Stabilization of flatband voltages and threshold voltages in hafnium oxide based silicon transistors for CMOS
a technology of silicon transistors and threshold voltages, which is applied in the field of semiconductor structure, can solve problems such as non-ideal thresholds, and achieve the effect of promoting the necessary flatband voltage shift and altering the effective alignment of the workfunction of the material stack
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example
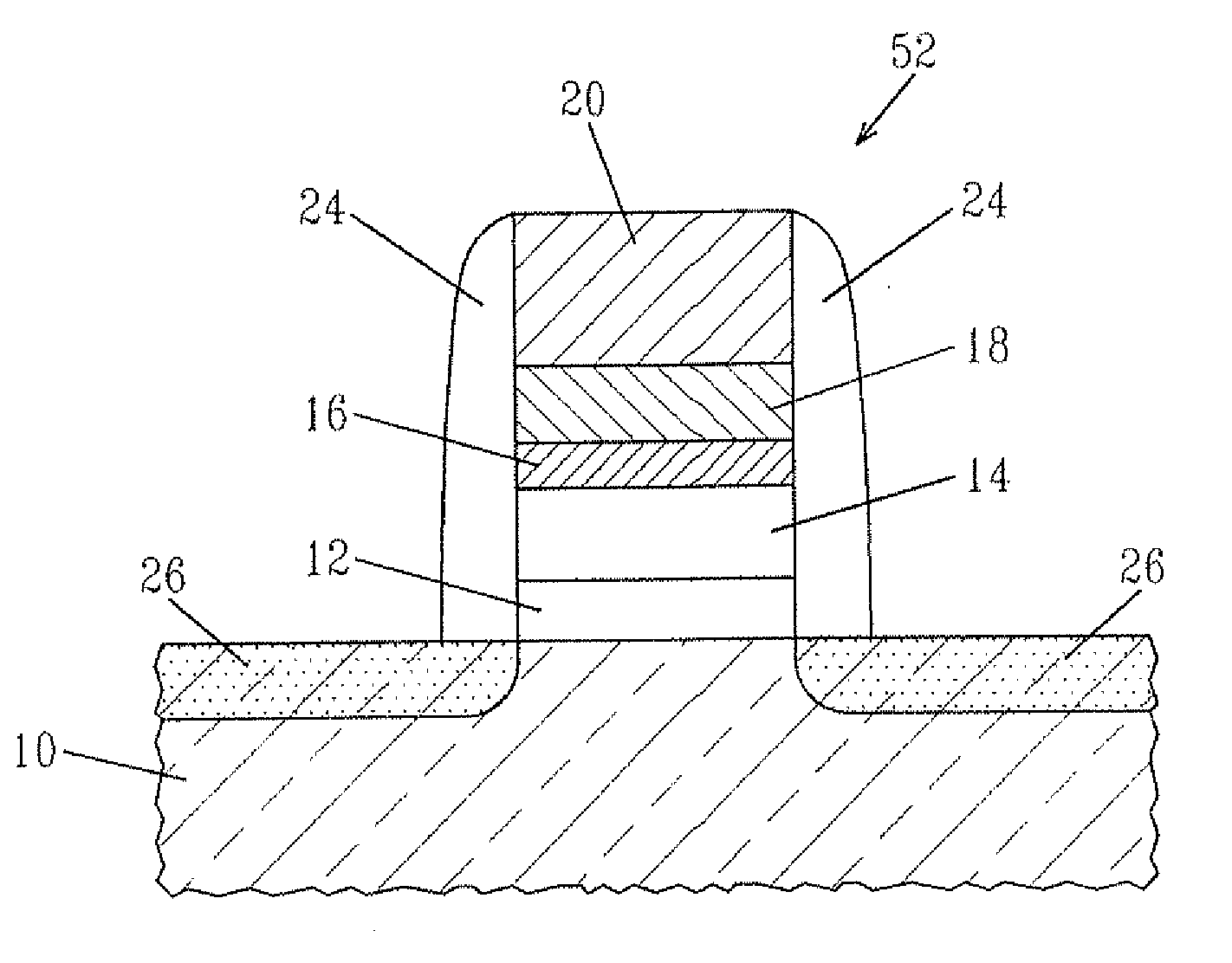
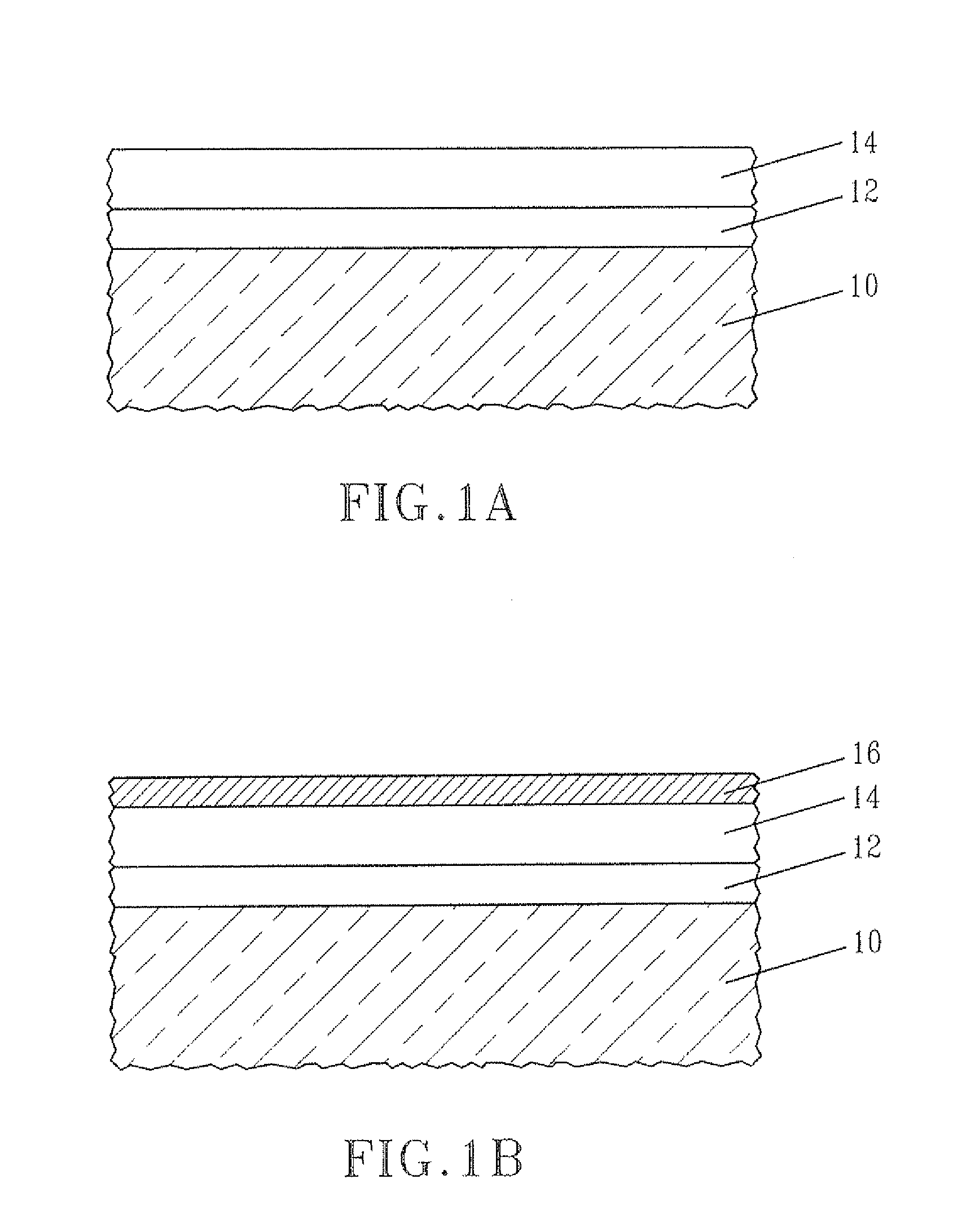
