Method for gene identification signature (GIS) analysis
a gene identification and signature technology, applied in the field of gene expression, can solve the problems of prohibitively expensive to tag every transcript in the transcriptome, inability to generate tags to improve specificity, and inability to complete sequencing analysis of all different transcriptomes, etc., to achieve easy recognition, increase the specificity of tags, and enhance sequencing efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
The Method
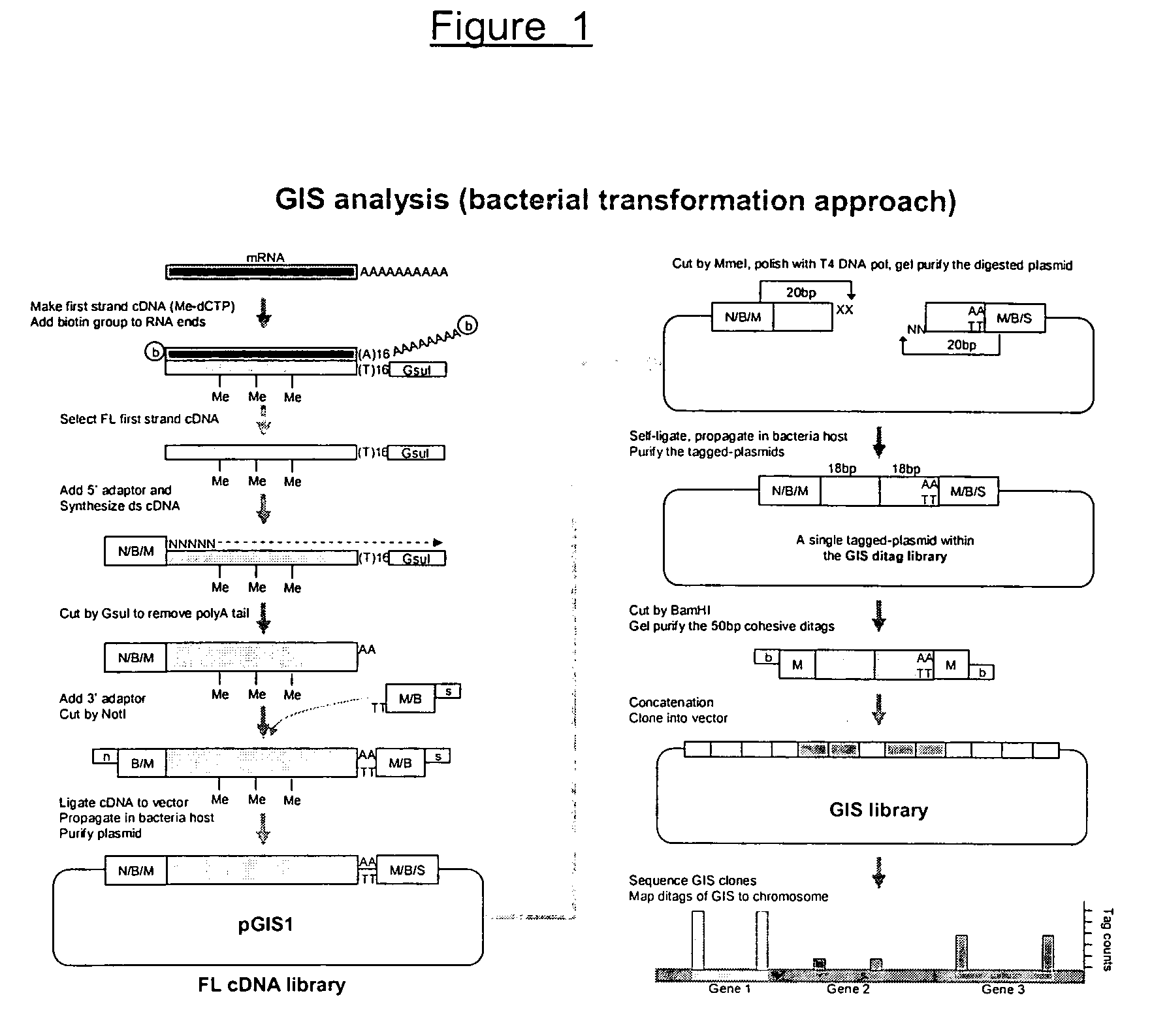
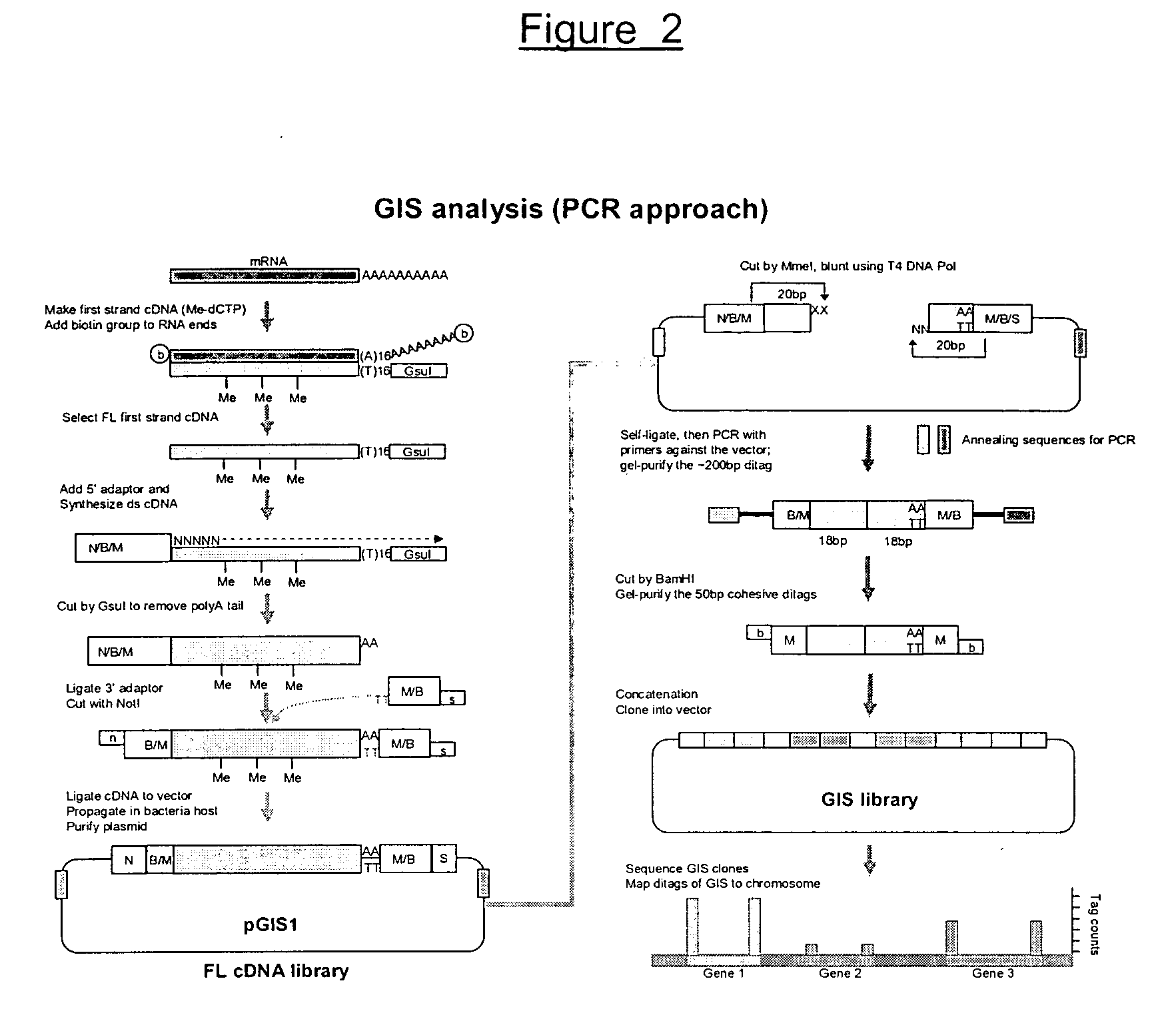
[0170] The experimental procedure of GIS ditag analysis has been carried out according to the following modules of cDNA library construction and analysis: [0171] (1) The full-length cDNA library which introduces the MmeI sites flanking both ends of each cDNA insert; [0172] (2) The GIS ditag library in which each clone contains a 5′ 18 bp signature and a 3′ 18 bp signature of a transcriptional unit; [0173] (3) The GIS library for clones of concatenated GIS ditags; [0174] (4) GIS sequencing analysis.
1. GIS Full-Length cDNA Library with Addition of MmeI sites for Each cDNA Inserts
[0175] The outline of procedure of this section was as follows: starting from high quality mRNA, the first cDNA was synthesized with a GsuI-oligo dT primer (SEQ ID NO:1).
[0176] The first strand cDNA / RNA hybrids was subjected to a full-length enrichment procedure by the biotinylation-based cap-trapper approach. Any cap-trapper approach known in the art can be used, for example Carninci et al., 1...
example 2
2. GIS Ditag Library
[0224] The cDNA clones made from steps 1-1 to 1-8 contained a MmeI site (TCCGAC) at the 5 side and another MmeI site (TCCAAC) in reverse orientation at the 3 end. Note that these two Mmel recognition sites are two isoforms that can be recognized by MmeI (TCCRAC 20 / 18, where R=(A / G)). The sequence difference here will be useful later for directional indication. Mmel restriction enzyme will cleave these clones 20 bp into the cDNA fragments from their 5 and 3 ends. Consequently, despite the variable sizes of the digested cDNA, the vector plus the 20 bp cDNA signature tags on each end of all clones will be of a constant size that can be easily recognized upon agarose gel electrophoresis, and can be easily purified from the unwanted cDNA fragments.
