Devices, systems and method for calibration of systems
a technology of system calibration and calibration method, applied in the direction of liquid/fluent solid measurement, testing/calibration for volume flow, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of equipment failure, fluid path element failure, and difficulty in direct measurement of fluid pressure in a syringe, so as to reduce the downtime of injection equipment and medical staff, the time to conduct pressure calibration can be reduced, and the effect of stable and repeatable calibration
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
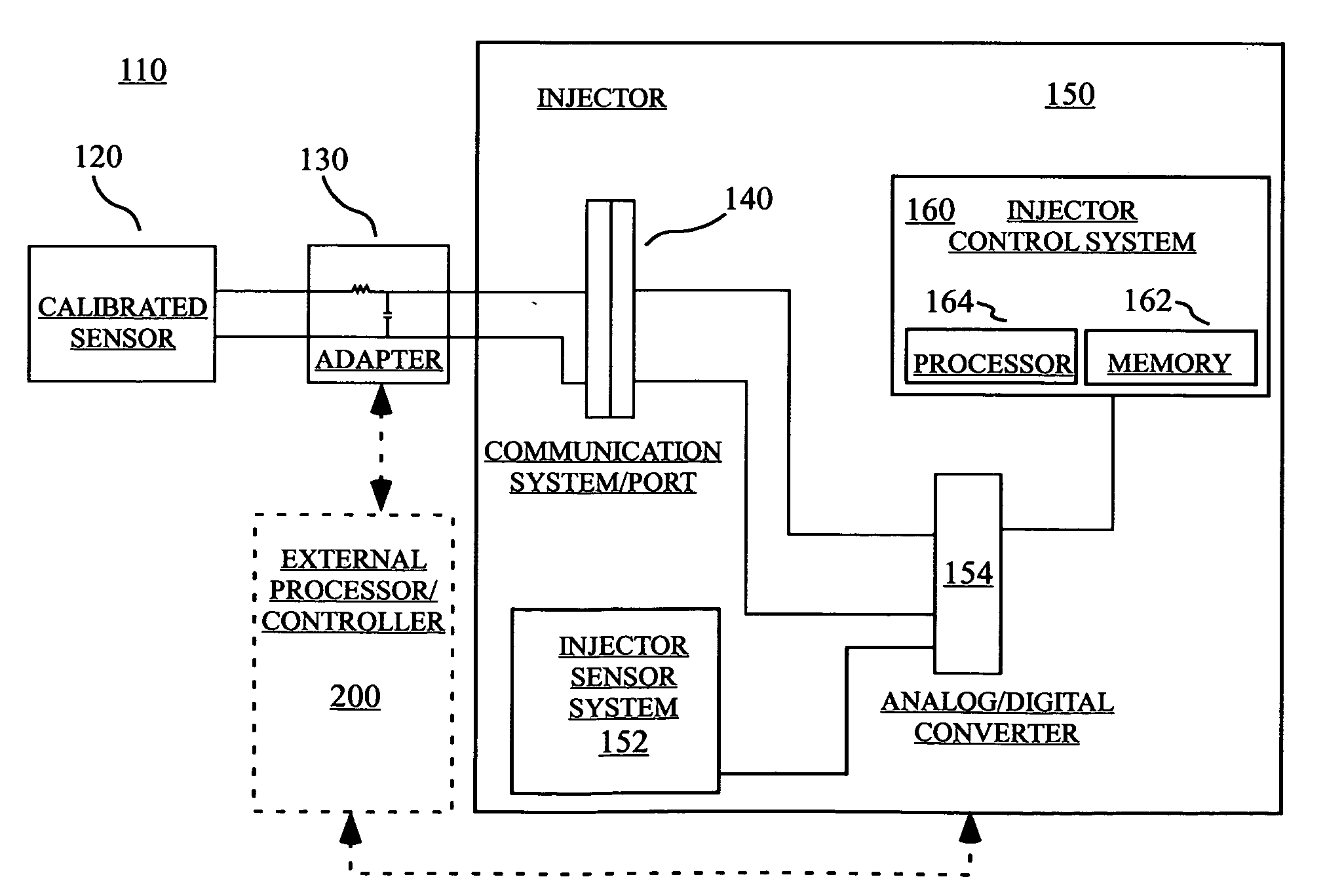
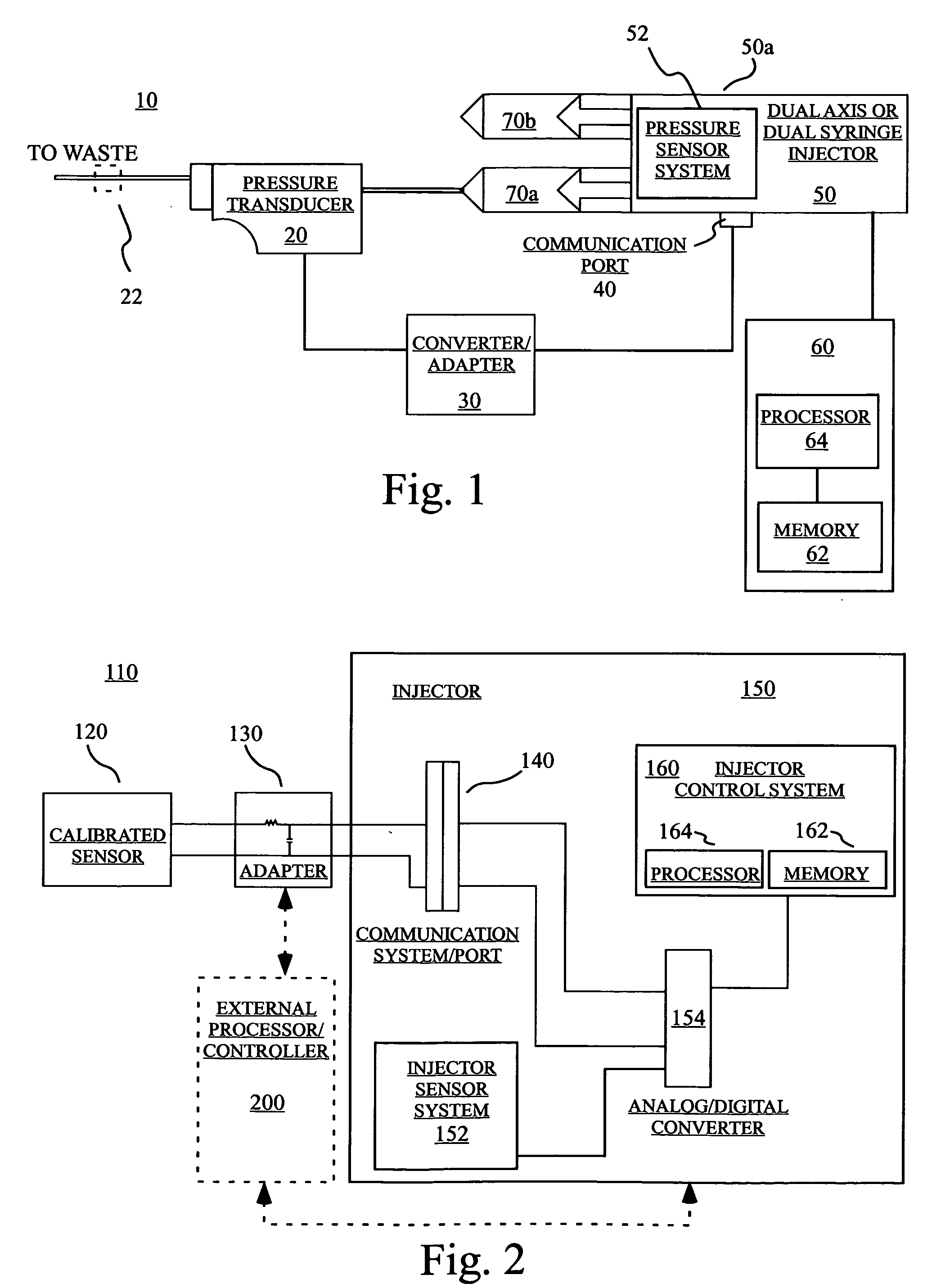
[0022] Several representative embodiments of the present invention are discussed in connection with the retrofitting of a STELLANT® Injector available from Medrad, Inc. of Indianola, Pa. for use with the calibration devices, systems and method of the present invention to calibrate one or more pressure measuring systems of the injector. However, one skilled in the art appreciates that the calibration devices, systems and methods are suitable for use in generally any injector system or in any other system to calibrate generally any measured variable.
[0023] In general, the pressure calibration devices, systems and methods of the present invention enable pressure calibration of an injector to be automatically performed by the injector with no (or minimal) user / manual interaction. In several embodiments of pressure calibration, this result is accomplished by communicating to the injector the output of a pressure transducer mounted on or placed in fluid connection with the tip of a syrin...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com