Modulation of synaptic maintenance
a technology of synaptic maintenance and maintenance, applied in the field of synaptic maintenance modulation, can solve the problems of post-synaptic receptor disassembly and withdrawal of axons, further complicated interpretation of these findings about synaptic density counts, and impairment of that system's functioning, so as to prevent the elimination of synapses from neurons
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
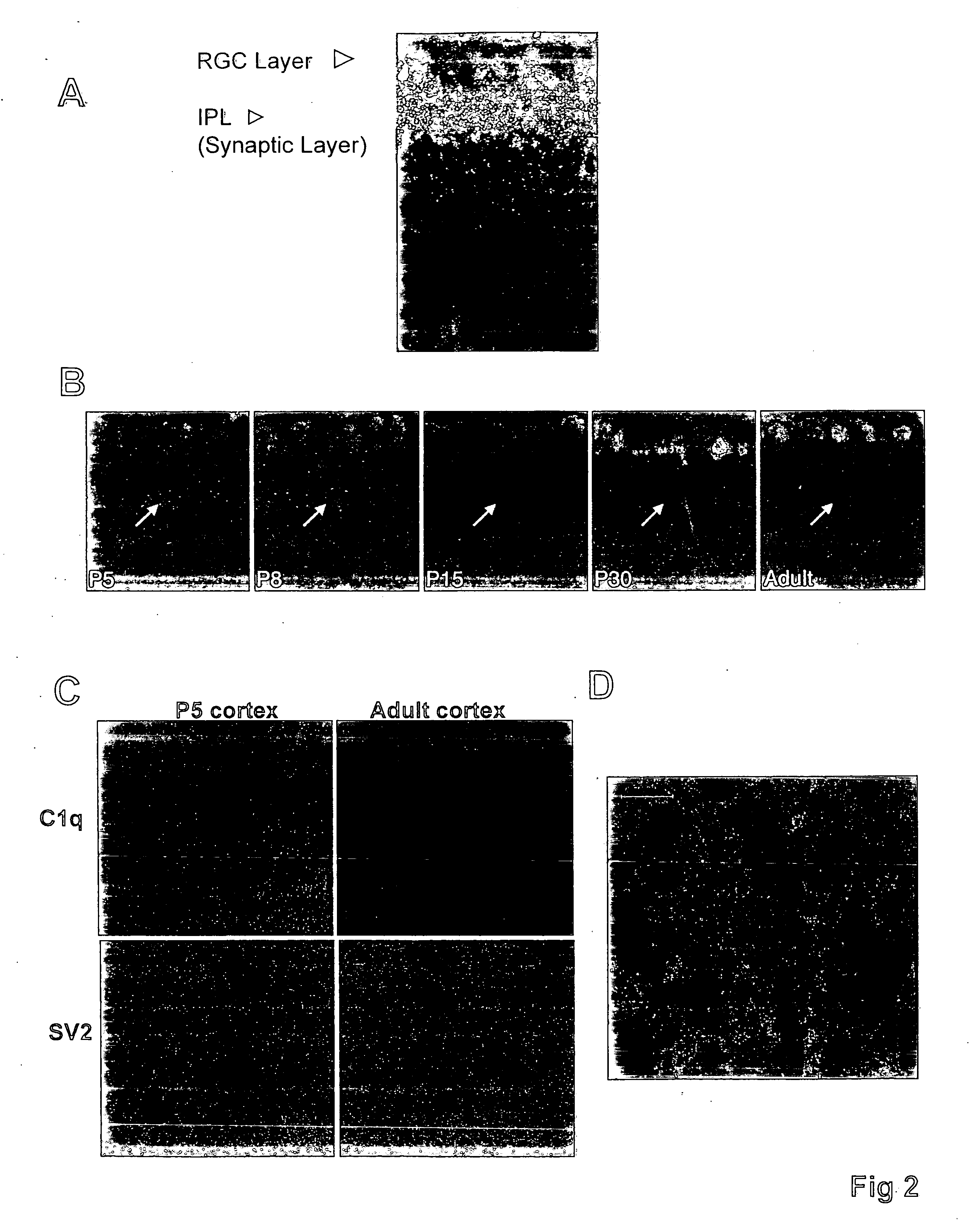
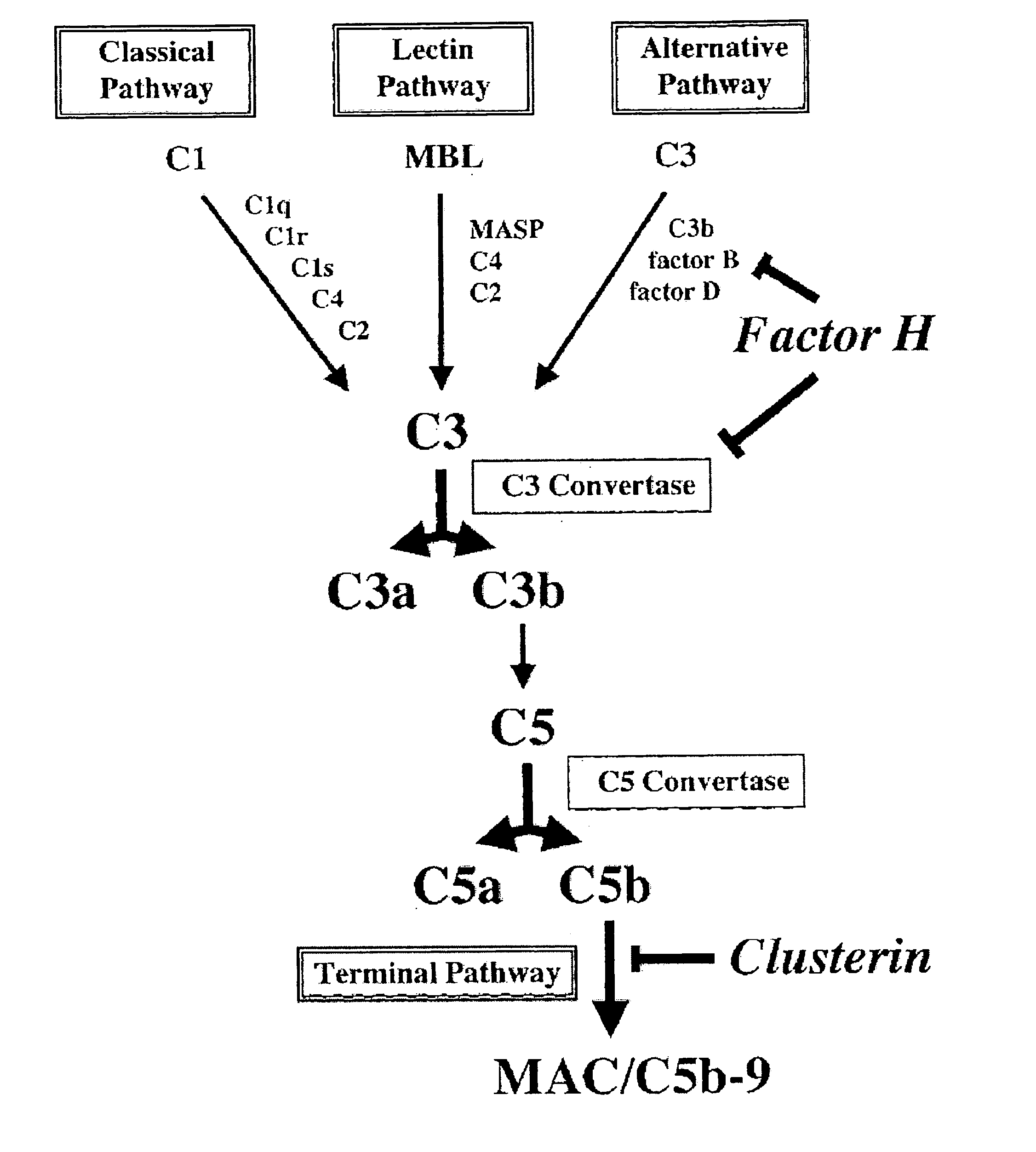
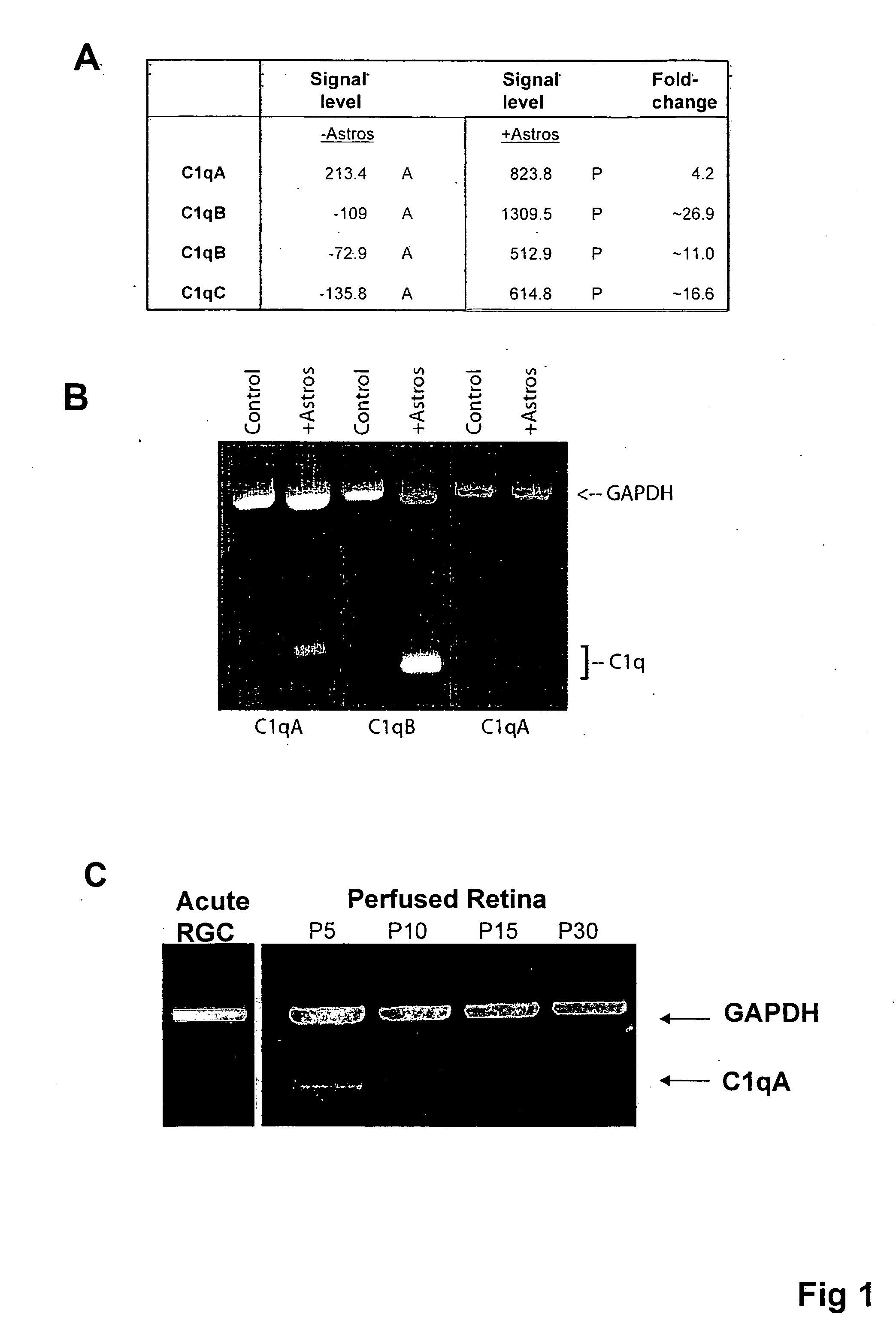
[0030] Methods are provided for protecting or treating an individual suffering from adverse effects of synapse loss. It is shown herein that immature astrocytes in normal development produce a signal that induces neurons to express specific complement proteins, thus enabling a developmental window during which synapse elimination occurs. Expression of these proteins in development mirrors the period of developmental synaptogenesis, being off in embryonic brain and adult brain but on at high levels in postnatal brain.
[0031] These findings have broad implications for a variety of clinical conditions, particularly neurodegenerative conditions where synapse loss is involved. Synapse loss is inhibited by contacting neurons with inhibitors or antagonists of the complement pathway. For example, inhibitors can block activation of the complement cascade, can block the expression of specific complement proteins in neurons, can interfere with signaling molecules that induce complement activat...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| neurodegenerative disorder | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| synaptic density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com