Method for, and a topology aware resource manager in an IP-telephony system
a resource manager and topology awareness technology, applied in the field of topology awareness resource manager in an iptelephony system, can solve the problems of low overall utilisation, low topology awareness, and denial of service to other users, and achieve the effects of flexible interaction, increased network utilisation, and increased bandwidth
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
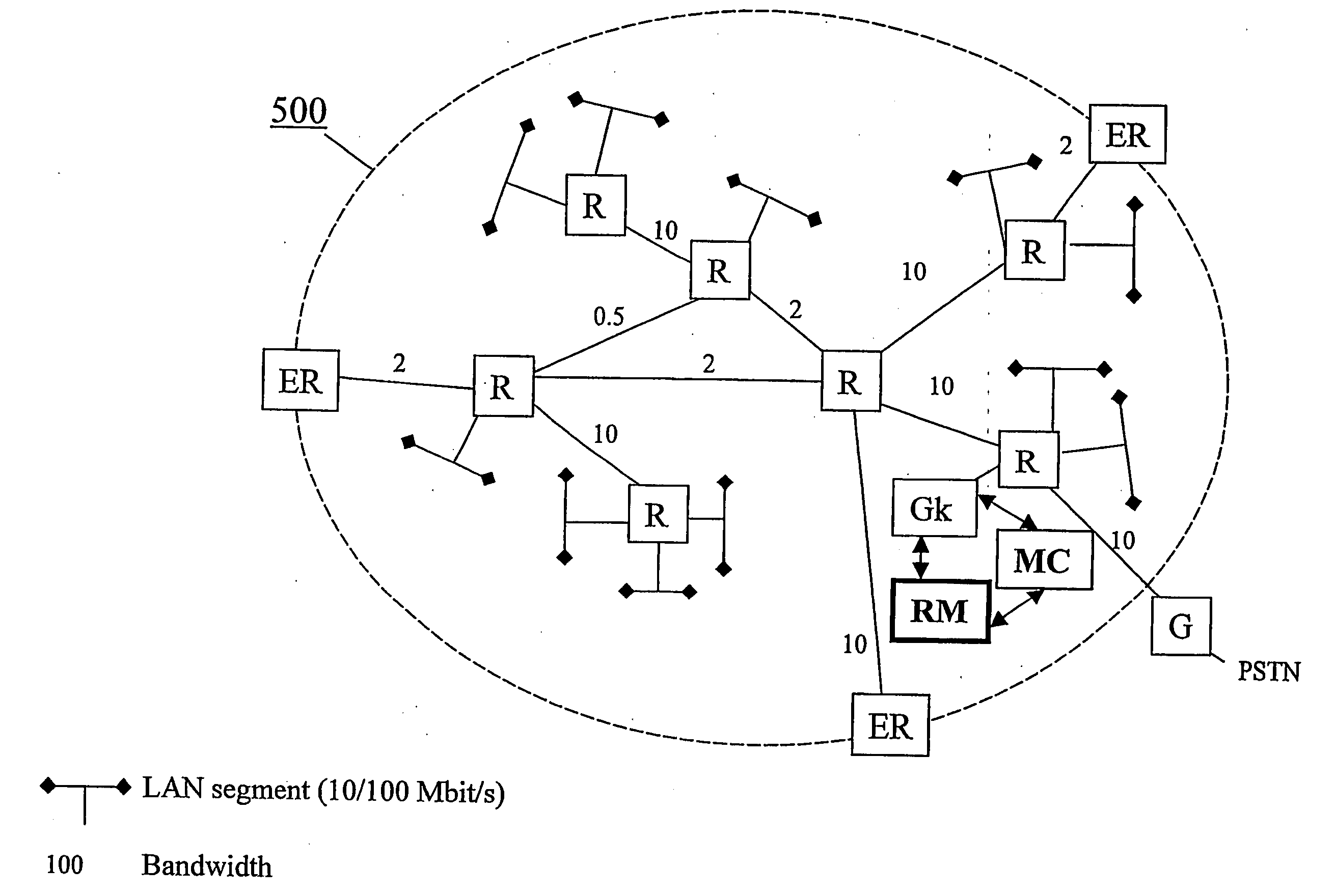
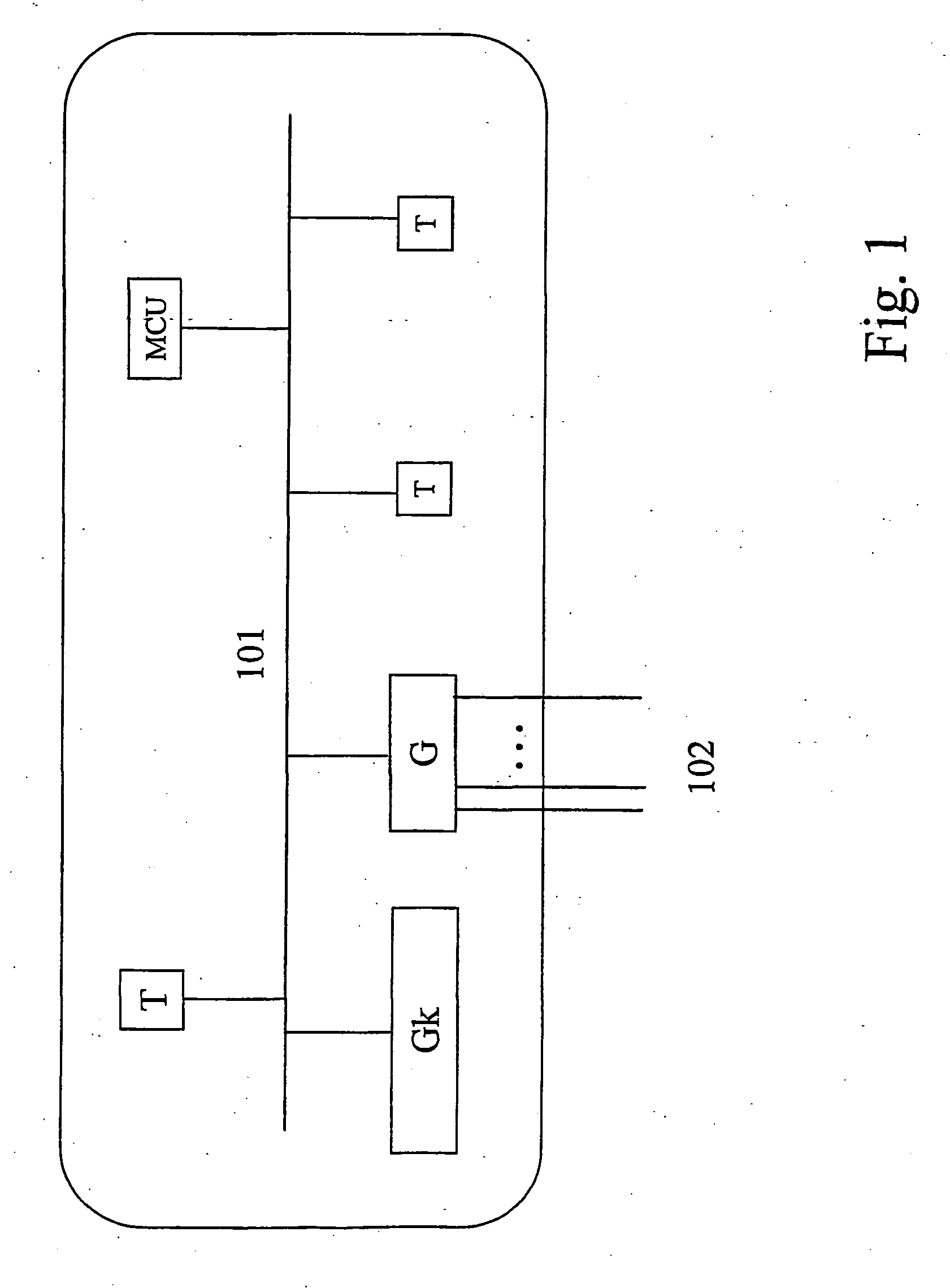
