Tactile warning system
a tactile warning and warning system technology, applied in the field of tactile warning systems, can solve the problems of previously developed tactile warning systems, the danger of sight impaired individuals, and the inability to detect the presence of objects,
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
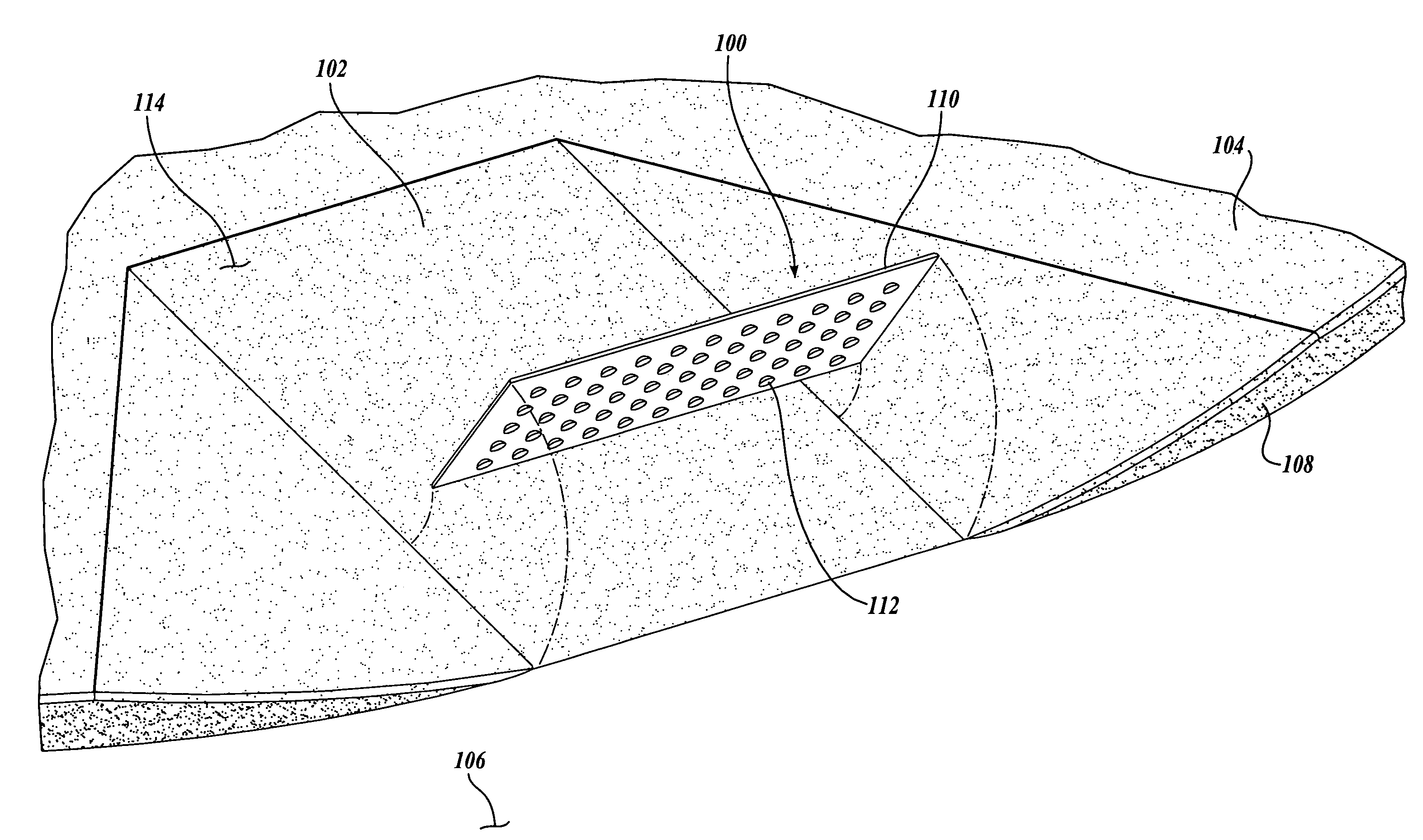
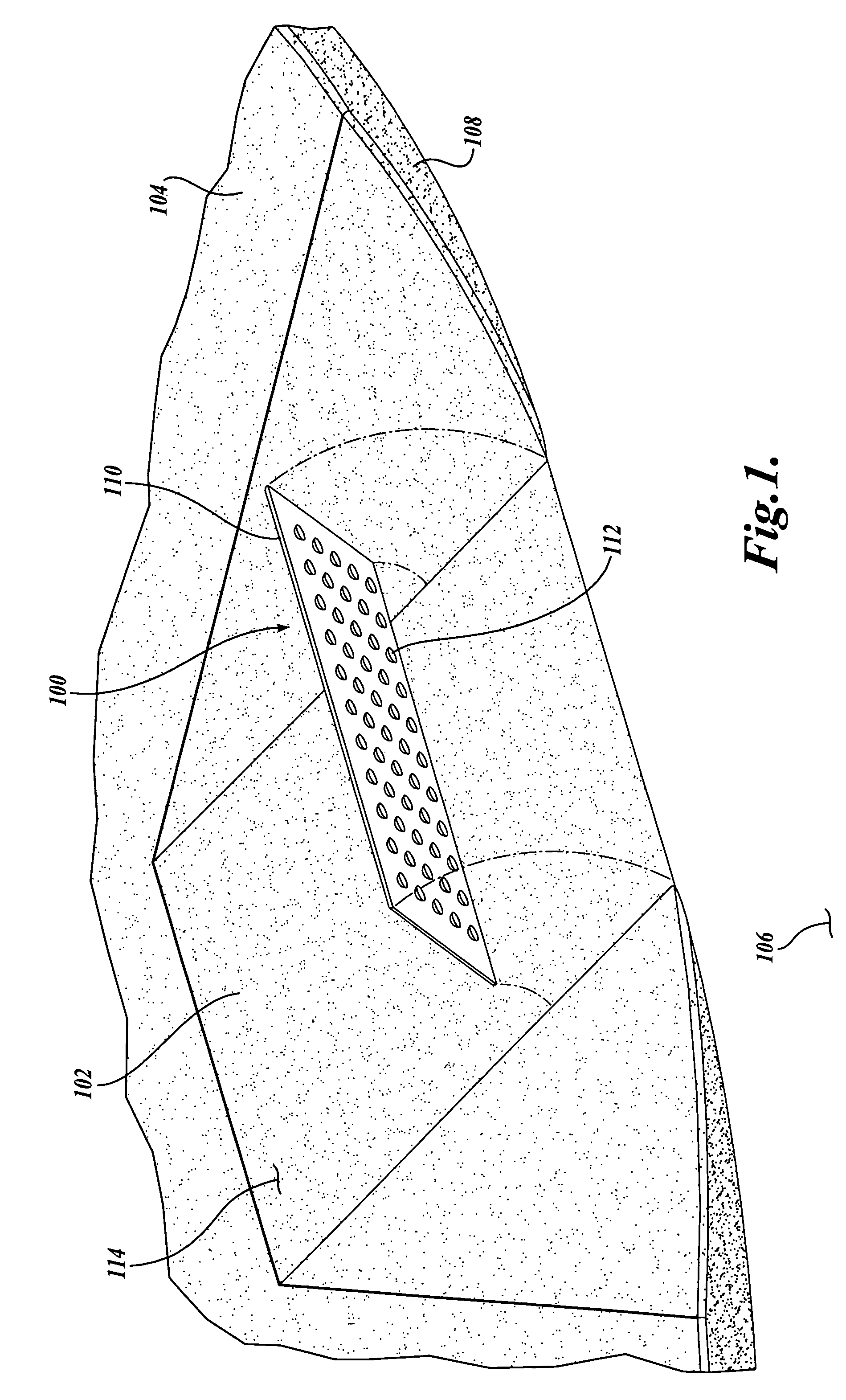
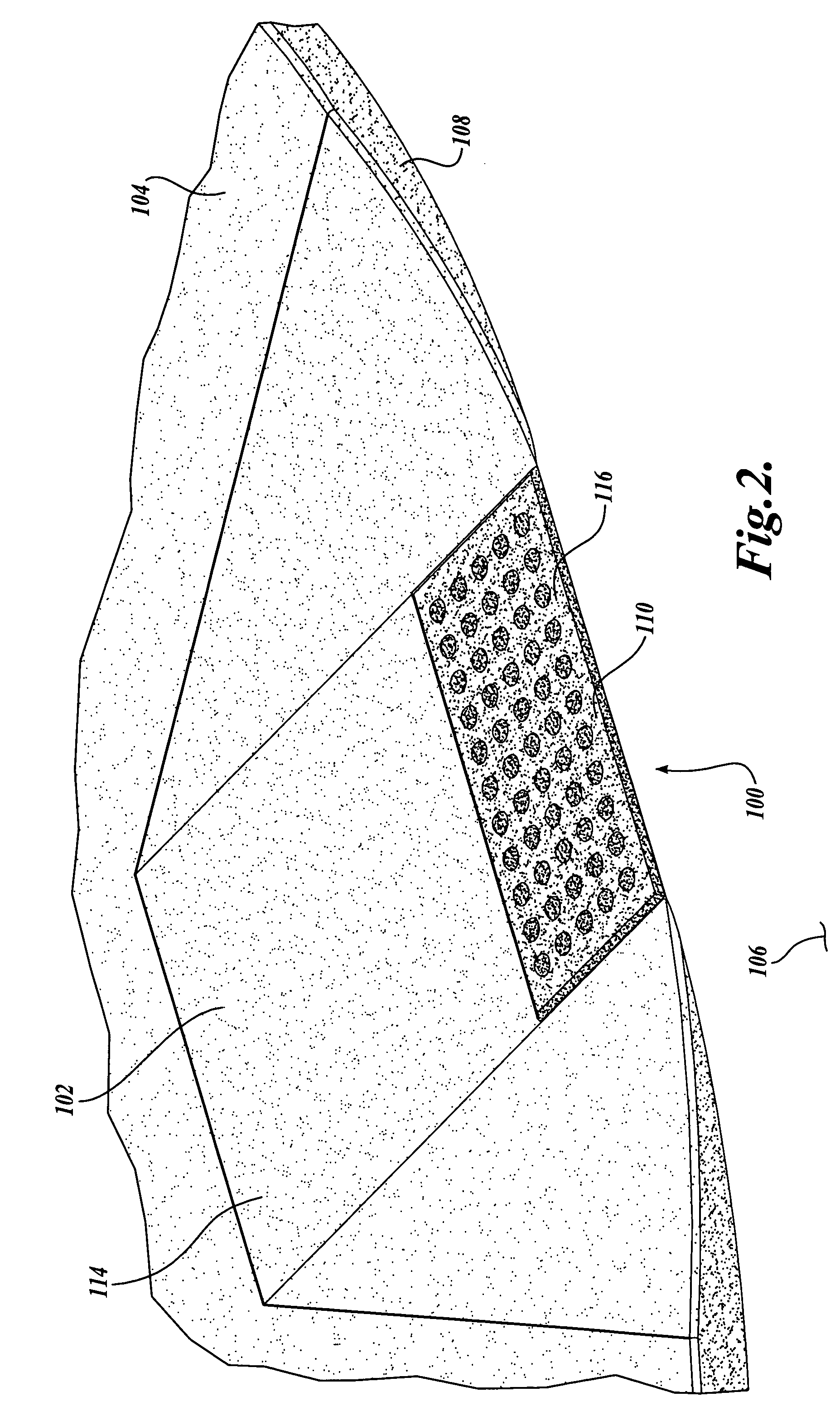
[0025] Referring to FIGS. 1-5, one embodiment of a tactile warning system 100 formed in accordance with the present invention is disclosed. Turning to FIG. 2, the tactile warning system 100 provides a textural change to warn sight impaired individuals of a hazard or obstacle in the vicinity of the sight impaired individual. Moreover, the tactile warning system 100 provides a contrasting texture that signals a potentially hazardous condition to the pedestrian, and thereby informs the pedestrian to exercise care.
[0026] In the illustrated embodiment, the tactile warning system 100 is shown as applied to a ramp 102 of a sidewalk 104. Normally, the raised height of the sidewalk 104 relative to the height of the adjacent roadway 106 provides a curb edge 108 which indicates to a sight impaired individual the presence of the roadway 106. However, it has been found that transitions, such as curb ramps 102, vehicle drop-offs, depressed corners, and the like, although accommodating access to ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com