
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
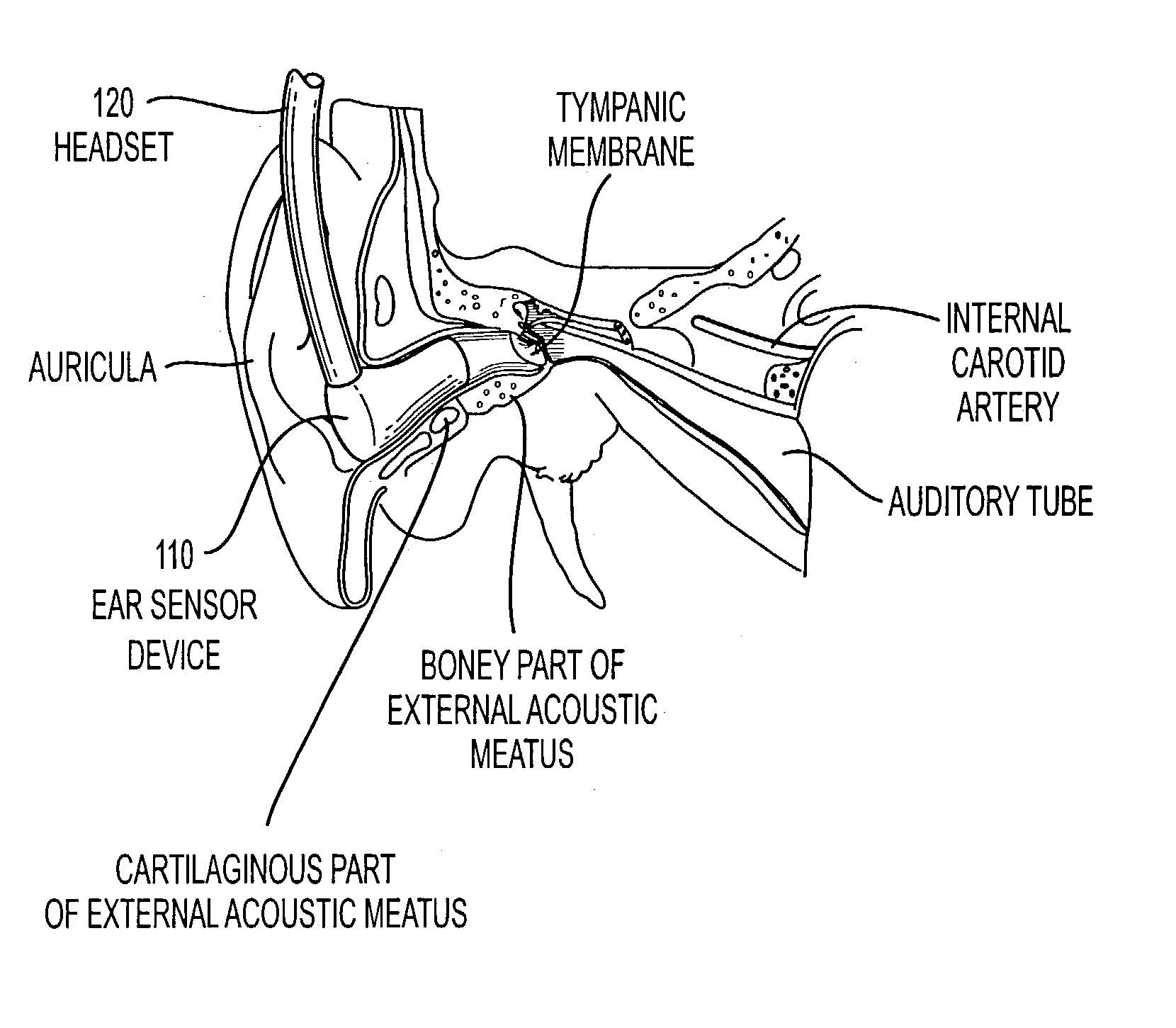
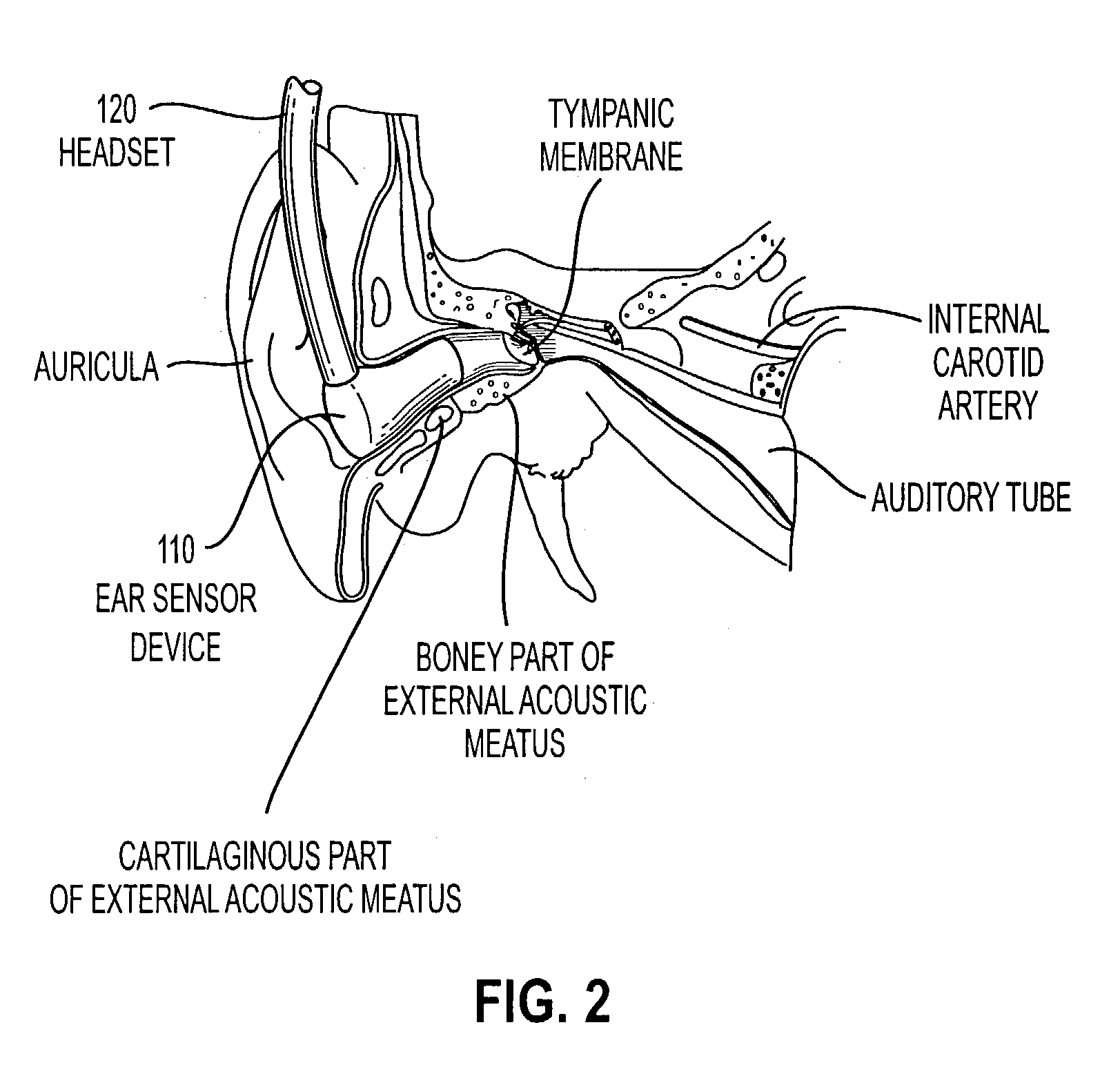
[0033] As described herein, this invention provides systems and methods for acquiring body sound information from a person's ear, which can then be converted to useful physiological parameters of interest, such as heart rate, heart valve closure timing, pulse wave velocity, blood pressure, and the like.
