Golf putter with compensation for stroking errors
a technology of stroking error and compensation, which is applied in the field of golf clubs, can solve the problems of insufficient stroking force for all players, inaccurate direction perception, and misalignment of stroking force with the aimline, and achieves the effects of reducing the effect, high energy transfer, and low friction
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
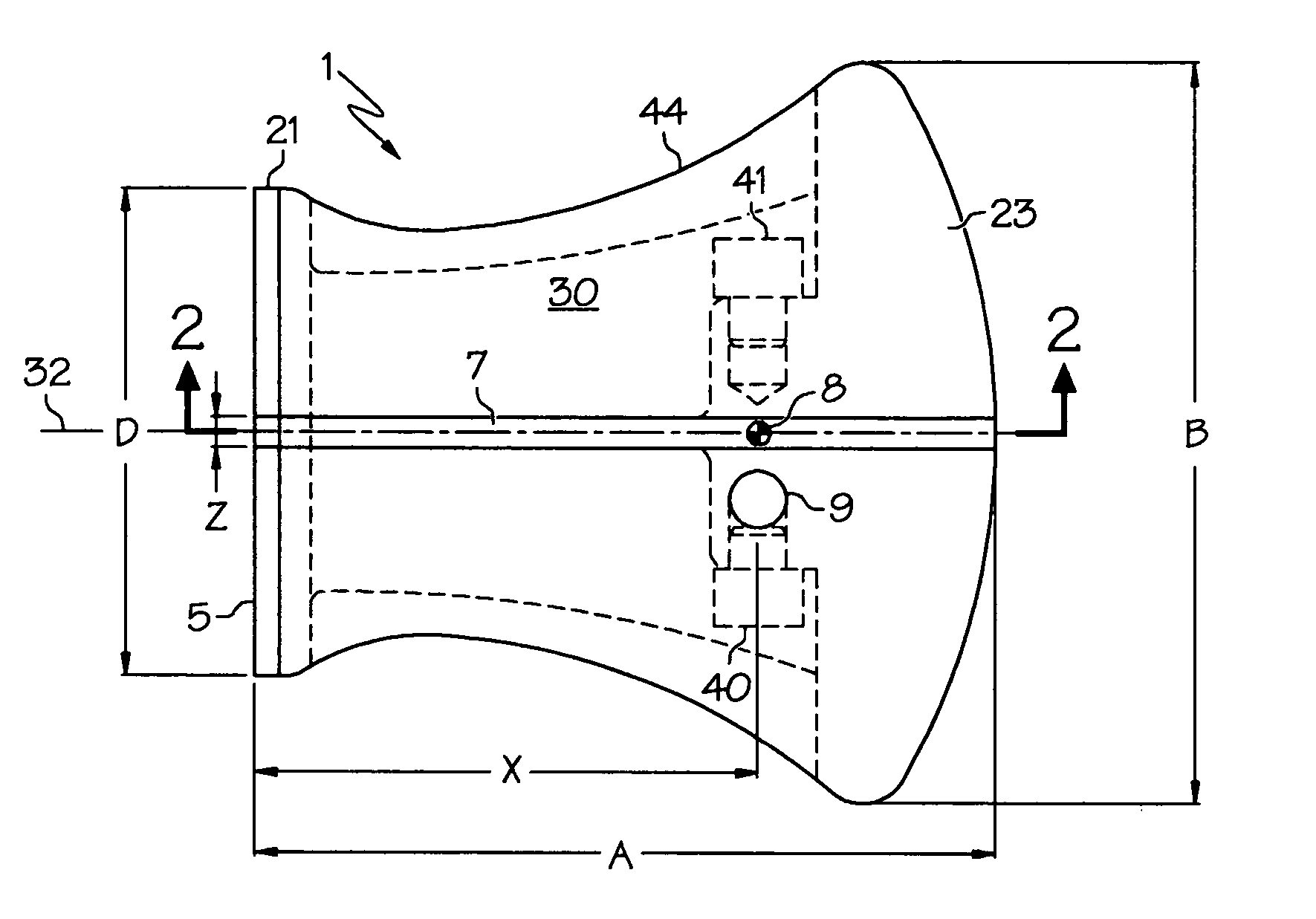
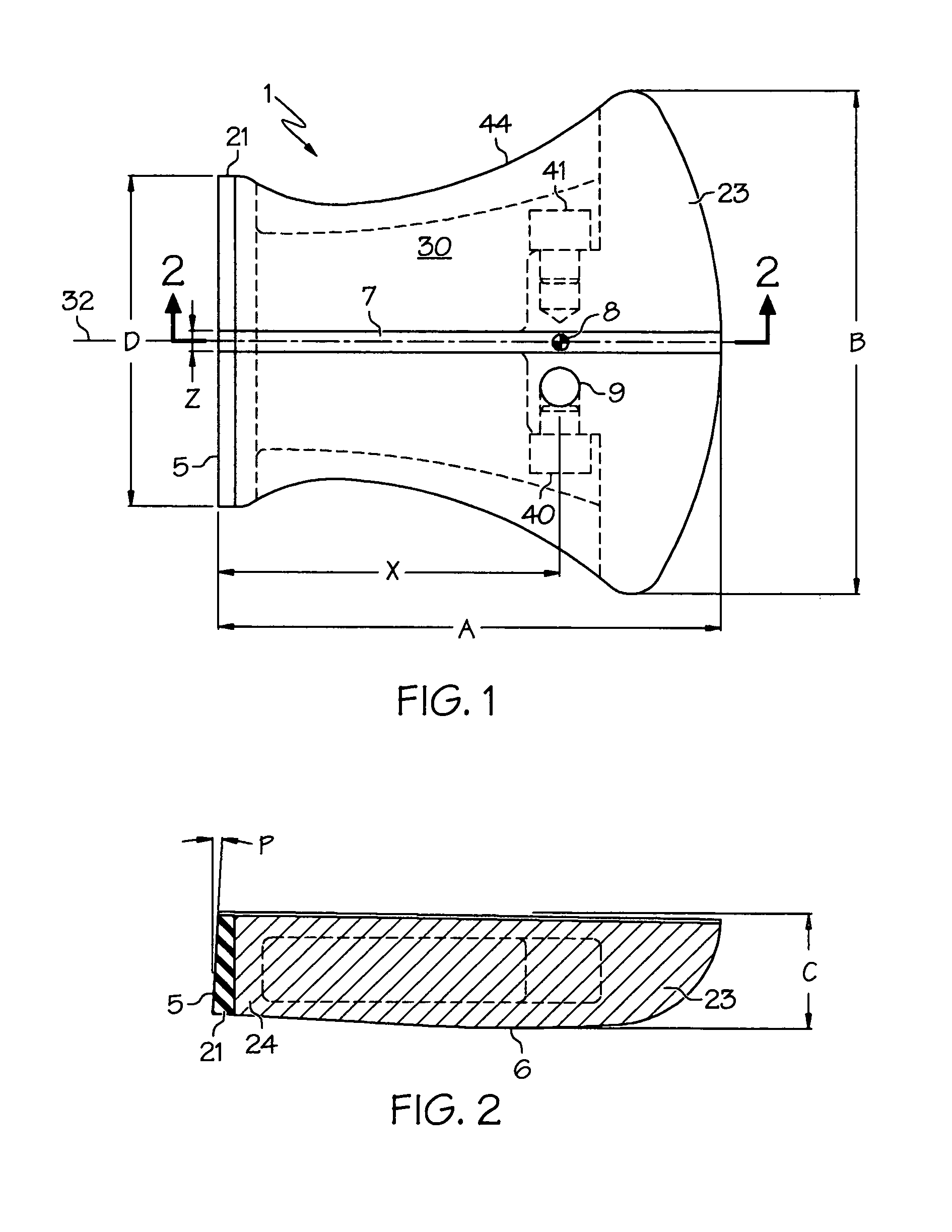