[0225] The gel-purified vector plus tags can then be self-ligated to give a agged plasmid containing the 5 and 3 GIS signature tags.
2-1. Plasmid Preparation
[0226] The GIS full-length cDNA library was amplified once by ...
example 3
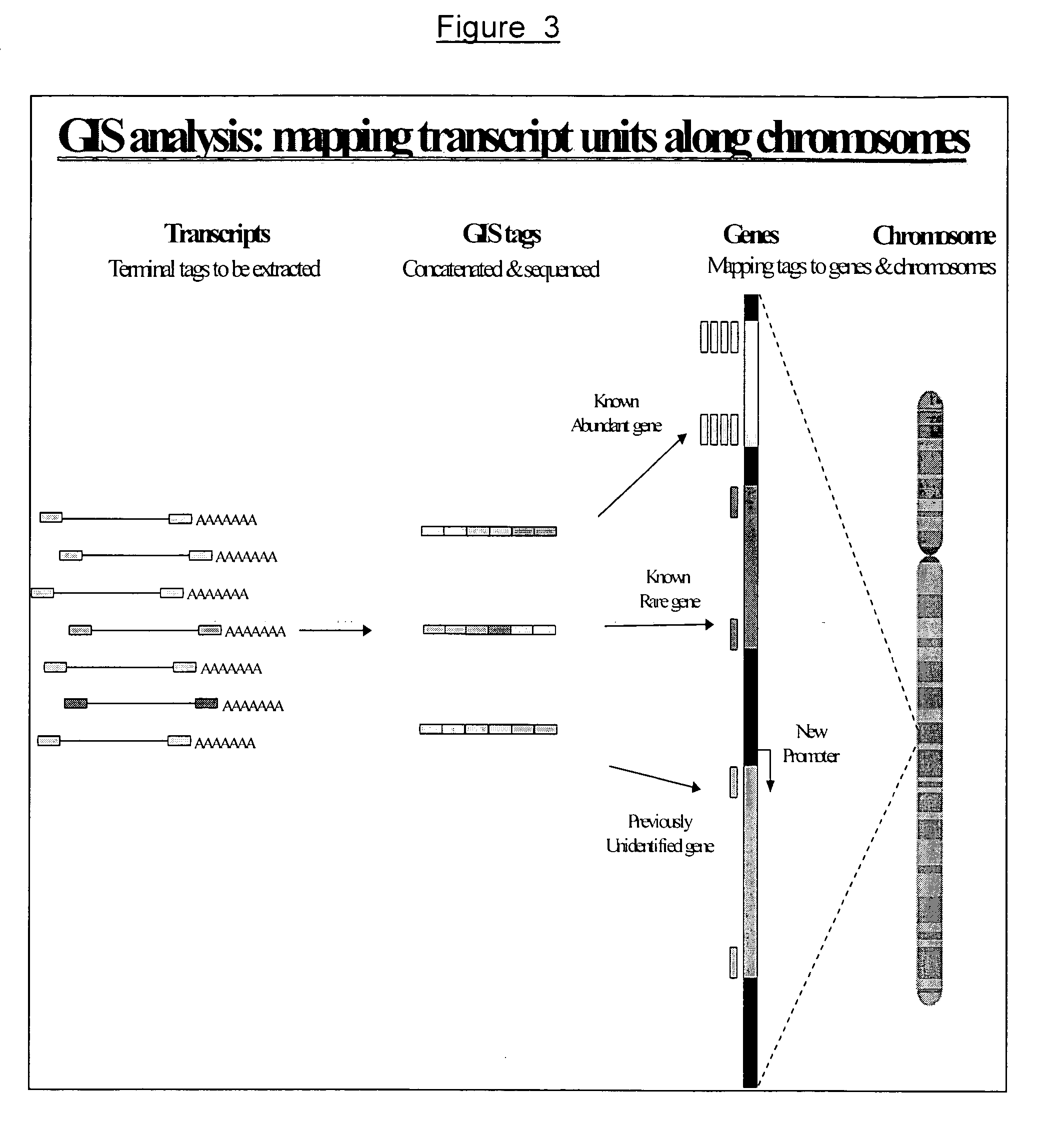
[0294] The GIS analysis method according to any embodiment of the invention is a complete gene discovery platform. It combines full-length cDNA library construction, cDNA tag sequencing, genome mapping and annotation into one operation from the same starting materials. For example, to study the genes expressed in human stem cells, we start with the stem cell mRNA, construct a stem cell GIS full-length cDNA library, and then the GIS library. We will only need to sequence 50,000 clones of the GIS library to reveal over a million transcripts. Such deep sampling will allow us to capture nearly all unique transcripts expressed in the human stem cell transcriptome. Each of the GIS ditags can be specifically mapped to the genome and therefore define the structural regions of the corresponding genes on the chromosomes. Most of the GIS ditags map to known genes on chromosomes and the counts of the GIS ditags provide the measurement of expression activity. Some of the GIS ditags may map to de...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pH | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pH | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pH | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com