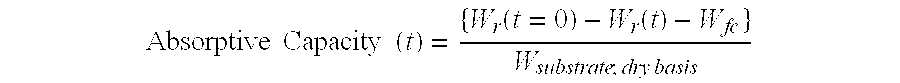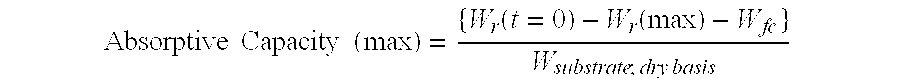100% synthetic nonwoven wipes
a technology wipes, applied in the field of synthetic nonwoven cloth, can solve the problems of increasing the cost of nonwoven cloth making, precursor web formation, increasing the stiffness of the web, etc., and achieves good machine and cross-directional strength and high absorption capacity.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0122] S-Tex 194050HO, manufactured by BBA Fiberweb, Nashville, Tenn. U.S.A., is used as the starting nonwoven. S-Tex 194050HO is a 50 gsm spunlaid nonwoven made from 100% polypropylene with a fiber titre of 2.0 dtex (dtex is the unit denoting grams per 10,000 linear meters of fiber) and thermally bonded. No surface treatment is added to the nonwoven.
[0123] The absorptive capacity, expressed in grams of liquid composition per gram of wipe of S-Tex 194050HO for the two different liquid compositions is summarized in the table below:
Absorptive CapacityLiquid[g liquid composition / g wipe]Deionized Water0.150.1% Triton ™ X-100-PC in Deionized8.9Water
[0124] This example demonstrates the influence of the liquid on absorptive capacity.
example 2
[0125] Fibrella 7458, manufactured by Suominen Nonwovens, Nakkila, Finland, is used as the starting nonwoven. Fibrella 7458 is a 58 gsm carded nonwoven made from 60% polypropylene staple fiber and 40% viscose fiber, each with a fiber titre of 1.5 dpf (dpf is the unit denoting grams per 9,000 linear meters of fiber) and hydroentangled. No surface treatment is added to the nonwoven.
[0126] The absorptive capacity of Fibrella 7458 for the two different liquid compositions is summarized in the table below:
Absorptive CapacityLiquid[g liquid composition / g wipe]Deionized Water8.20.1% Triton ™ X-100-PC in Deionized8.5Water
[0127] When compared with Example 1, this example demonstrates that adding absorbent material to the nonwoven desensitizes the influence of the liquid composition on absorptive capacity.
example 3
[0128] Avspun™ Phobic, manufactured by Avgol Nonwoven Industries, Holon, Israel, is used as the starting nonwoven. Avspun™ Phobic is a 50 gsm spunlaid nonwoven made from 100% polypropylene with a fibre titre of 1.4 dpf and hydroentangled. No surface treatment is added to the nonwoven.
[0129] The absorptive capacity of Avspun™ Phobic for the two different liquid compositions is summarized in the table below:
Absorptive CapacityLiquid[g liquid composition / g wipe]Deionized Water0.140.1% Triton ™ X-100-PC in Deionized12.8Water
[0130] In conjunction with Example 1, this example demonstrates the influence of the liquid on absorptive capacity regardless of the method of nonwoven construction. This also illustrates that a significant increase in total absorptive capacity can be achieved by combining hydroentangled, continuous thermoplastic nonwovens and a low surface tension fluid.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Mass | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Mass | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com