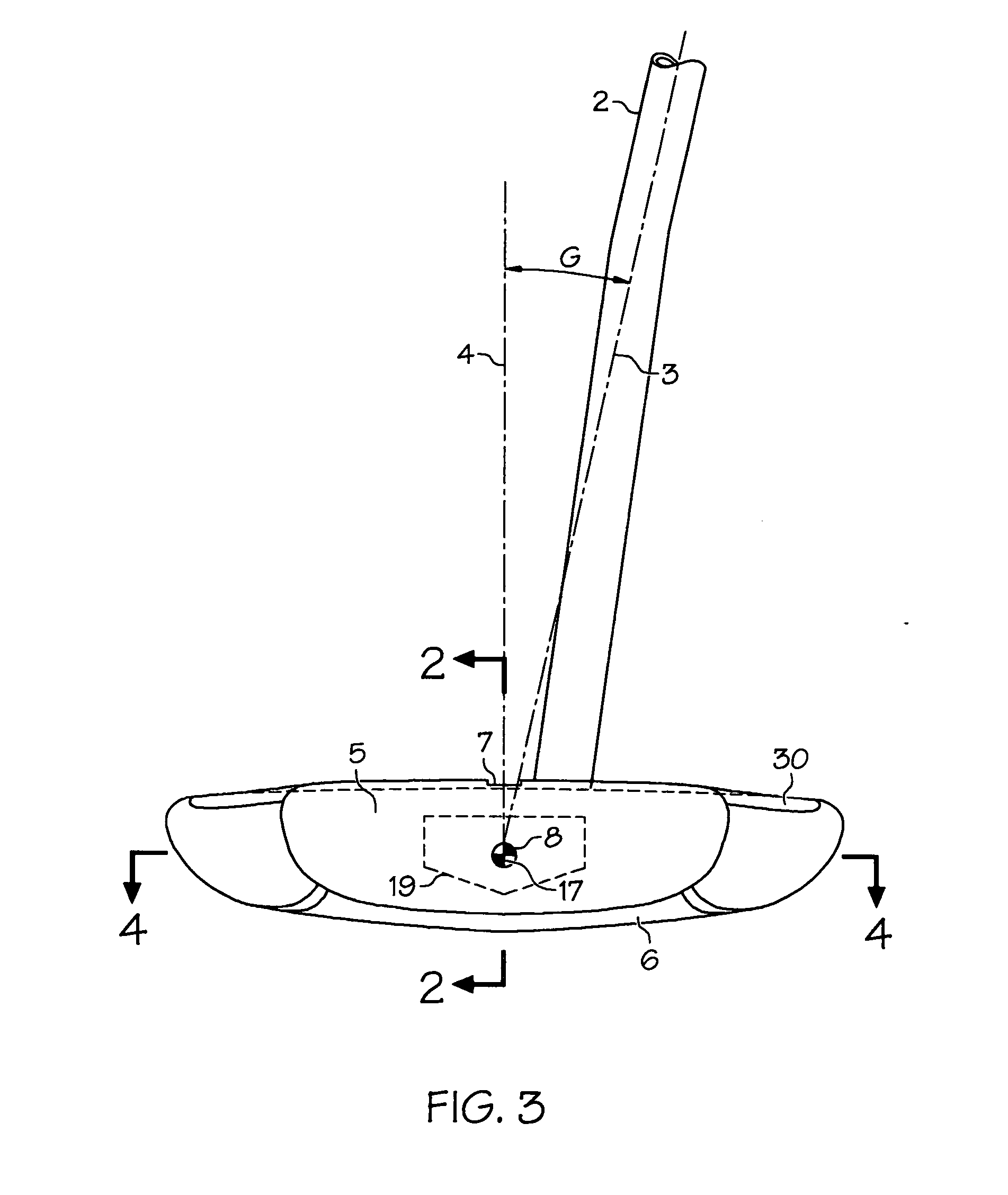
[0026] With reference to FIG. 1, a putter head 1 has a generally trapezoidal shape but with concave inner and outer edges, and a convex base (at the rear). Head 1 is substantially symmetrical in shape and is shown for a right-handed player. A front face 5 is used to strike a ball. A face width D may be less than a head width B. A rear weight 23 extends across the back and may be in one or more sections. In accordance with USGA rules, head width B is greater than a head length A. Width B is minimally greater than length A to minimize size.
[0027] The weight of head 1 varies with the player preference and the type of putter, and may be about 325 g. for conventional free held putters. There may be higher weight values, especially for stomach supported and pendulum-style putters. Head 1 includes a body 44 with the possibility of adding a separate face structure such as a layer 21, and / or a selectable weight 40 or 41. Body 44 may be cast and / or machined. Body 44 is preferably one-piece a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com