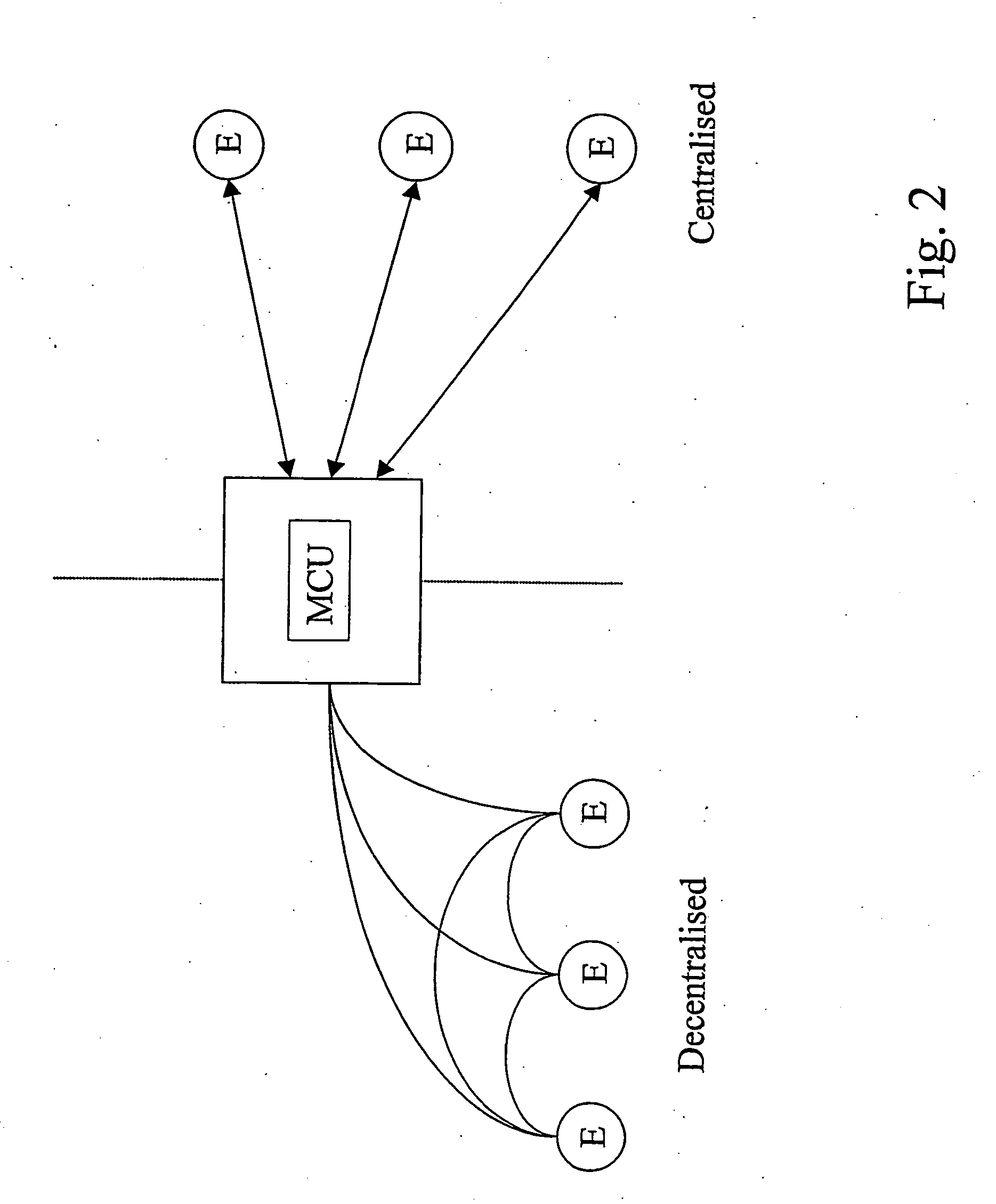
[0040]FIG. 4 is a block diagram illustrating an exemplary topology aware resource manager entity RM within an IP telephony system 400, according to a first embodiment of the present invention. The resource manager RM comprises topology aware resource manager functionality. It is comprised in an IP telephony system e.g. an H323 system. Such a system is described FIG. 1, above under “background of the invention”. Hence, in addition to the resource manager RM, the IP telephony system typically comprises IP telephony components such as one or many gatekeepers Gk, gateways G, and terminals, as well as IP network elements such as routers R, edge routers ER and Local Area Network (LAN) segments to which the terminals typically are connectable. The IP telephony system (400) is used to enables end-users to use an IP network as the transmission medium for multimedia.
[0041] The resource manager RM interacts with the gatekeeper Gk and handles all resource management issues for initiated and on...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com