Replication system having the capability to accept commands at a standby-system site before completion of updating thereof
a technology of a standby system and a command, applied in the field of replication systems, can solve the problems of rapid switching, increase in processing amount, performance drop, etc., and achieve the effect of reducing performance drop
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
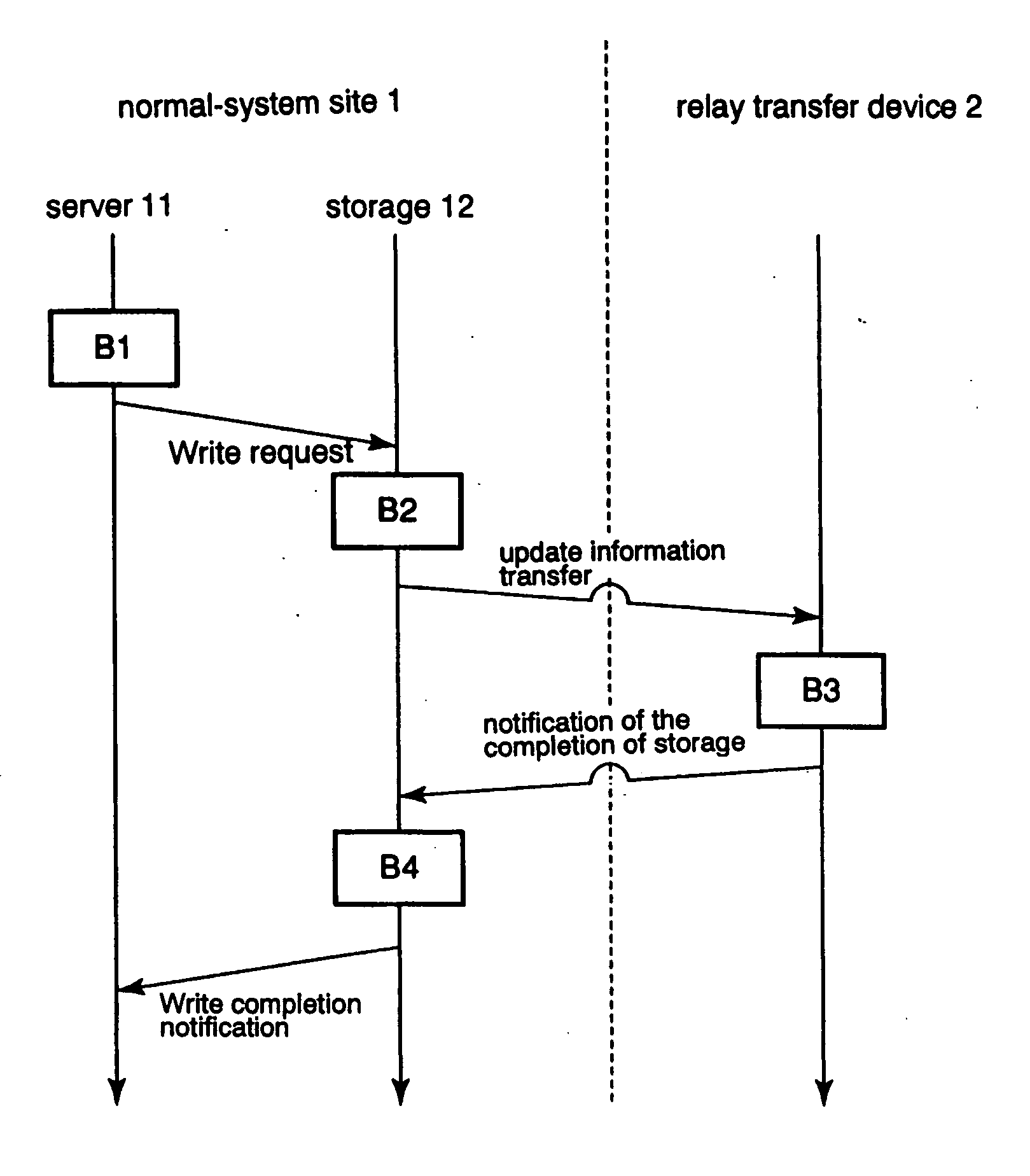
