Fiber-to-the-seat in-flight entertainment system
a technology of entertainment system and fiber-to-seat seat, which is applied in the direction of selective content distribution, sport apparatus, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of significant price drop of terrestrial vod system, heavy system cost, and difficult realization of legacy ife system costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
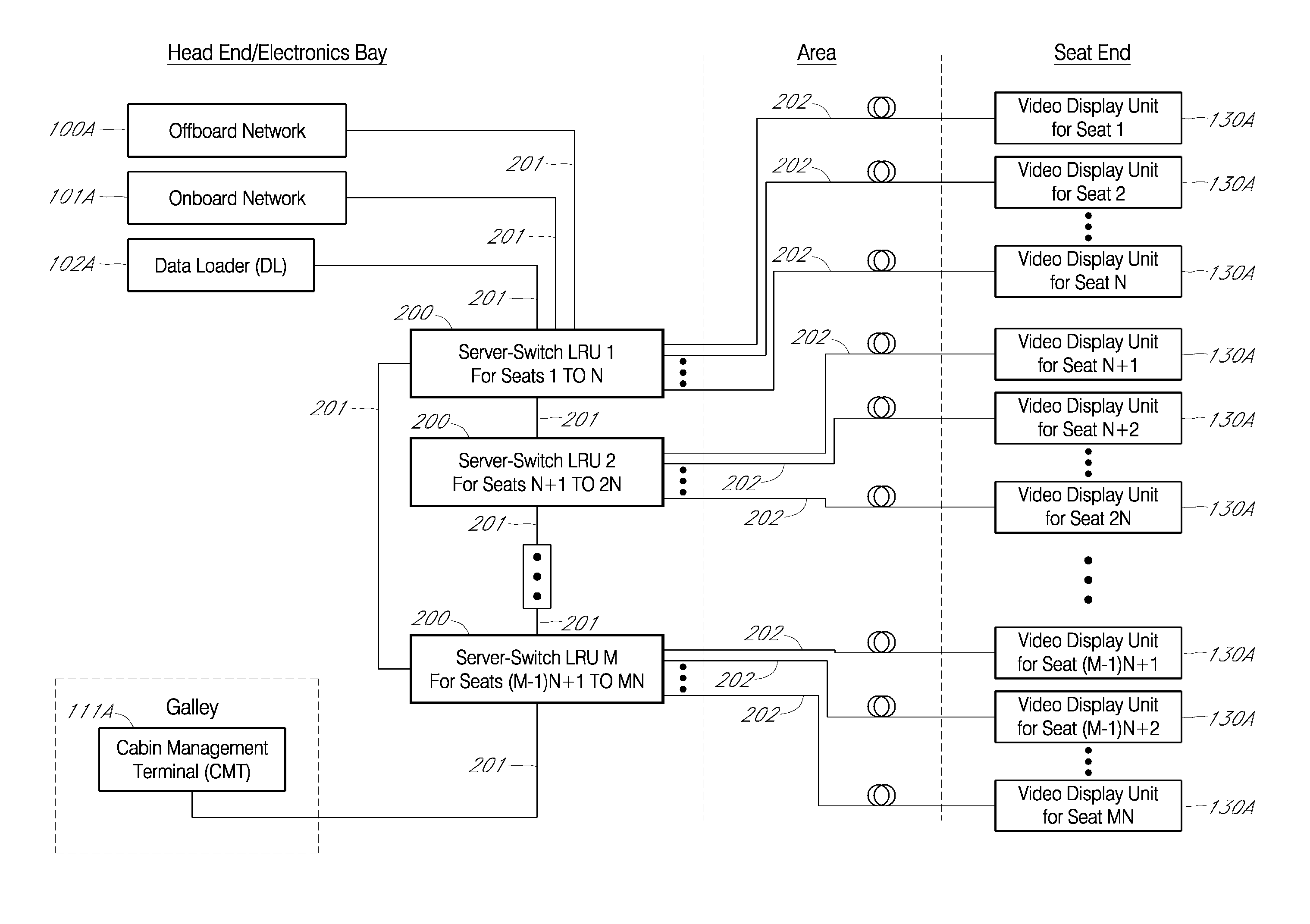
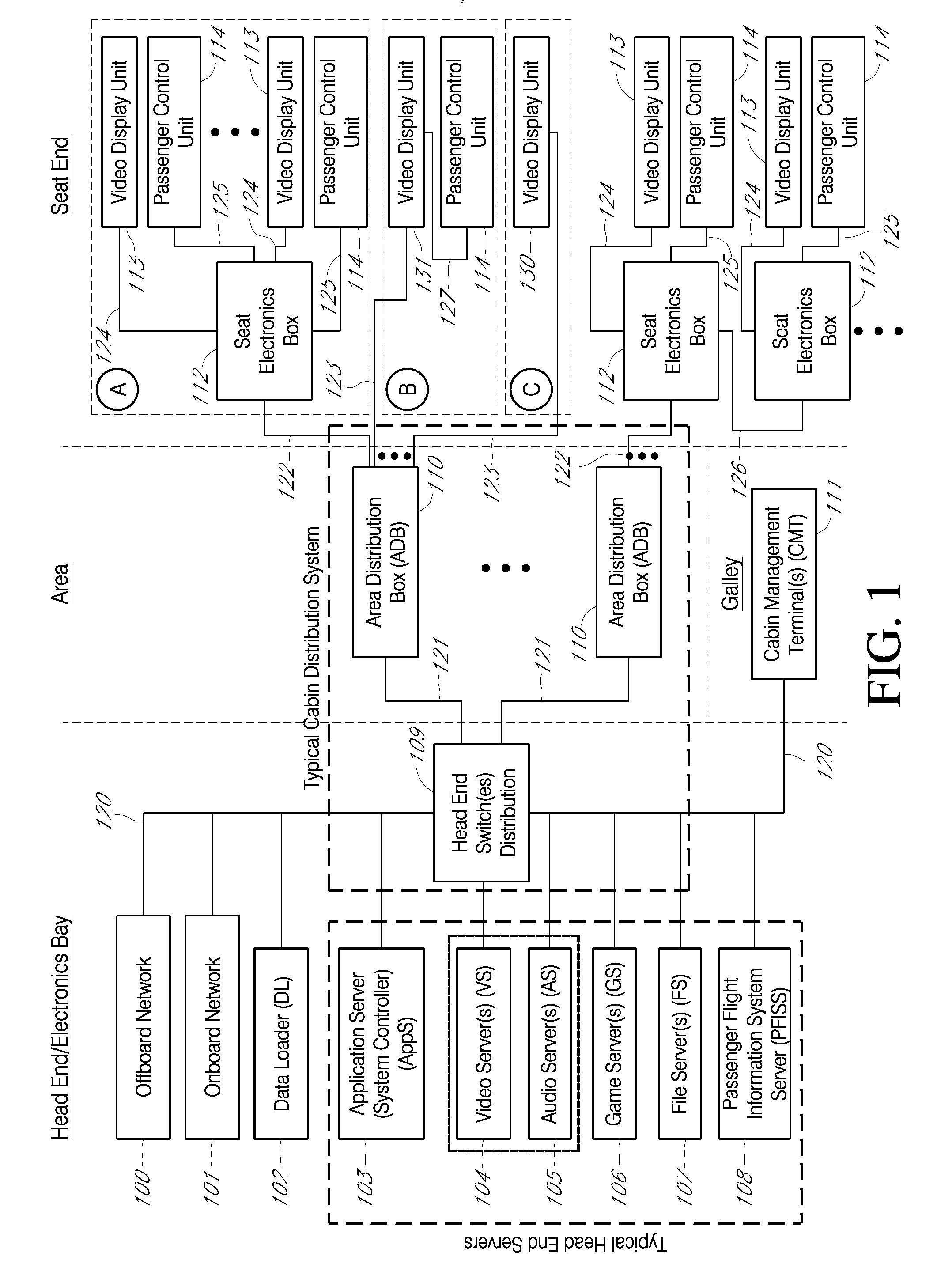
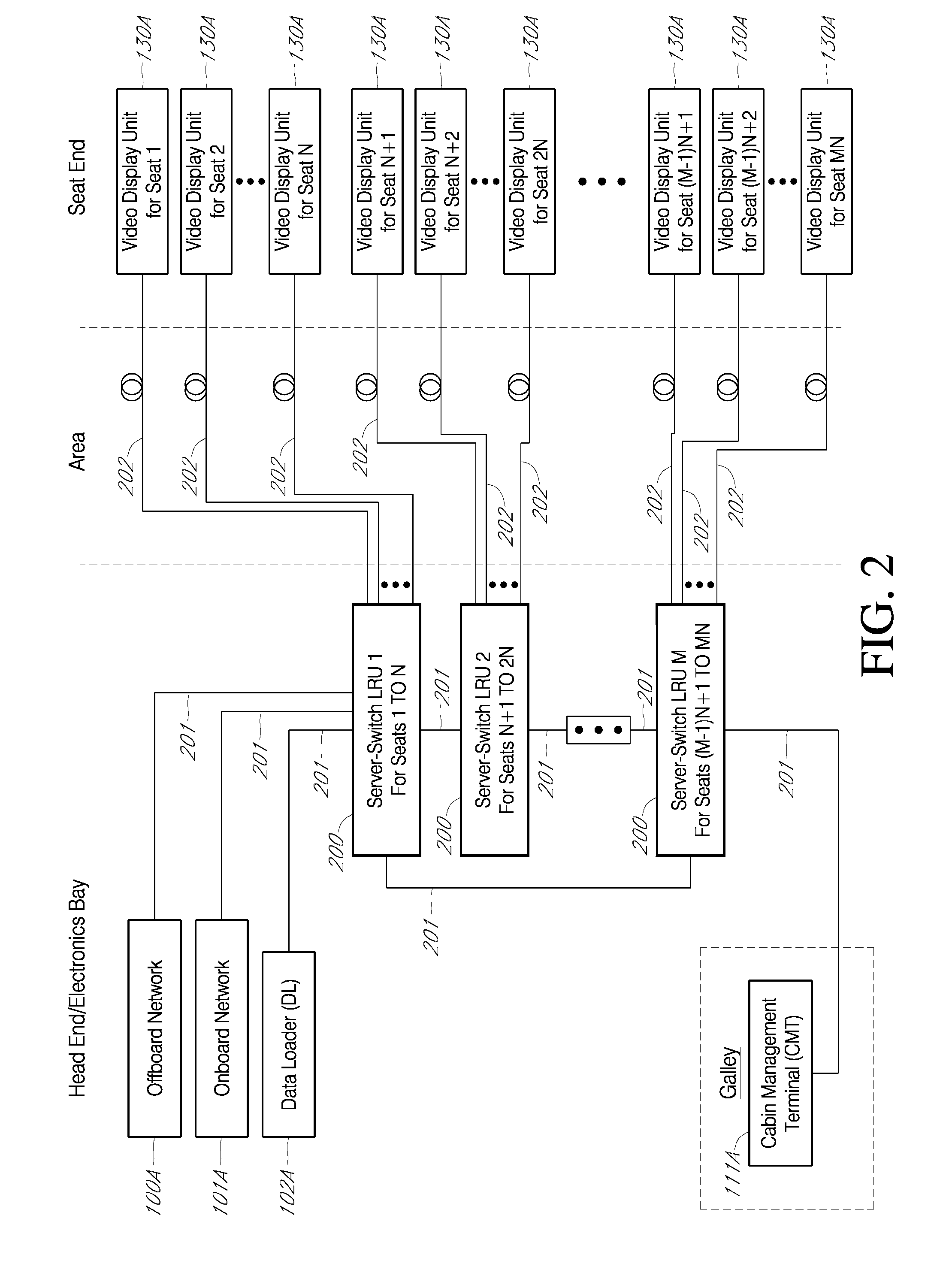
[0044]FIG. 1 shows an example of a traditional IFE system architecture that includes an offboard network 100, an onboard network 101, an onboard network 101, a data loader 102, a cabin management system 111, and one or more head-end servers provided to a head-end switch 109. The head-end servers shown in FIG. 1 include a application server(s) 103, video server(s) 104, audio server(s) 105, game server(s) 106, file server(s) 107, and a passenger flight information server 108. The head-end switch 109 is provided to a plurality of area distribution boxes 110. The area distribution boxes 110 are provided to a plurality of video display units 113 and passenger control units 114 directly or through seat electronic boxes 112.
[0045] The offboard network 100 communicates with terrestrial networks typically through satellite-based or ground-based radio frequency (RF) networks. Offboard network 100 is typically connected to an IFE head-end switch 109 through one of head-end network cables 120....
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com