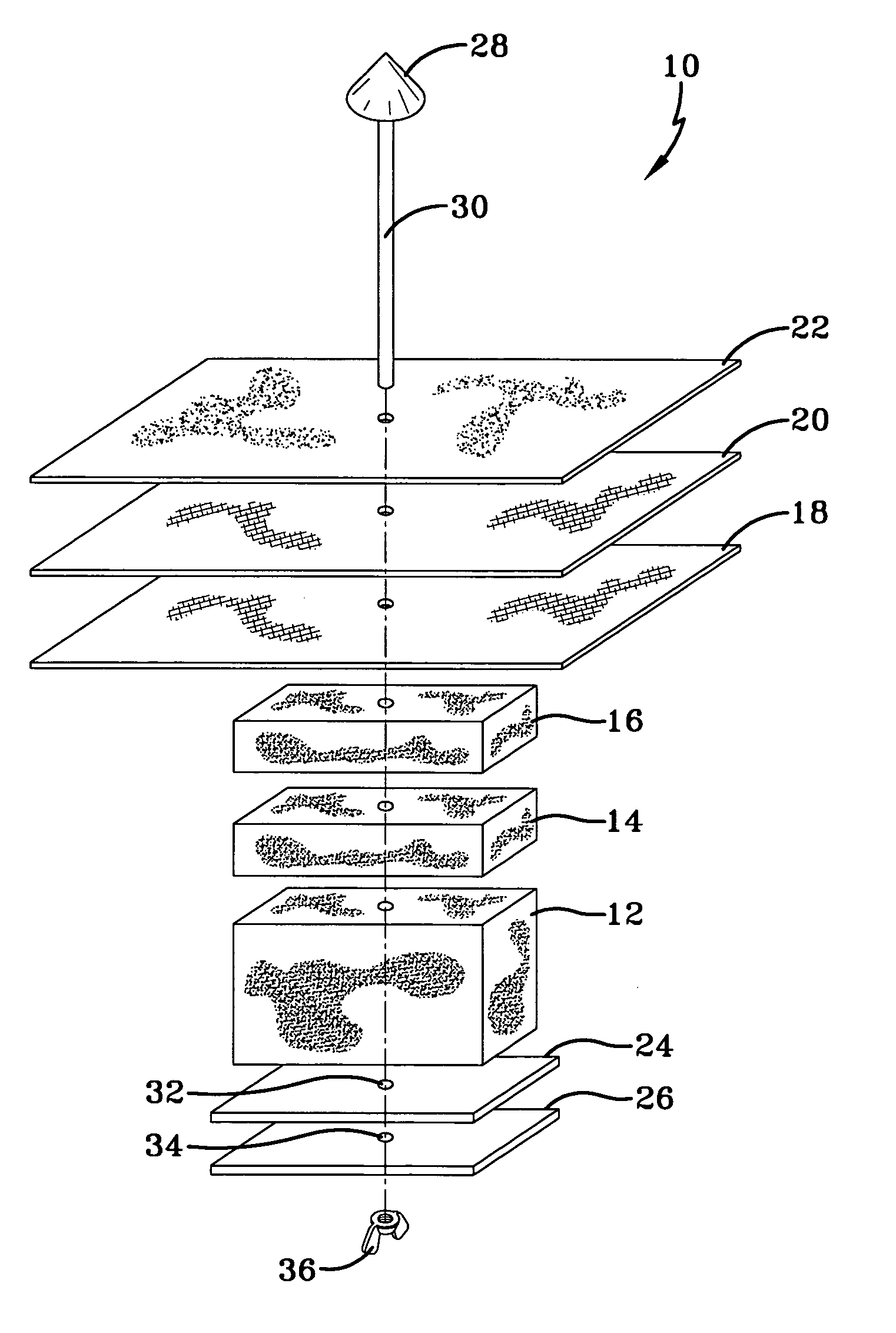
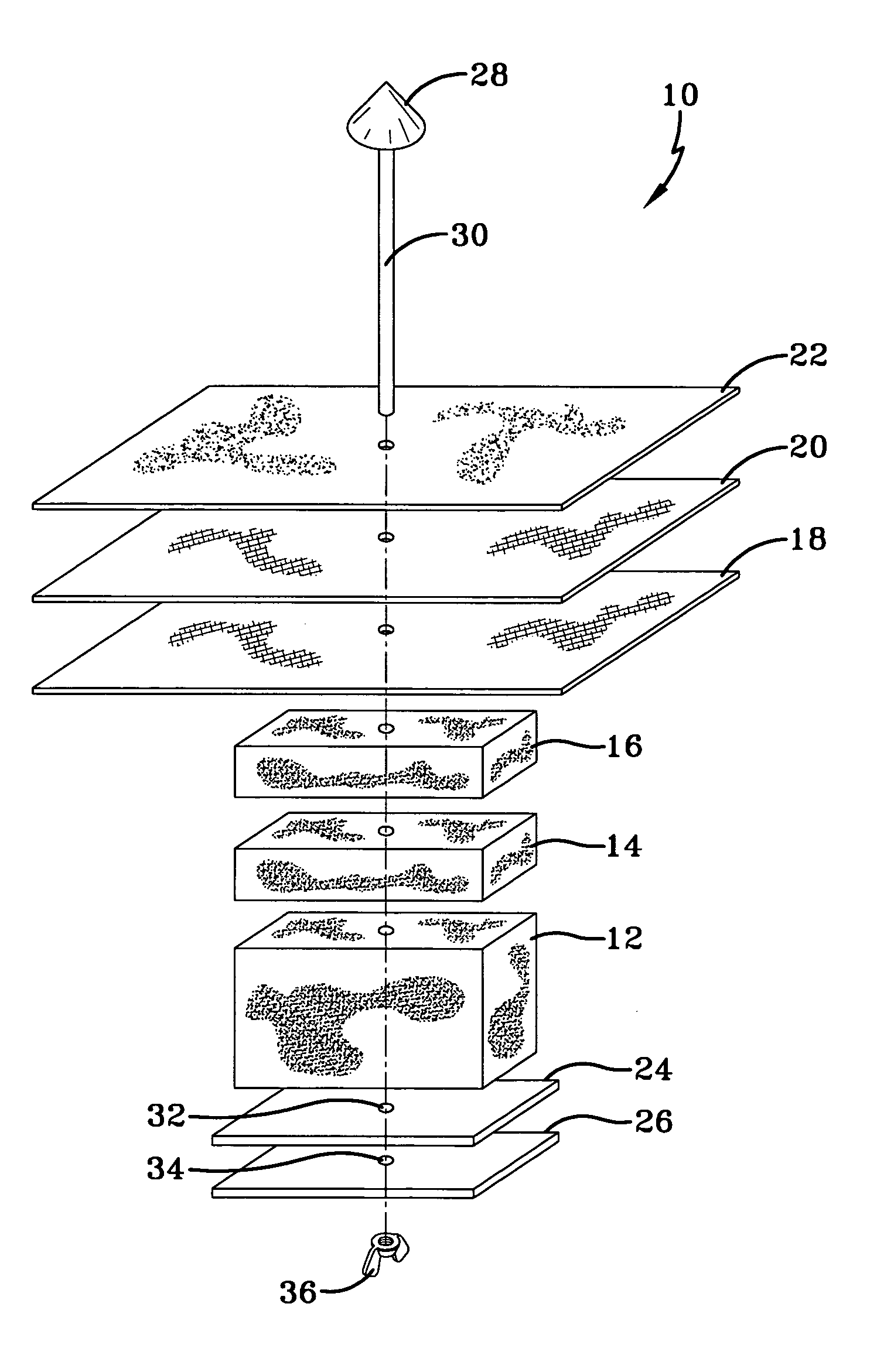
Flame resistant fiber blend and fabrics made therefrom
a technology of flame-resistant fibers and blends, which is applied in the field of flame-resistant fiber blends, can solve the problems of reduced wear life and poor durability of fiberglass flame barriers, and achieve the effects of improving the strength to weight ratio of non-woven fabrics containing amorphous silica, improving char strength, and improving char strength
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
examples
Example Nos. 1-12
[0047] The samples were prepared on a miniature card and needleloom. The fiber was first hand-opened and layered on the card feed apron. The carded sample was run back through the card a second time to assure intimate blending of fibers. The carded web, layered around the wind-up roll, was cut transversely and removed from the card. Then it was fed into the needlepunch line for needling. A second pass was performed to accomplish needling from the opposite side.
[0048] Standard tensile strength testers were modified to measure the char strength of the barrier fabric of the present invention. More specifically, the fabric stiffness test typically used with pocket coil material was modified to measure the amount of force, measured and reported in pounds, required to push a fabric sample through a hole with a plunger. To force the material to break, a template was fabricated so that the fabric could be sandwiched between the template and the existing test plate.
[0049]...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Percent by mass | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Percent by mass | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Percent by mass | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com