High power, end pumped laser with off-peak pumping
a laser system and laser pump technology, applied in laser details, laser optical devices, semiconductor lasers, etc., can solve the problems of system generating output power levels in excess of several hundred watts that are difficult to meet the requirements of laser operation, system generating such high-powers only at the expense of beam quality, etc., and achieves easy production of over 100 watts output power. , the effect of high quality
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0025] A detailed description of embodiments of the present invention is provided with reference to the FIGS. 1-6.
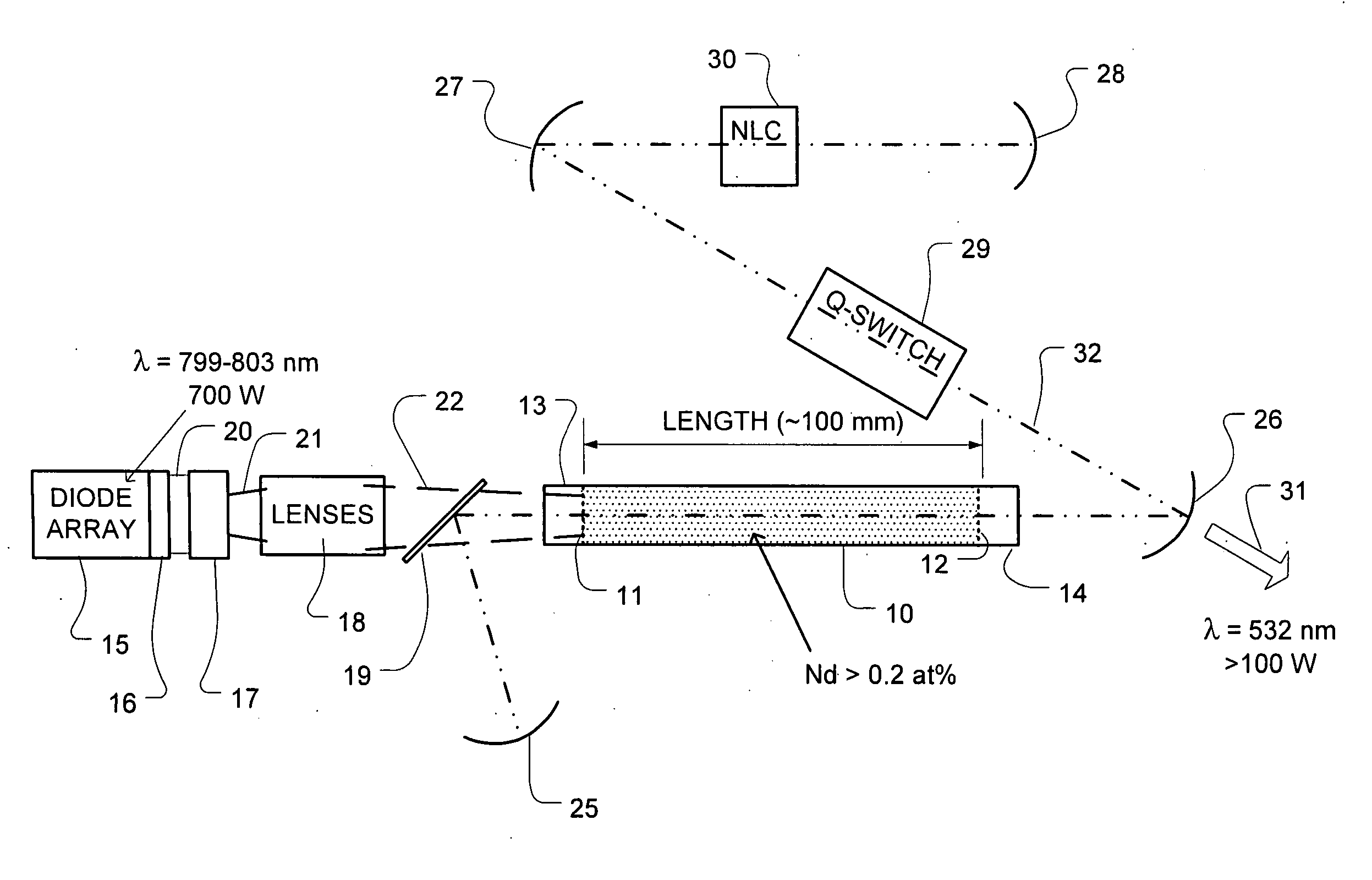
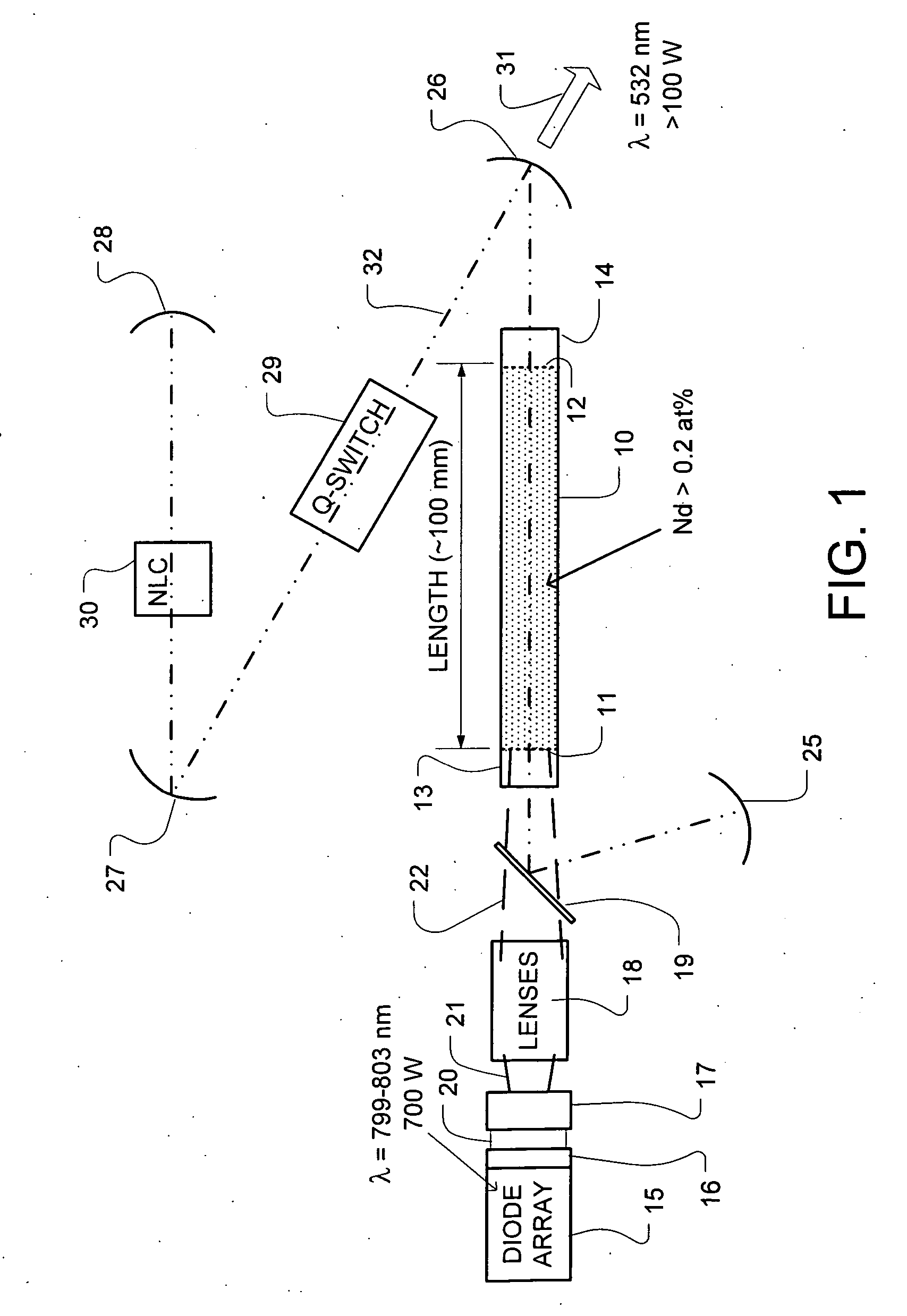
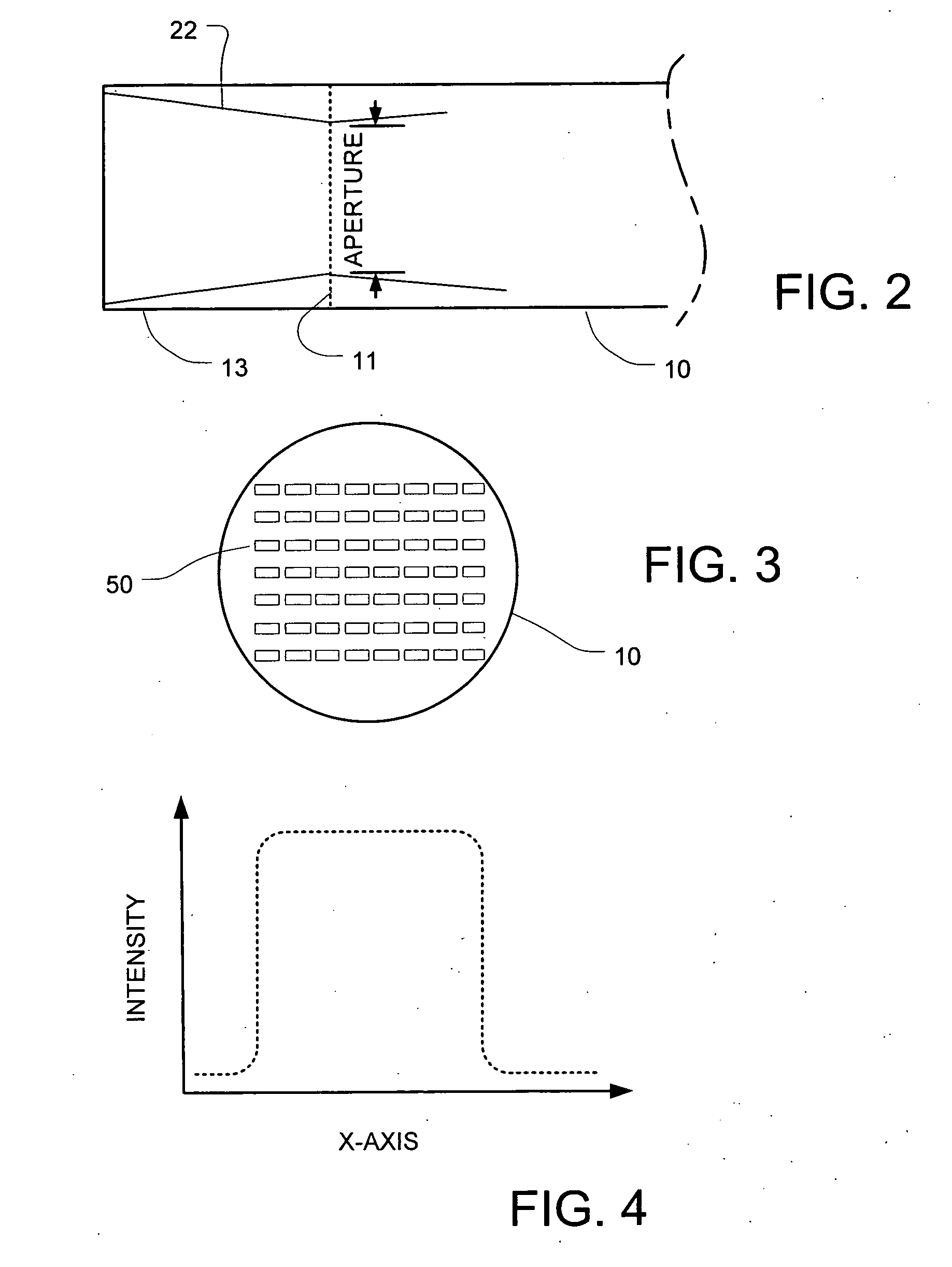
[0026]FIG. 1 illustrates a high-power laser system comprising a gain medium 10 that includes a doped crystalline host, having a first end 11 and a second end 12. The gain medium 10 in a representative embodiment comprises Nd:YAG having a length of about 100 millimeters and a diameter of about 4.5 millimeters. The gain medium 10 is water cooled in exemplary embodiments, along the sides of the host. Undoped endcap 13 about 10 millimeters long in this example, is bonded on the first end 11 of the gain medium 10, and undoped endcap 14 also about 10 millimeters long in this example, is bonded on the second end 12 of the gain medium 10.
[0027] In the high-power end-pumped configuration shown, the undoped endcap 13 can be diffusion bonded but preferably grown on at least the first end 11. In embodiments where significant pump energy reaches the second end of the host 10, anoth...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com