Fairing for a combustion chamber end wall
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
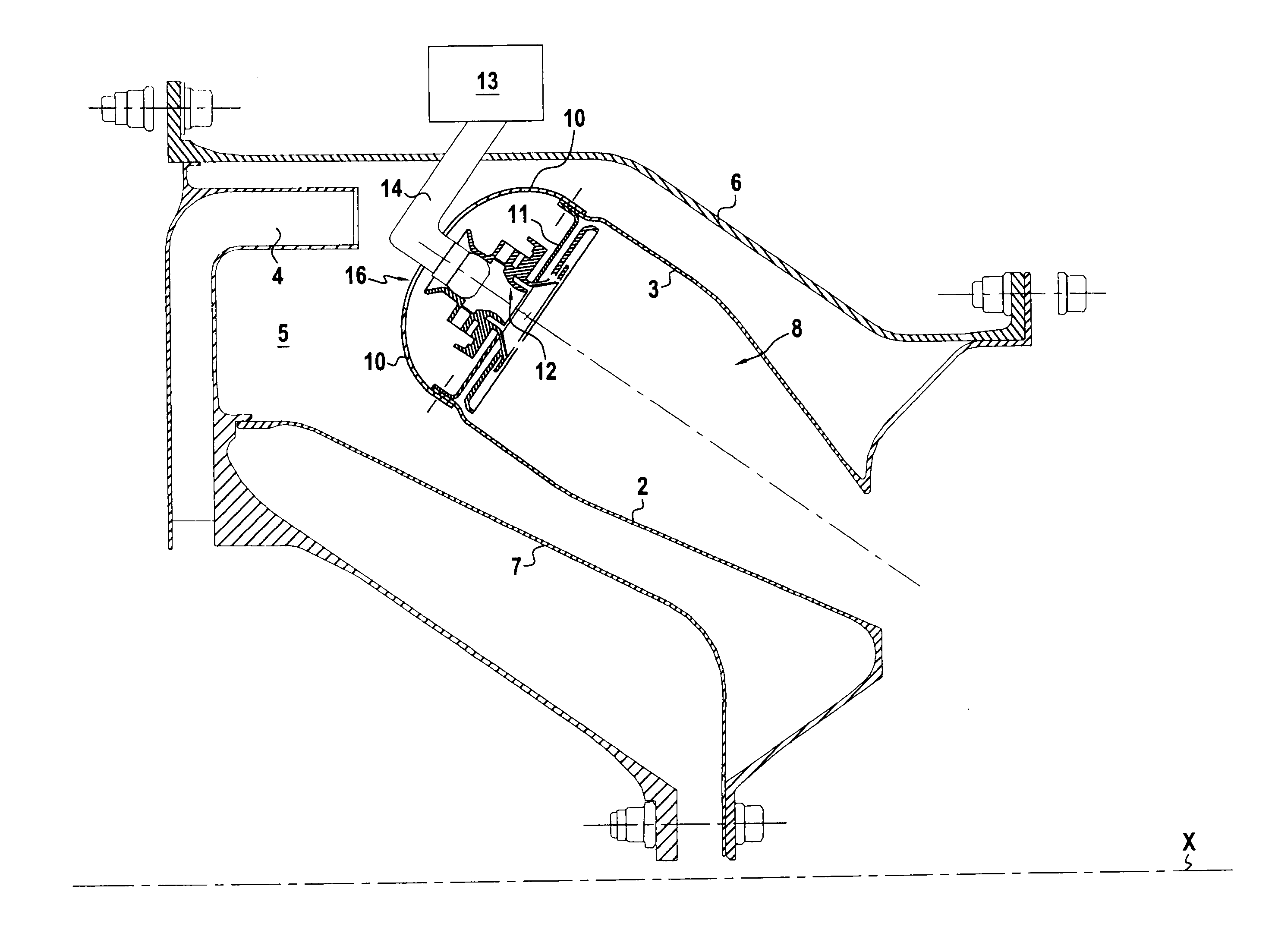
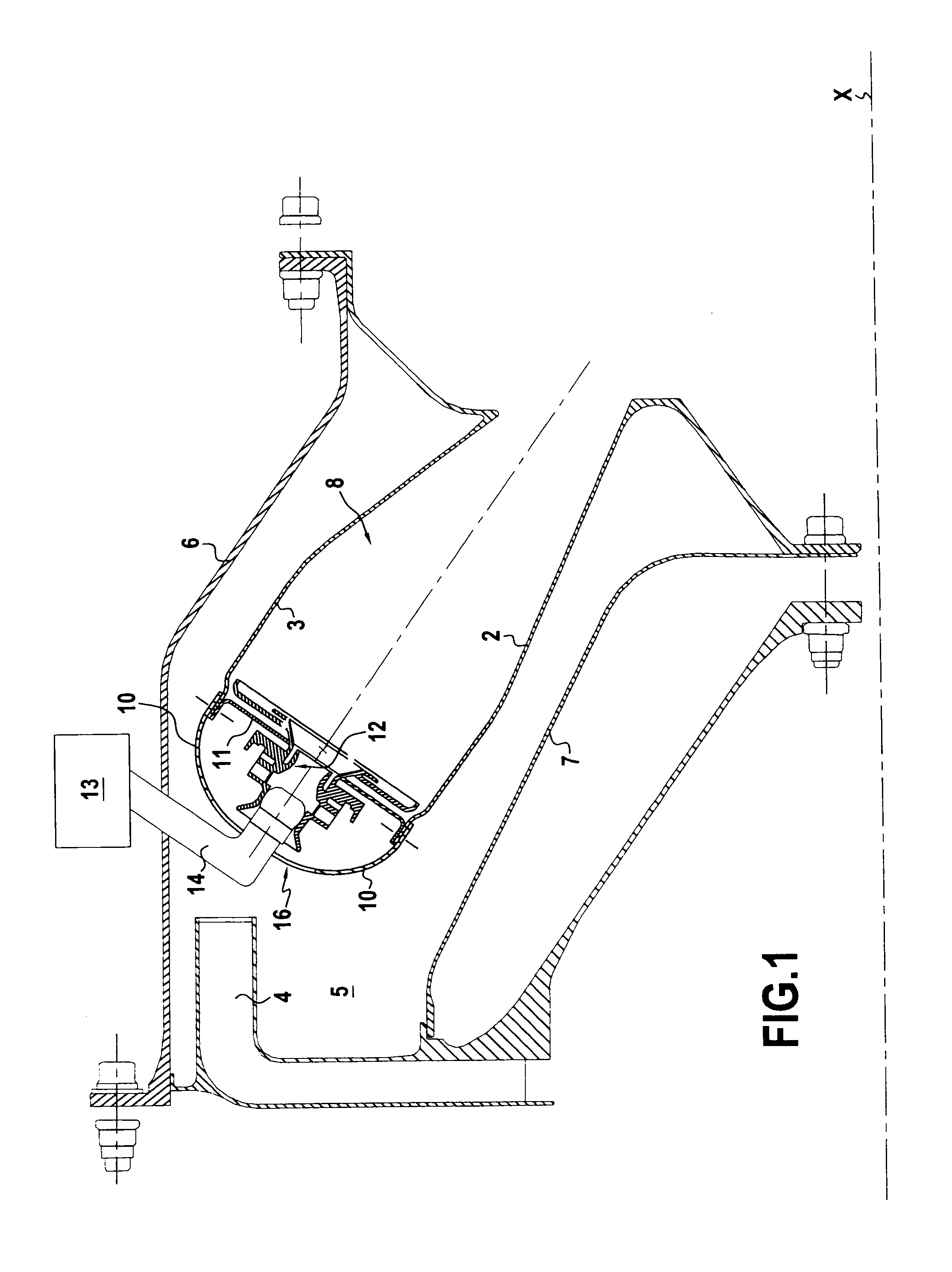
[0028]FIG. 1 shows an example of a turbojet in half-section on a section plane containing the axis of rotation X of the turbojet rotor. The turbojet comprises a centrifugal high-pressure compressor (not shown), and downstream therefrom a diffuser 4 opening out into a space 5 defined between concentric outer and inner casings 6 and 7, and occupied by an annular combustion chamber 8 supported by the casings 6 and 7.
[0029]Although FIG. 1 relates to a turbojet with a centrifugal compressor, the invention is not limited to this type of turbomachine.
