Method and a device for detecting an abnormality of a heat exchanger and the use of such a device
a technology of abnormality and heat exchanger, which is applied in the direction of material thermal analysis, lighting and heating apparatus, steam/vapor condensers, etc., can solve the problems of reduced heat exchange, insufficient fluid flow, and increased power consumption, so as to reduce the sensibility to fluctuations
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
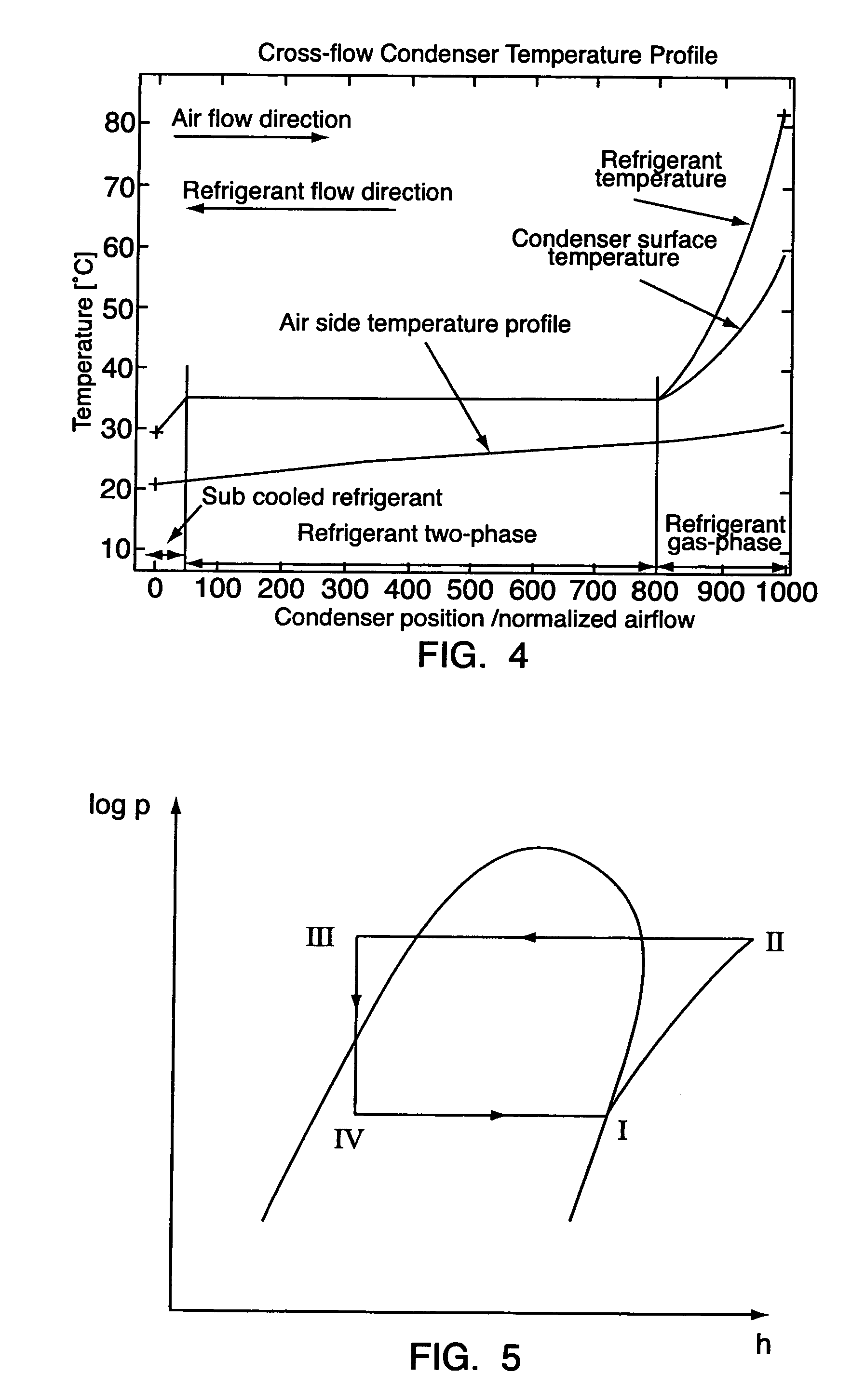
[0039] In the following reference will be made to a heat exchanger in a simple refrigeration system, although the principle is equally applicable to a heat exchanger in other heat exchanging systems, and as understood by the skilled person, the invention is in no way restricted to a refrigeration system.