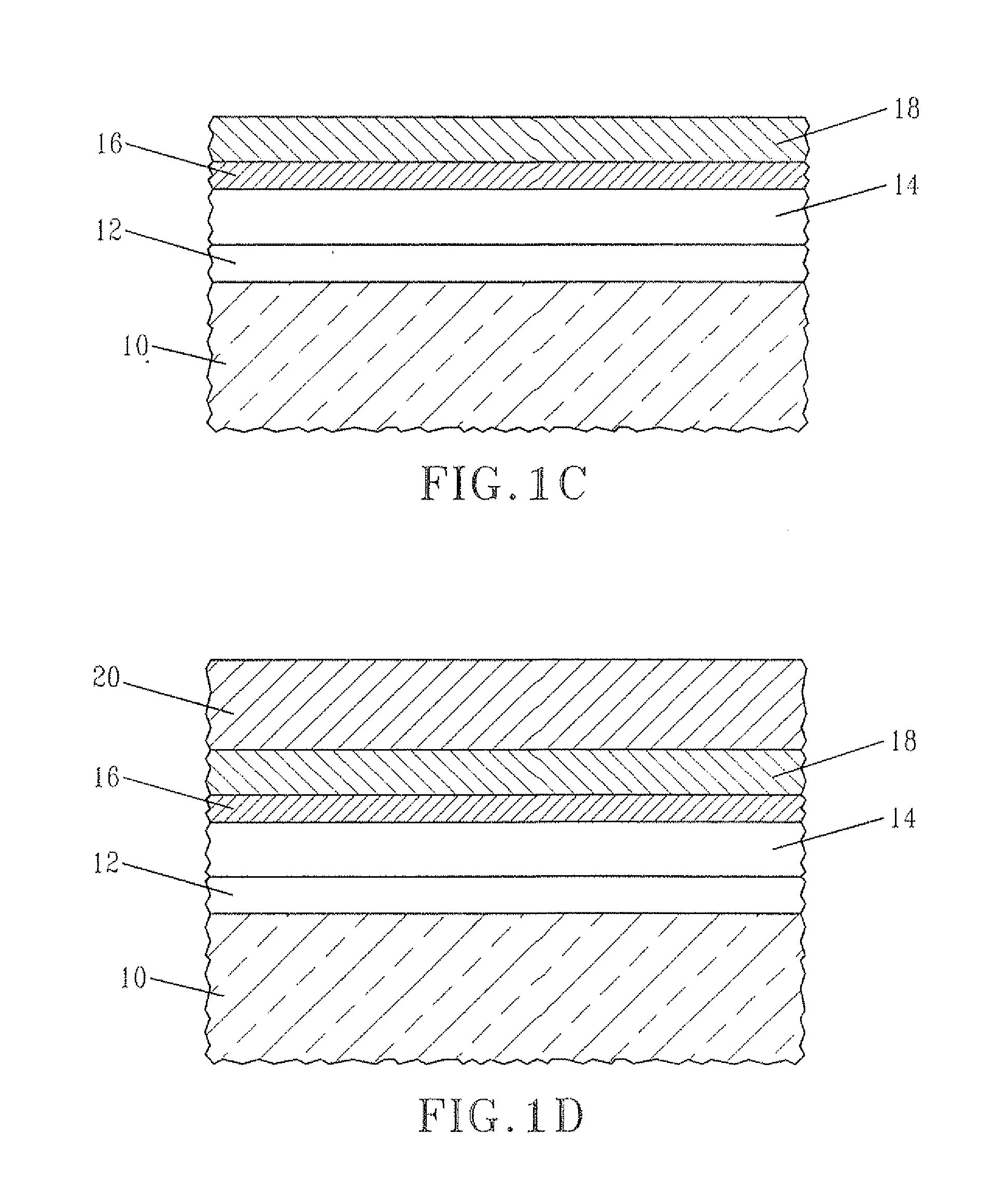
[0059]In this example, an nMOSCAP was prepared utilizing a material stack of the present invention and it was compared with a prior art nMOSCAP which did not include the inventive material stack. Specifically, a material stack comprising SiO2 / HfO2 / 0.8 nm La2O3 / 30 nm TiN / PolySi stack (Inventive) was prepared utilizing the processing steps mentioned above and that material stack was used as a component of an nMOSCAP. A prior art material stack, not including La oxide was prepared and was used a component for a prior art nMOSCAP (Prior Art). Each material stack after processing on a Si substrate was subjected to a 1000° C. rapid thermal anneal in nitrogen, followed by a 500° C. forming gas anneal.
[0060]FIG. 3 shows the CV curves of the two nMOSCAP. The CET (Capacitance Equivalent Thickness) and the EOT (Equivalent Oxide Thickness) of the Inventive material stack were 10.2 Å and 6.5 Å, respectively. The CET and the EOT of the Prior Art material stack were 14.7 Å and 10.5 Å, respectively...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com