Sequential Display With Motion Adaptive Processing for a Dmd Projector
a dmd projector and sequential display technology, applied in the field of sequential display operation, can solve the problems of increasing color breakup, affecting the quality of dmd projectors, and only working well for low brightness objects, so as to reduce motion blurring, reduce the incidence of motion blurring, and minimize color break-up
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
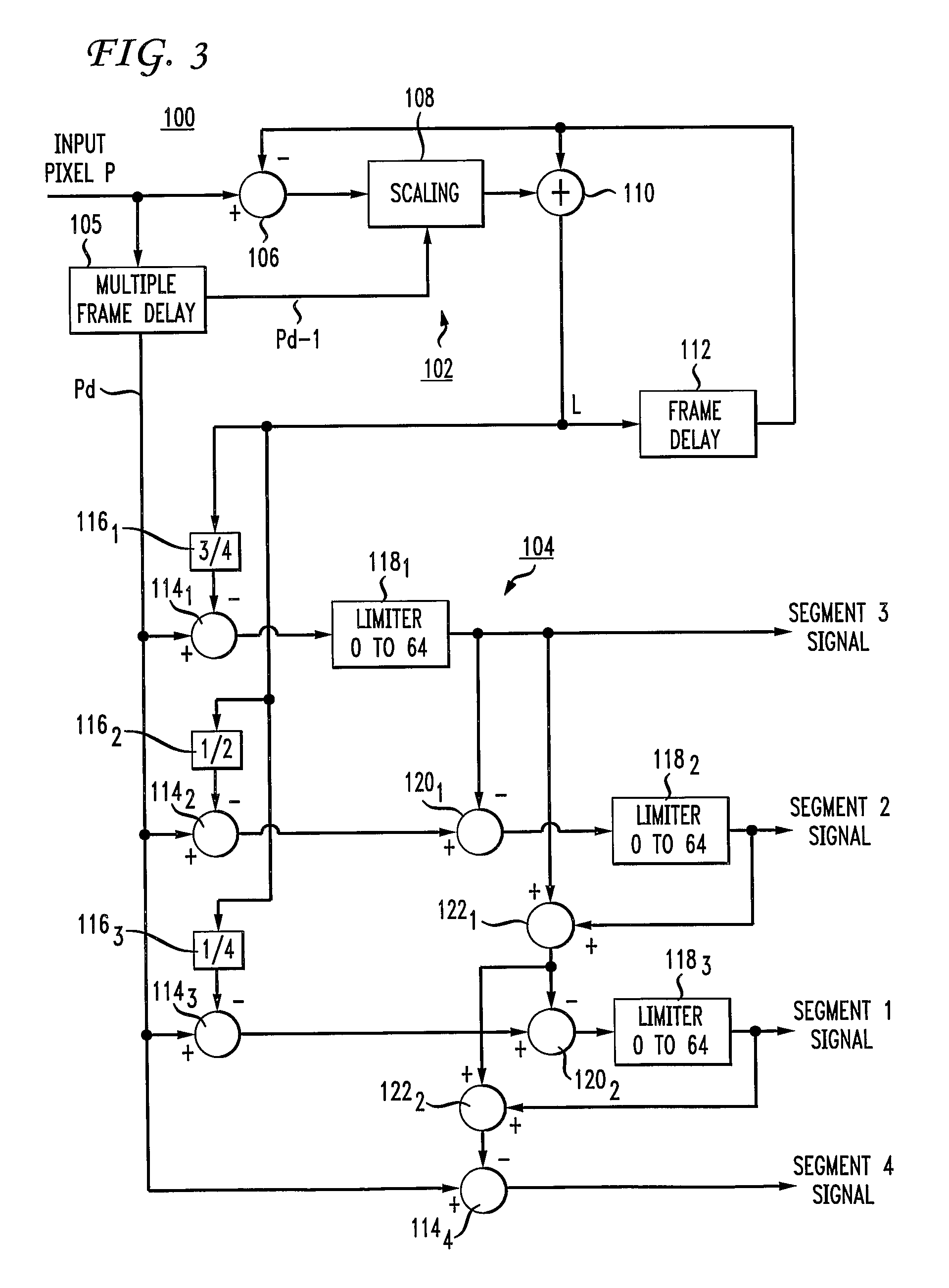
Embodiment Construction