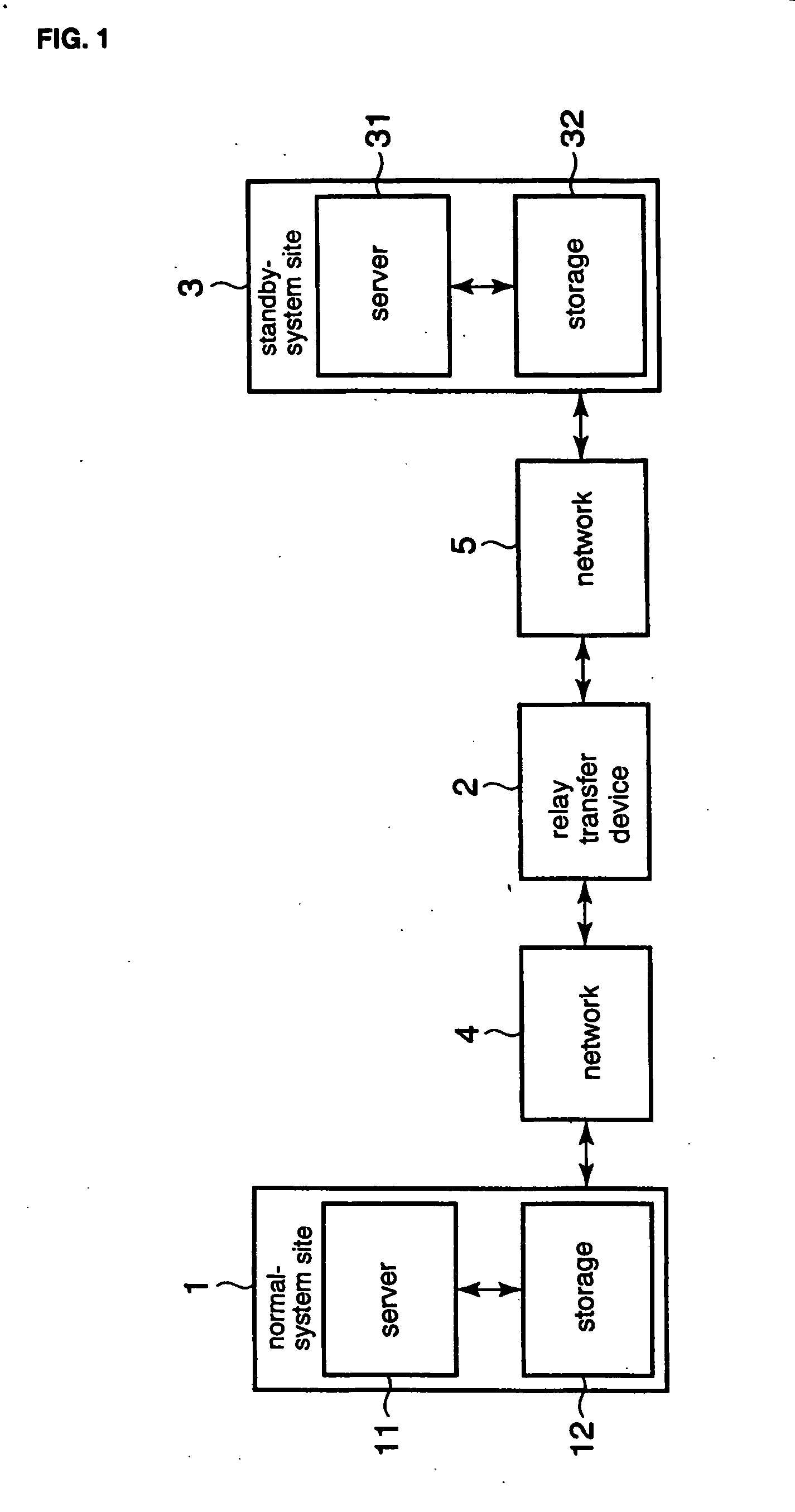
[0080]FIG. 1 is a block diagram showing the replication system of the first embodiment of the present invention. The replication system of the first embodiment is a computer system that provides services and that includes normal-system site 1, standby-system site 3, and relay transfer device 2. Normal-system site 1 and relay transfer device 2 are connected by network 4; and standby-system site 3 and relay transfer device 2 are connected by network 5.