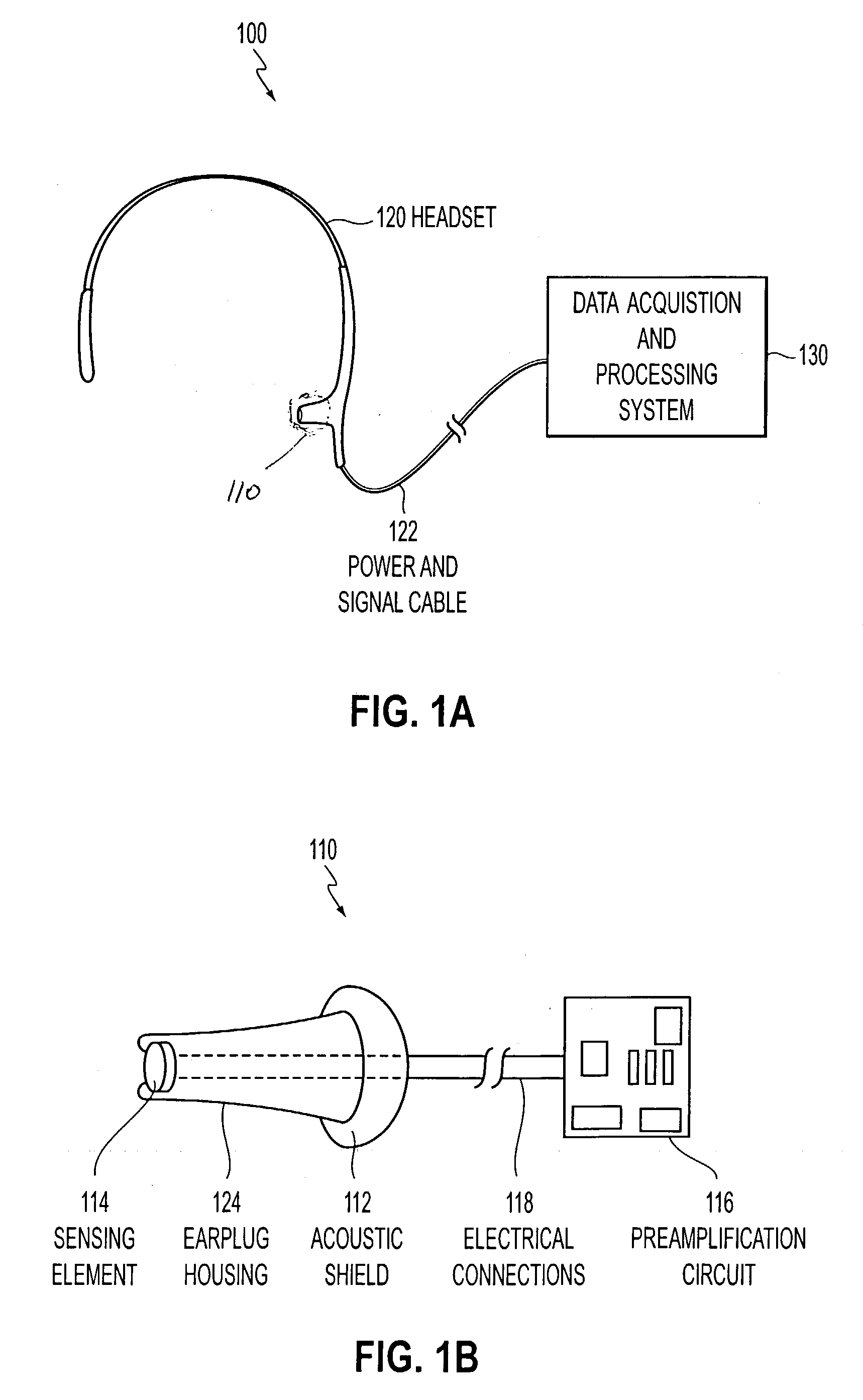
[0034] FIGS. 1A and 1B show one exemplary embodiment of a system 100 according to this invention in which internally generated body sounds are detected or measured using an ear sensor device 110 inserted into the ear of a person. As shown in FIGS. 1A-1B, the ear sensor or ear sensing device 110 includes an ear plug housing 124, a sensor element 114 disposed within a portion of the ear plug housing 124, an acoustic shield 112 and a preamplification circuit 116 electrically coupled to sensor element 114 via electrical connections 118. The purpose of the acoustic shield 112 is to shield the sensor element 114 from ambient noise generated outside the person's body. The preamplification ci...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com