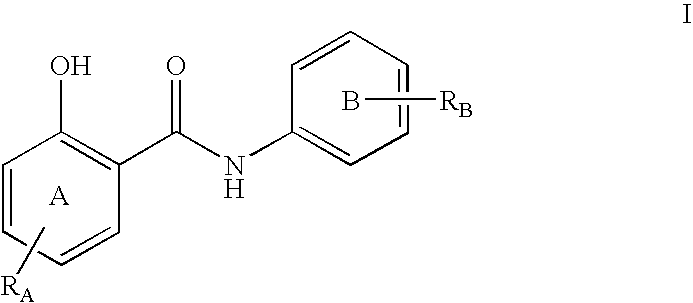
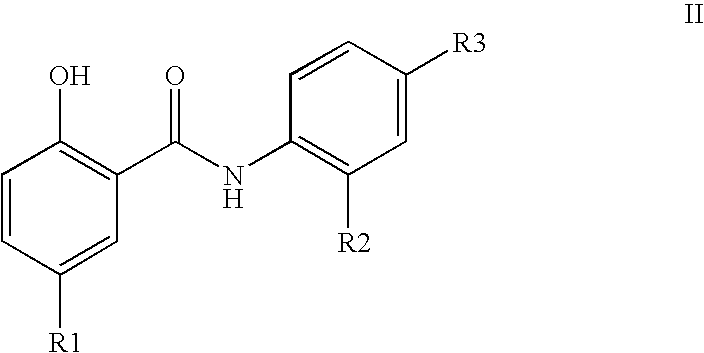
Inhibitors of transcription factor NF-kappaB
a transcription factor and inhibitor technology, applied in the field of salicylanilide inhibitors of transcription factor nfb, can solve problems such as organ destruction
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Preparation of N-(4-Acetylphenyl)-2-hydroxy-5-iodocarboxamide
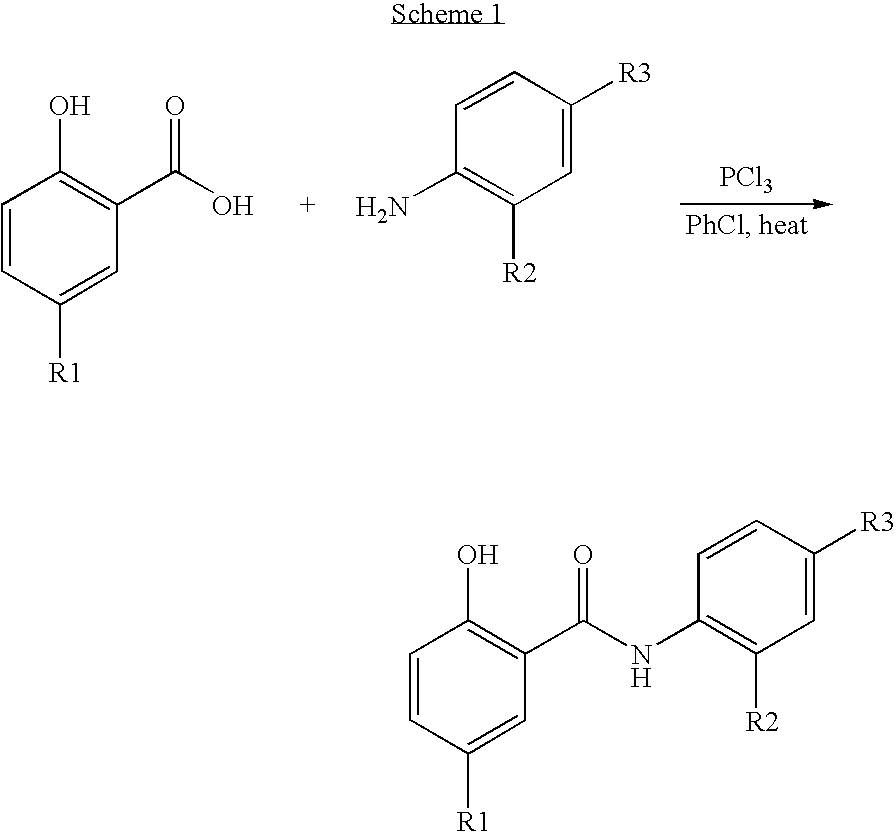
[0099] A solution of iodosalicylic acid (1.9 g, 7.4 mmol) and 4-aminoacetophenone (0.97 g, 7.4 mmol) in chlorobenzene (40 mL) was treated with PCl3 (0.323 mL, 3.7 mmol). The solution was heated at reflux under an argon atmosphere. After 2 h. the solution was filtered hot and the filtrate was left standing at RT. After 18 h solution was filtered and the solid was recrystallized from MeOH to give the title compound (0.095 g, 5% yield): 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 2.5-2.6 (s, 3H), 6.8-8.2 (m, 7H), 10.1-10.2 (s, 1H).
example 2
Preparation of N-(2,4-Difluorophenyl)-2-hydroxy-5-nitrophenylcarboxamide
[0100] A solution of 5-nitrosalicylic acid (1.4 g, 7.7 mmol) and 2,4difluoroaniline (0.8 mL, 7.7 mmol) in chlorobenzene (40 mL) was treated with PCl3 (0.338 mL, 3.8 mmol). The solution was heated at reflux under an argon atmosphere. After 2 h. the solution was filtered hot and the filtrate was left standing at RT. After 18 h the solution was filtered and the solid was recrystallized from MeOH to give the title compound (0.733 g, 35% yield): 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 2.5-2.6 (s, 3H), 7.1-8.9 (m, 6H), 10.6-10.7 (s, 1H)
example 3
Preparation of N-(2,4-Difluorophenyl)-2-hydroxy-5-iodophenylcarboxamide
a) 5-Iodosalicylic acidchloride
[0101] 5-Iodosalicylic acid (2.0 g, 7.58 mmol) in toluene was treated with SOCl2 (1.66 mL, 22.7 mmol) and catalytic DMF at reflux for 1 h. The reaction mixture was evaporated to dryness and the acid chloride used in the next step without purification.
b) 2,4-Difluorophenyl)-2-hydroxy-5-iodophenylcarboxamide
[0102] The compound of Example 3(a) (3.79 mmol) and 2,4-difluoroaniline (380 uL, 3.79 mmol) in toluene was heated at reflux for 24 h. The reaction mixture was evaporated, the residue washed with ether and the solid residue recrystallized from MeOH to give 159 mg of N-(2,4-difluorophenyl)-2-hydroxy-5-iodophenylcarboxamide. ES MS (M+H)− m / e 373.7.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Molar density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Molar density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Molar density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com