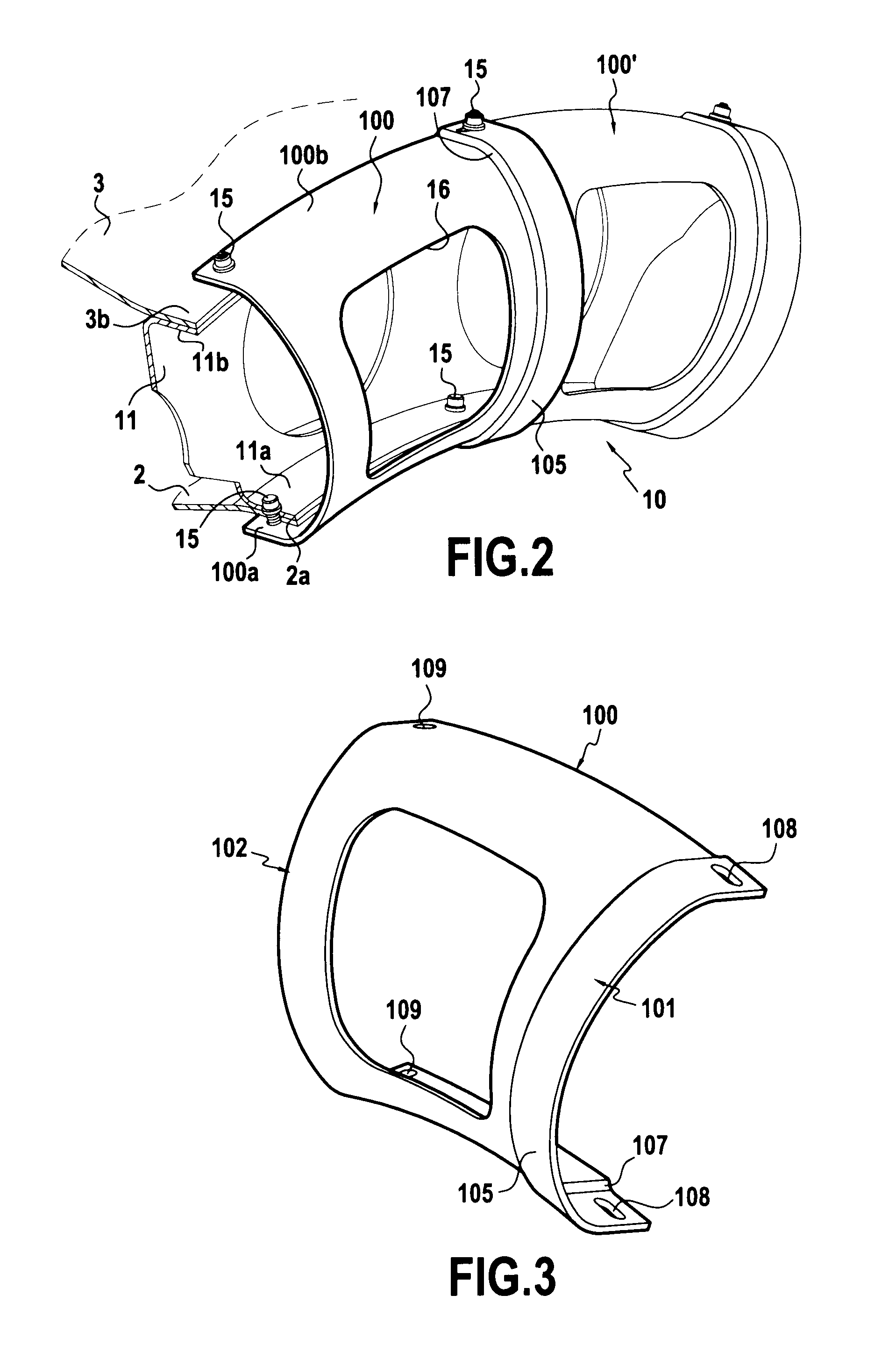
[0030]The combustion chamber 8 has an inner 2 wall, an outer wall 3, and, in the upstream region of said chamber, an annular end wall 11 disposed between said inner and outer walls. This end wall 11 presents inner and outer fastener rims 11a and 11b folded upstream relative to the main portion of the end wall 11.
[0031]The end wall 11 carries injector heads 12 forming part of a system 13 for feeding fuel via fuel injectors 14 passing through th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com