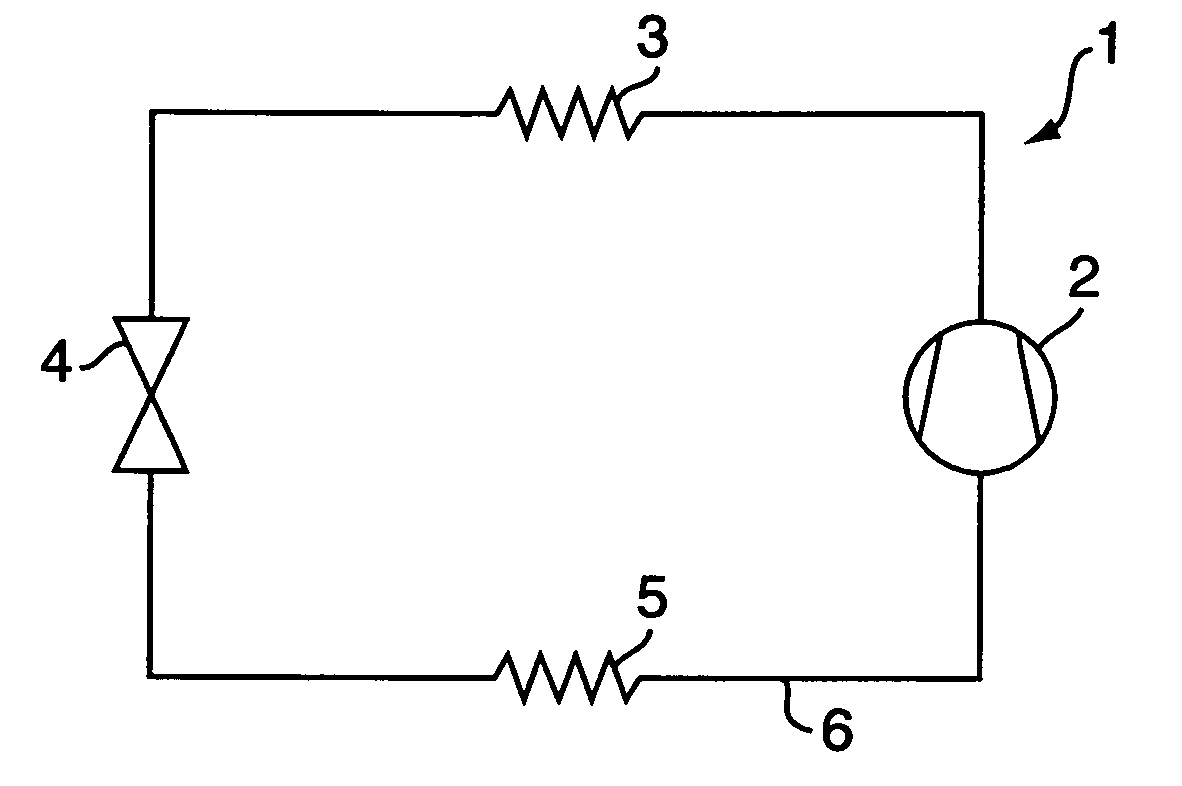
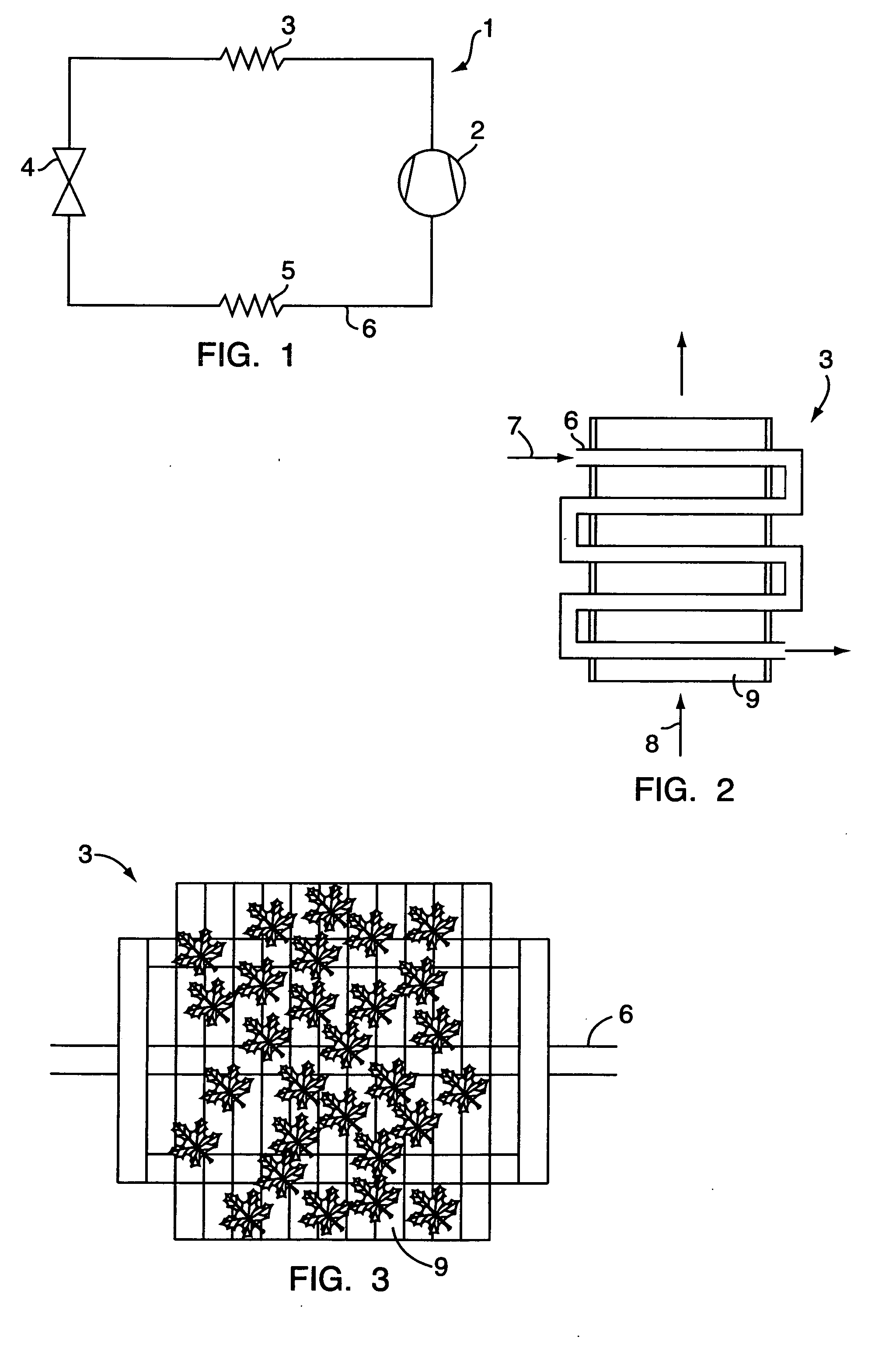
[0040] In FIG. 1 is shown a simple refrigeration system 1 comprising a compressor 2, a condenser 3, an expansion device 4 and an evaporator 5, which are connected by a conduit 6 in which a refrigerant is circulating. In vapour-compression refrigeration or heat pump systems the refrigerant circulates in the system and undergoes phase change and pressure change. In the system 1 a refrigerant gas is compressed in the compressor 2 to achieve a high pressure refrigerant gas, the refrigerant gas is fed to the condenser 3 (heat exchanger), where the refrigerant gas is cooled and condensates, so the refrigerant is in liquid state at the exit from the condenser 3, expanding the refrigerant i...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com