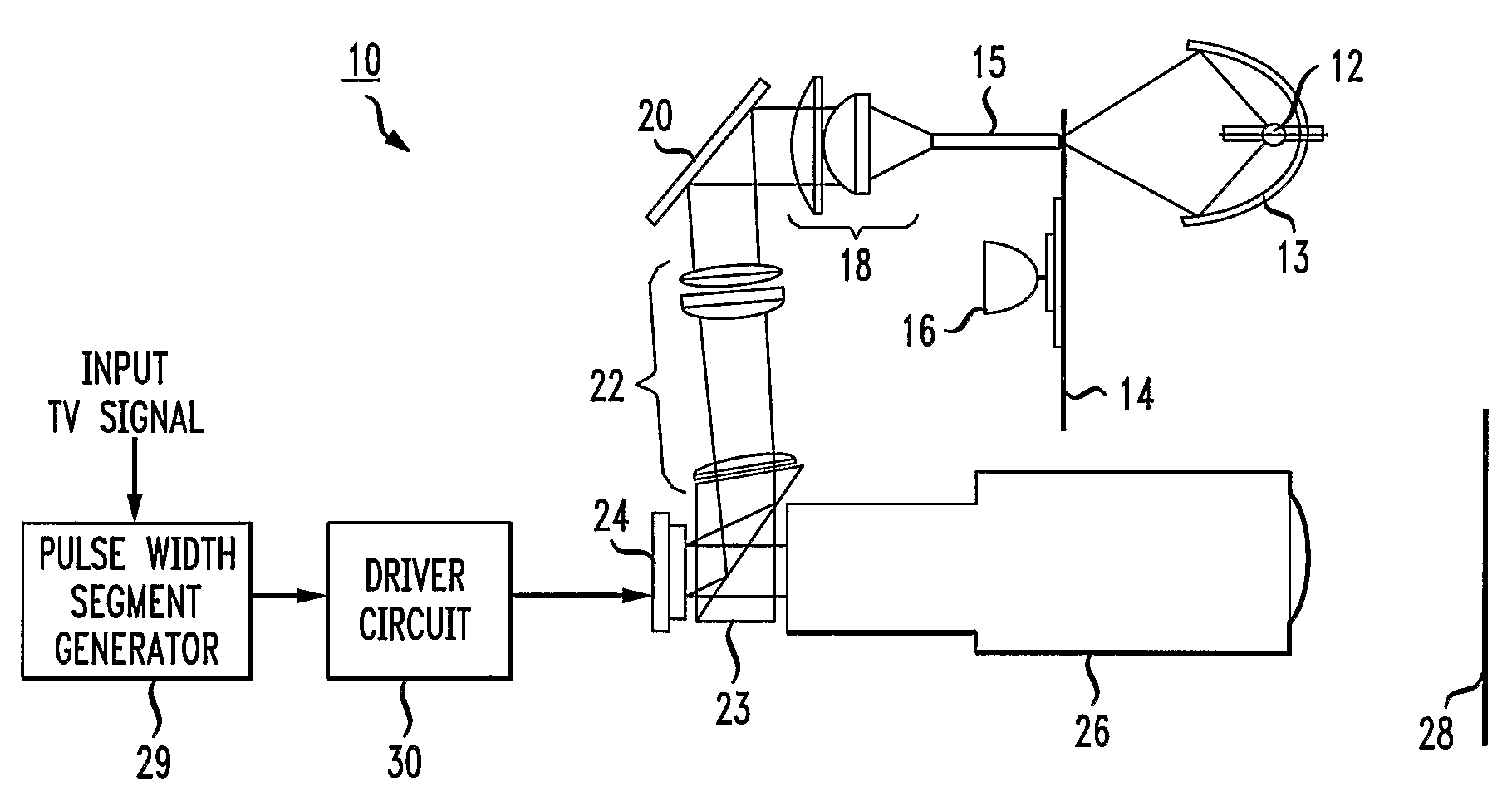
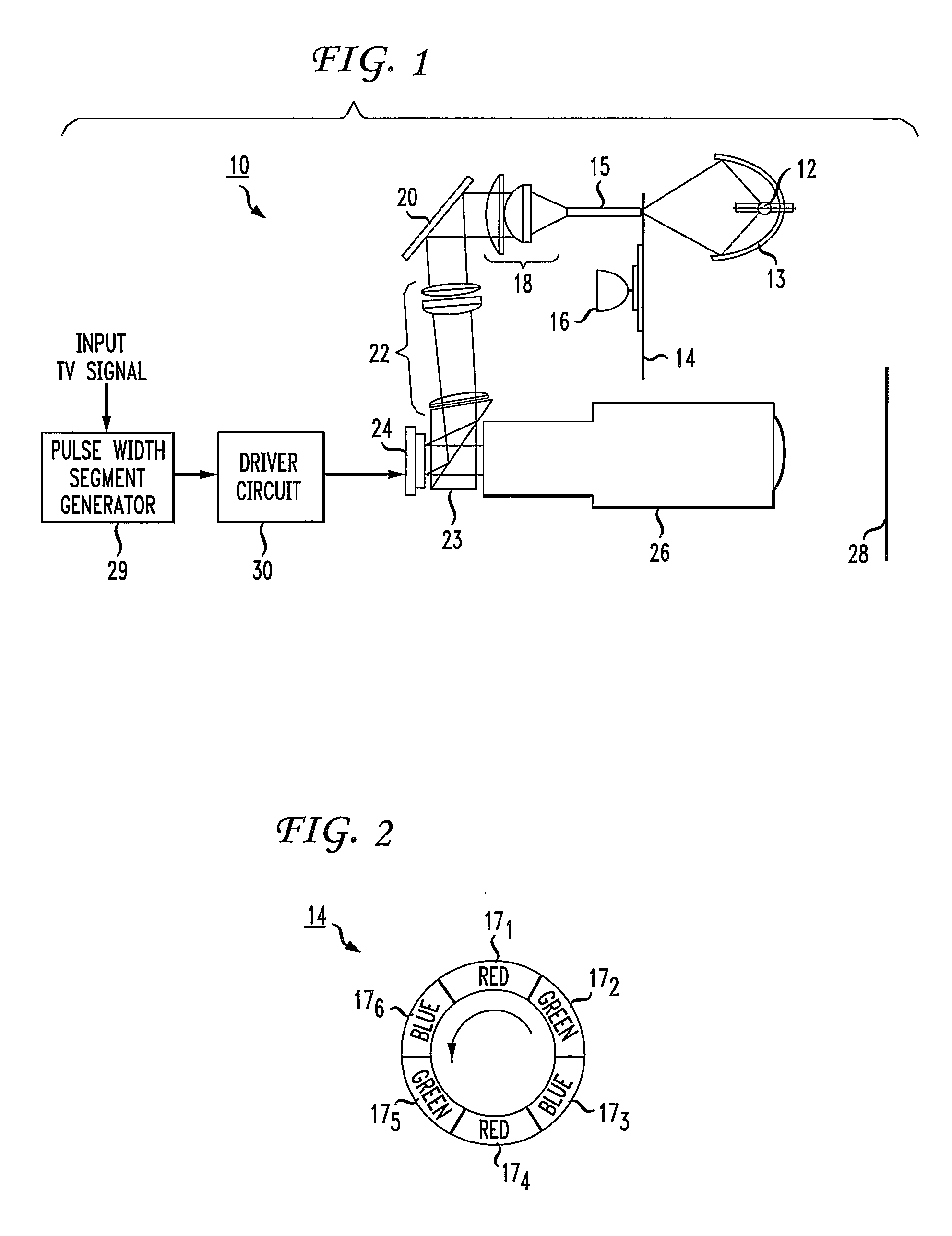
[0014]FIG. 1 depicts a present-day color sequential display system 10 of the type disclosed in the Application Report “Single Panel DLP™ Projection System Optics” published by Texas Instruments, June 2001 and incorporated by reference herein. The system 10 comprises a lamp 12 situated at the focus of an elliptical reflector 13 that reflects light from the lamp through a color wheel 14 and into an integrator rod 15. A motor 16 rotates the color wheel 14 to place a separate one of red, green and blue primary color windows between the lamp 12 and the integrator rod 15. In an exemplary embodiment depicted in FIG. 2, the color wheel 14 has diametrically opposed red, green and blue color windows 171 and 174, 172 and 175, and 173 and 176, respectively. Thus, as the motor 16 rotates the color wheel 14 of FIG. 2 in a counter-clockwise direction, red, green and blue light will strike the integrator rod 15 of FIG. 1 in an RGBRGB sequence. In practice, the motor 16 rotates the color wheel 14 at...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com