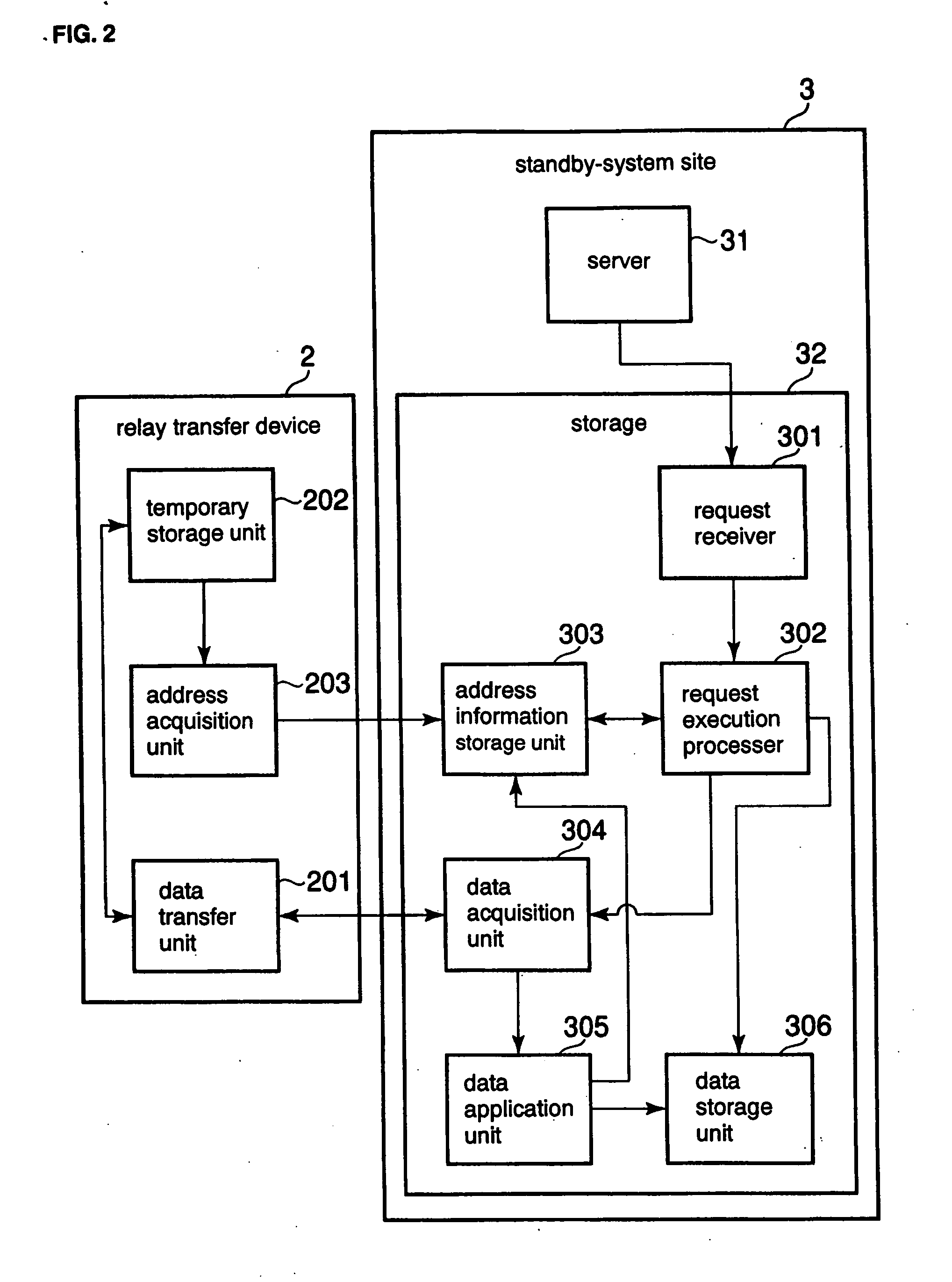
[0081] Normal-system site 1 is the site that is used during normal operation and includes server 11 and storage unit 12.
[0082] Storage 12 is a memory device for storing data. As an example, storage 12 may be a single disk device or a disk array device that is composed of a plurality of disk devices. As another example, storage 12 may be a magneto-optical device or an array device that is a collection of such devices. As yet another example, storage 12 may be a memory device that is realized by a single or a plurality of semiconductor m...
second embodiment
[0235] The second embodiment of the present invention is a system in which, when there is a plurality of types of data, a transfer priority is assigned to each data type in accordance with a fixed policy, and data are then transferred from relay transfer device 2 to standby-system site 3 in accordance with the transfer priority. This form can be widely applied, including in the first embodiment and in Modifications 18 of the first embodiment. An example is here shown in which this form is applied to the first embodiment.
[0236]FIG. 40 is a block diagram showing the configuration of the replication system of the second embodiment. Referring to FIG. 40, the replication system of the second embodiment includes normal-system site 1, relay transfer device 2, standby-system site 3, and networks 4 and 5, as in the first embodiment. In addition, normal-system site 1 includes server 11 and storage 12. Standby-system site 3 includes server 31 and storage 32.
[0237] In the second embodiment, s...
modification 1
of the Second Embodiment
[0259] Modification 1 of the second embodiment is a form that allows alteration of the data transfer policy of relay transfer device 2.
[0260]FIG. 46 is a block diagram showing the configuration of the replication system in Modification 1 of the second embodiment. Referring to FIG. 46, the replication system of the present modification includes policy control device 6 in addition to normal-system site 1, relay transfer device 2, standby-system site 3, and networks 4 and 5. Normal-system site 1, relay transfer device 2, standby-system site 3, and networks 4 and 5 are all equivalent to the second embodiment shown in FIG. 40.
[0261] Policy control device 6 supplies instructions to relay transfer device 2 for controlling the policy of policy storage unit 206 of relay transfer device 2 during operation or during a halt in operation. For example, policy control device 6 detects the states of normal-system site 1, relay transfer device 2, standby-system site 3 or ot...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com