Light-guided transluminal catheter
a transluminal catheter and light-guided technology, applied in the field of medical devices, can solve the problem of only being able to achieve the technique, and achieve the effect of easy detection
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
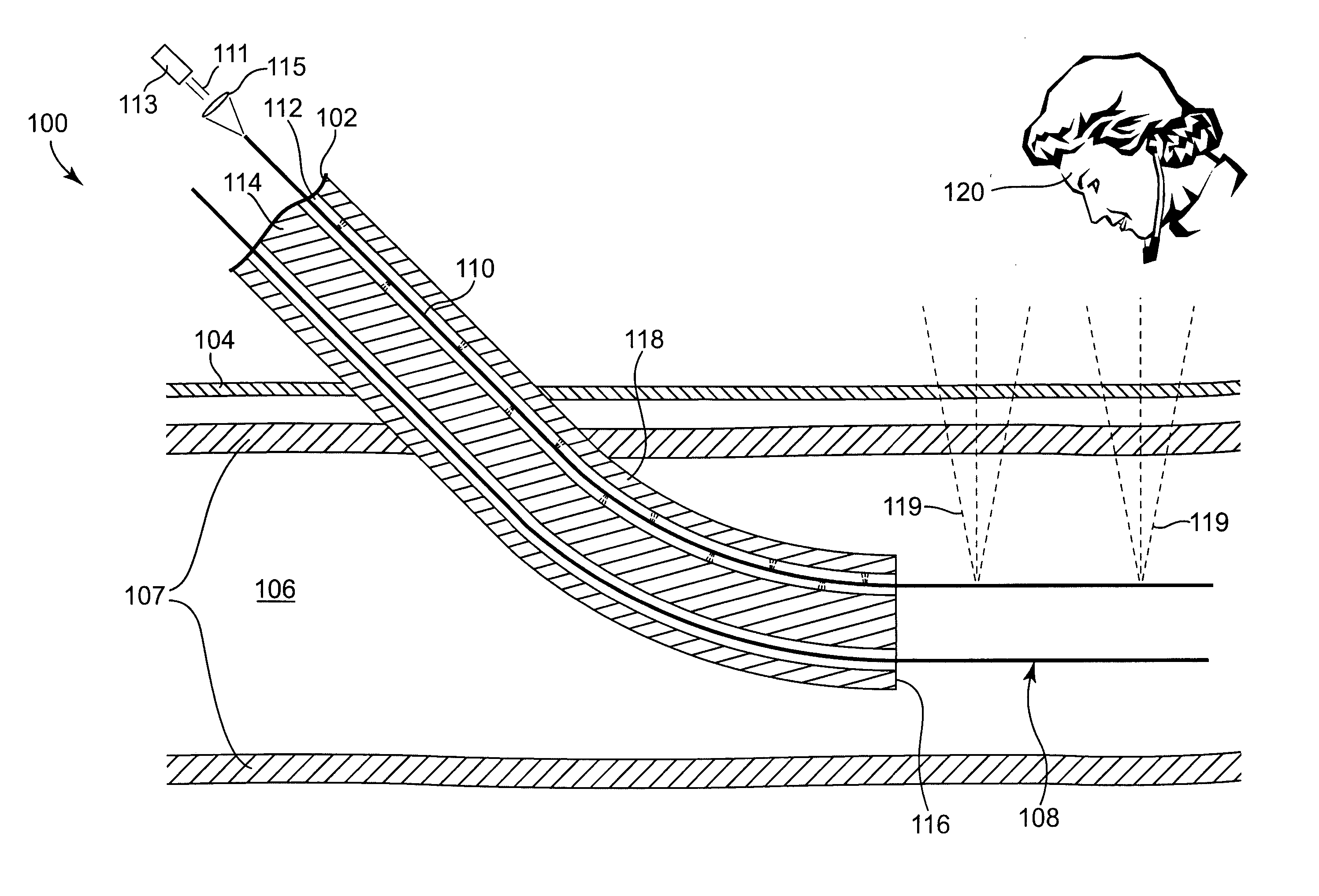
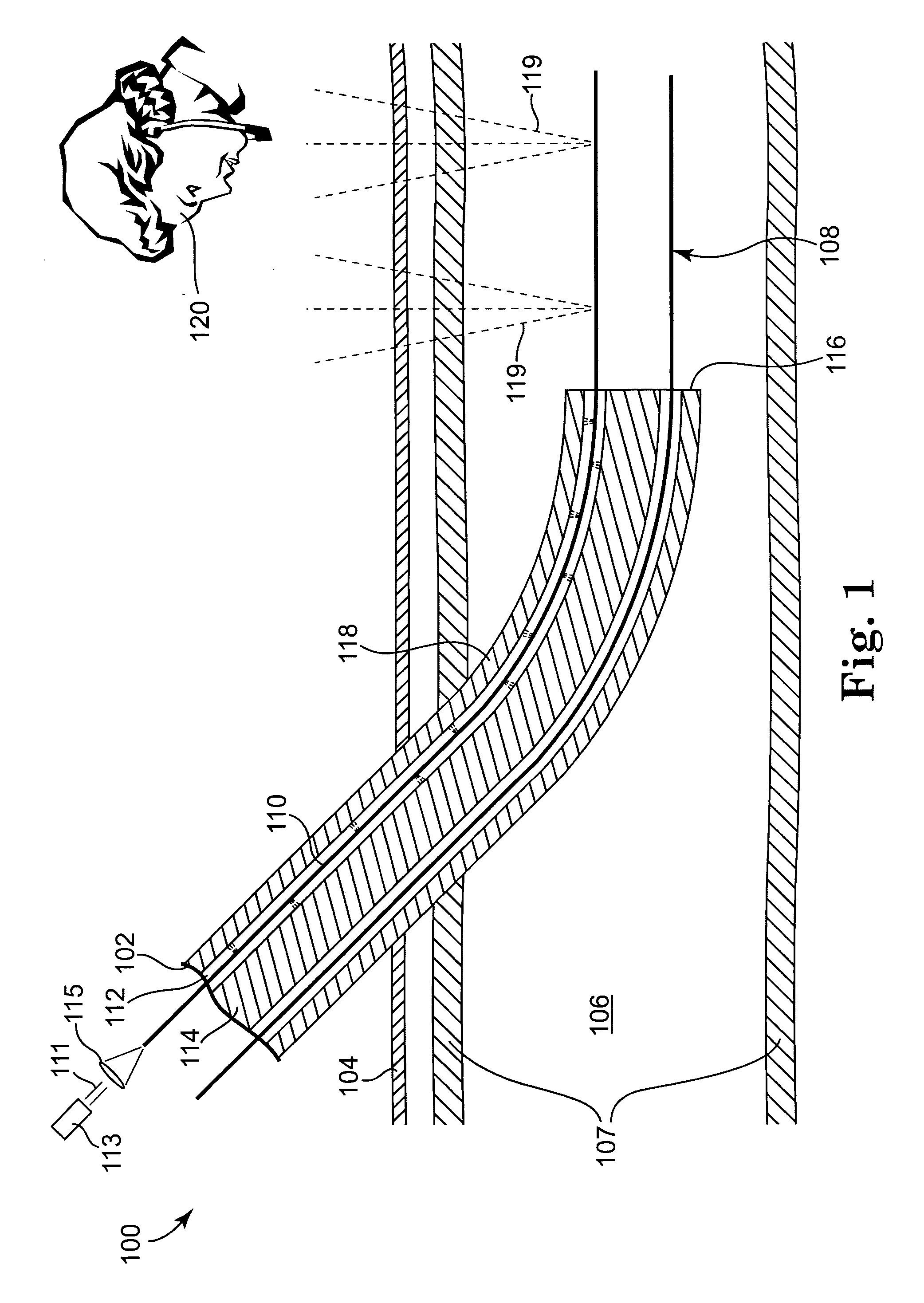
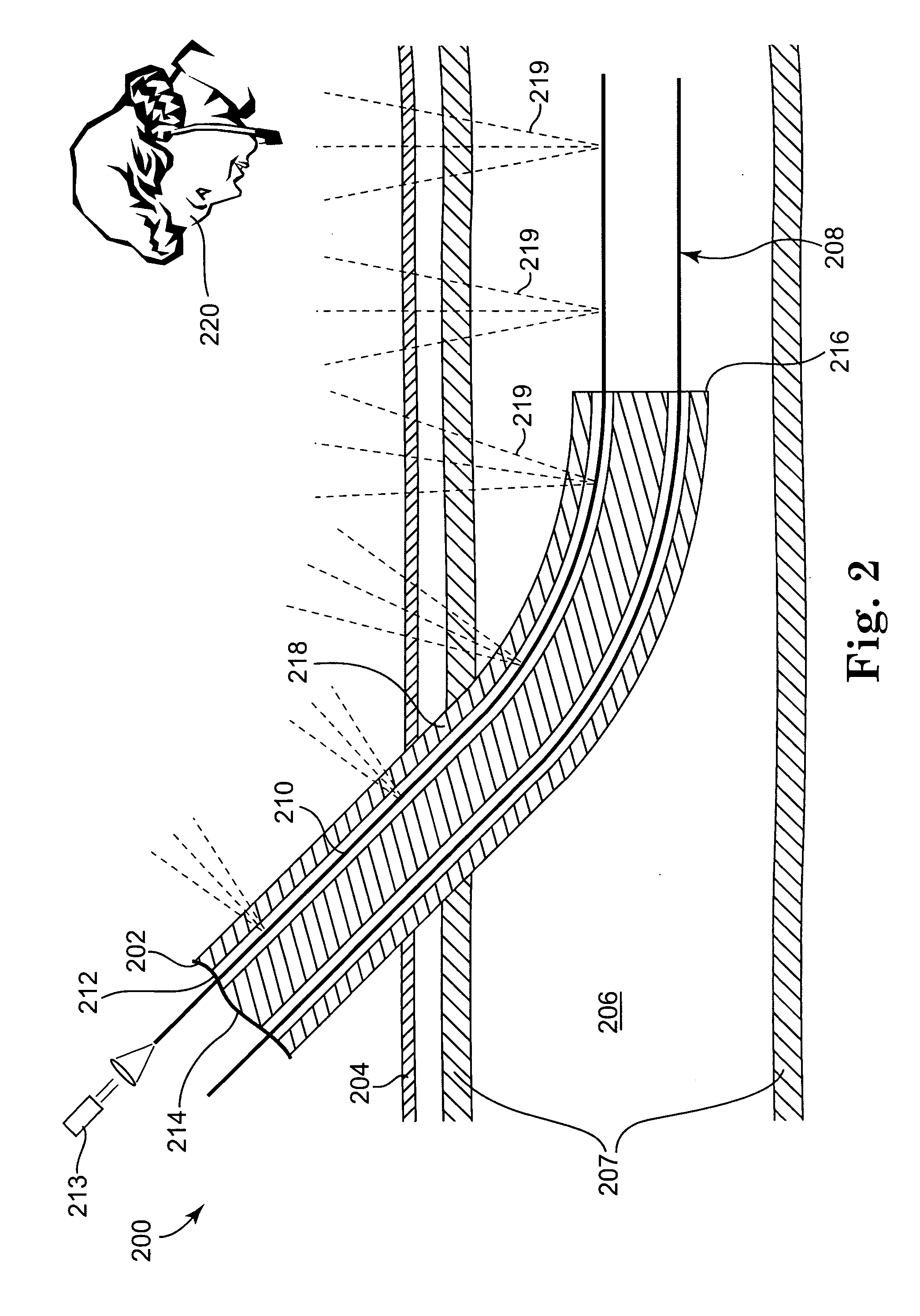
[0036] In general, the present invention is directed to medical devices and more particularly to a light-guided catheter for direct visualization of placement through the skin. The catheter may be placed intracorporeal (inside the body) by any of the catheterization techniques known to those skilled in the art, and the invention includes, but is not limited to intravenous, intraarterial, or intraluminal placement of the catheter.
[0037] One embodiment of a light-guided transluminal catheter device 100 is depicted schematically in FIG. 1. A multi-lumen catheter 102 is shown having been inserted through the patient's skin 104 and into the blood vessel lumen 106 over the guidewire 108 via the usual insertion techniques (e.g., the Seldinger technique mentioned earlier). A similar catheter without initial guidewire may also be inserted directly through the lumen of the puncturing needle. This is commonly done in the case of peripherally-inserted central catheters (PICC) inserted in an ex...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com