Implant
a technology of implants and implants, applied in the field of implants, can solve problems such as fractures in bone tissue, and achieve the effect of increasing the stiffness of implants
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
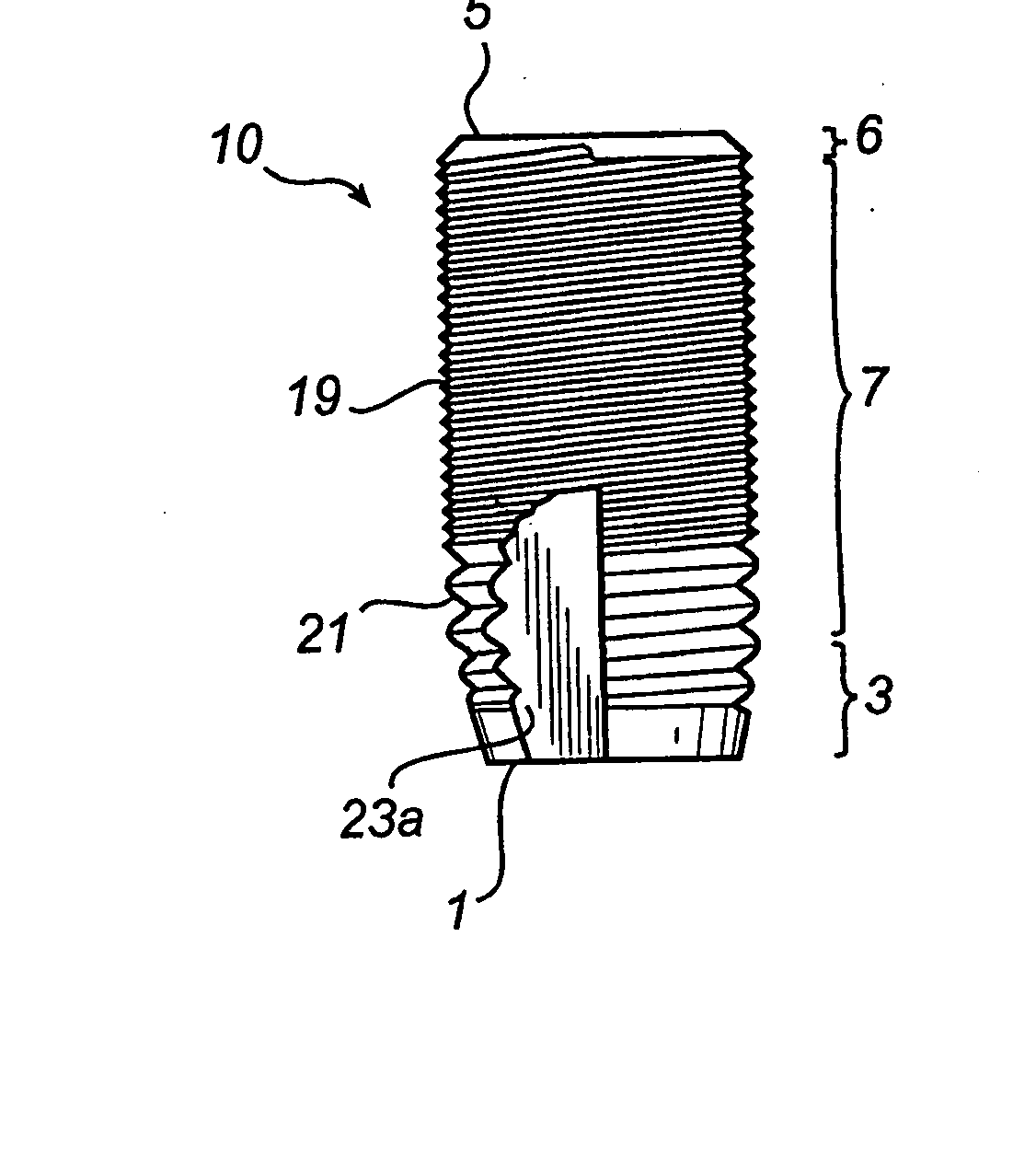
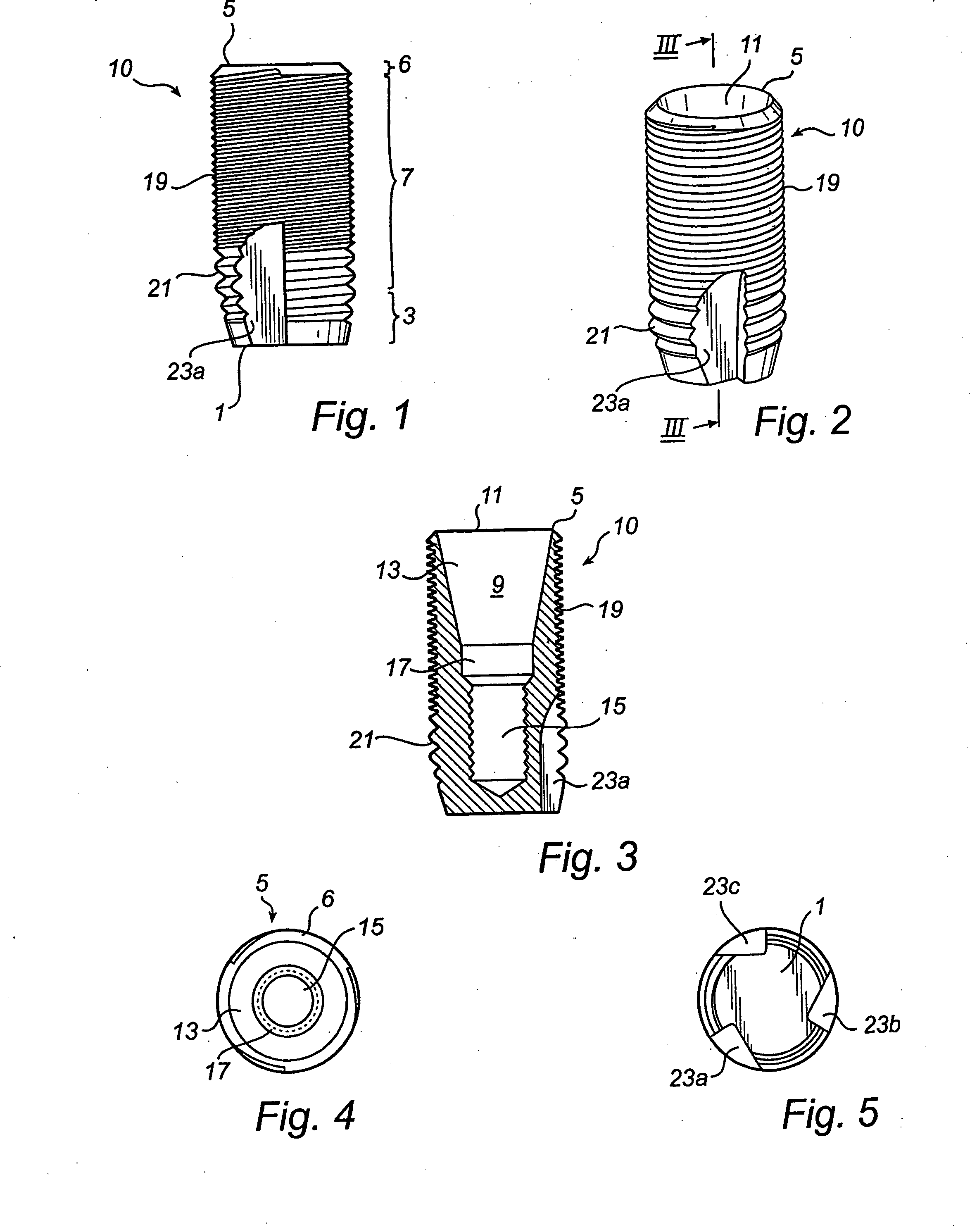
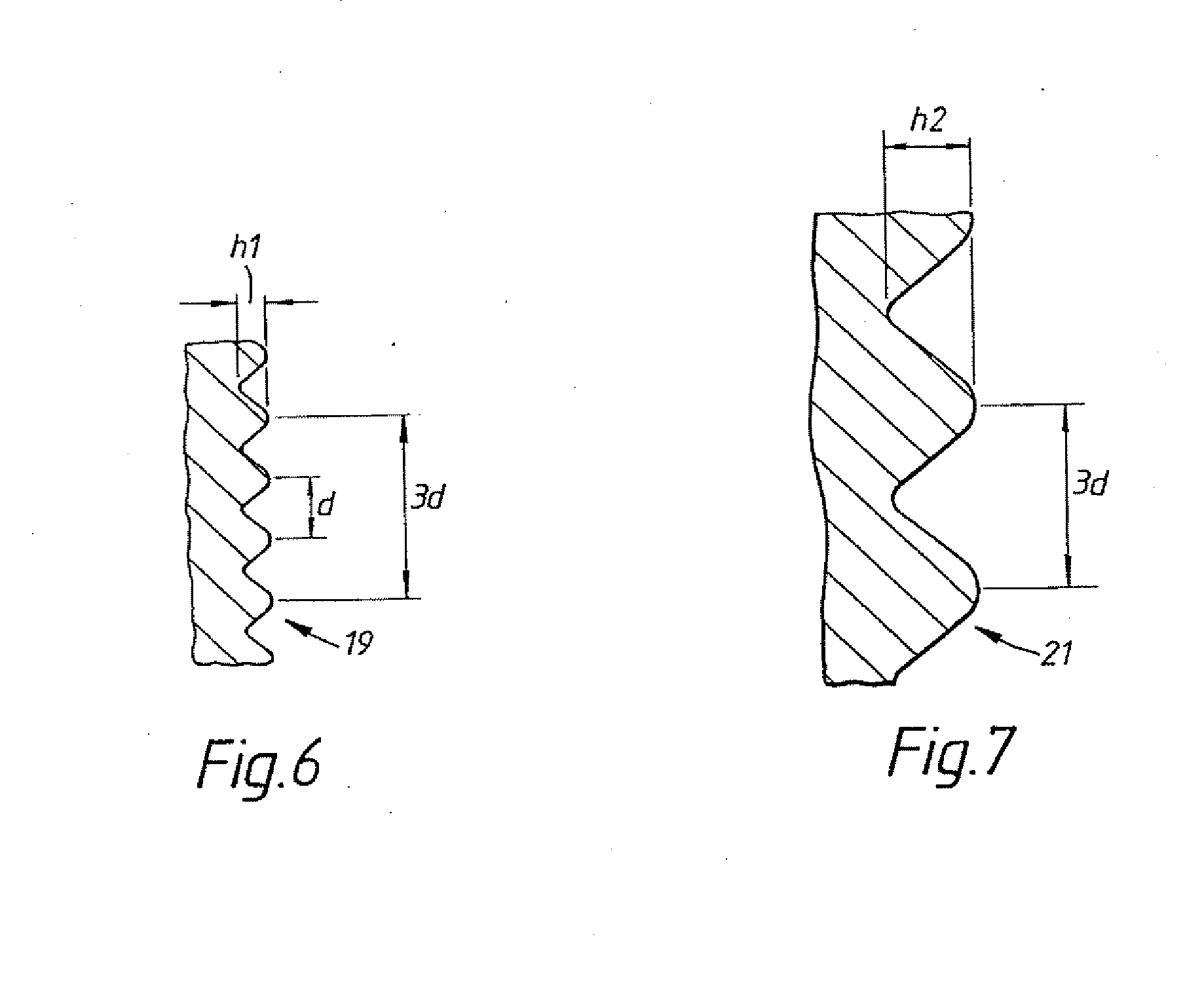
[0041] In the accompanying Figures of drawings there is shown various views of a self-tapping endosseous screw-type dental implant 10 of a dental prosthesis in accordance with the present invention. The implant 10 is for insertion into a bore-hole drilled into a toothless-site in a maxilla or mandible of a partially or fully edentulous patient to anchor to the maxilla or mandible a superstructure of the prosthesis which comprises a prosthetic part, namely one or more artificial teeth. The implant 10 is made from commercially pure titanium, a titanium alloy, another biocompatible metal or metal alloy or a ceramic to promote osseointegration of the implant with the bone tissue of the boundary walls of the bore-hole.
[0042] Referring to FIG. 1, the implant 10 has an apical end 1 which is presented by a first conical section 3 to ease insertion of the implant 10 into the bore-hole, a coronal end 5 presented by a second conical section 6 and an intermediate section 7 of constant diameter...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com