Intranasal Administration of Active Agents to the Central Nervous System
a technology of active agents and central nervous system, which is applied in the direction of immunological disorders, antibody medical ingredients, metabolism disorders, etc., can solve the problems of difficult delivery of drugs to the central nervous system (cns), poor access to cns targets from the peripheral circulation, and little evidence of protein macromolecule delivery to the cns via intranasal pathways, etc., to achieve the effect of improving intranasal administration
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Brain Distribution of α-Melanocyte Stimulating Hormone Mimetibody after Intranasal Administration
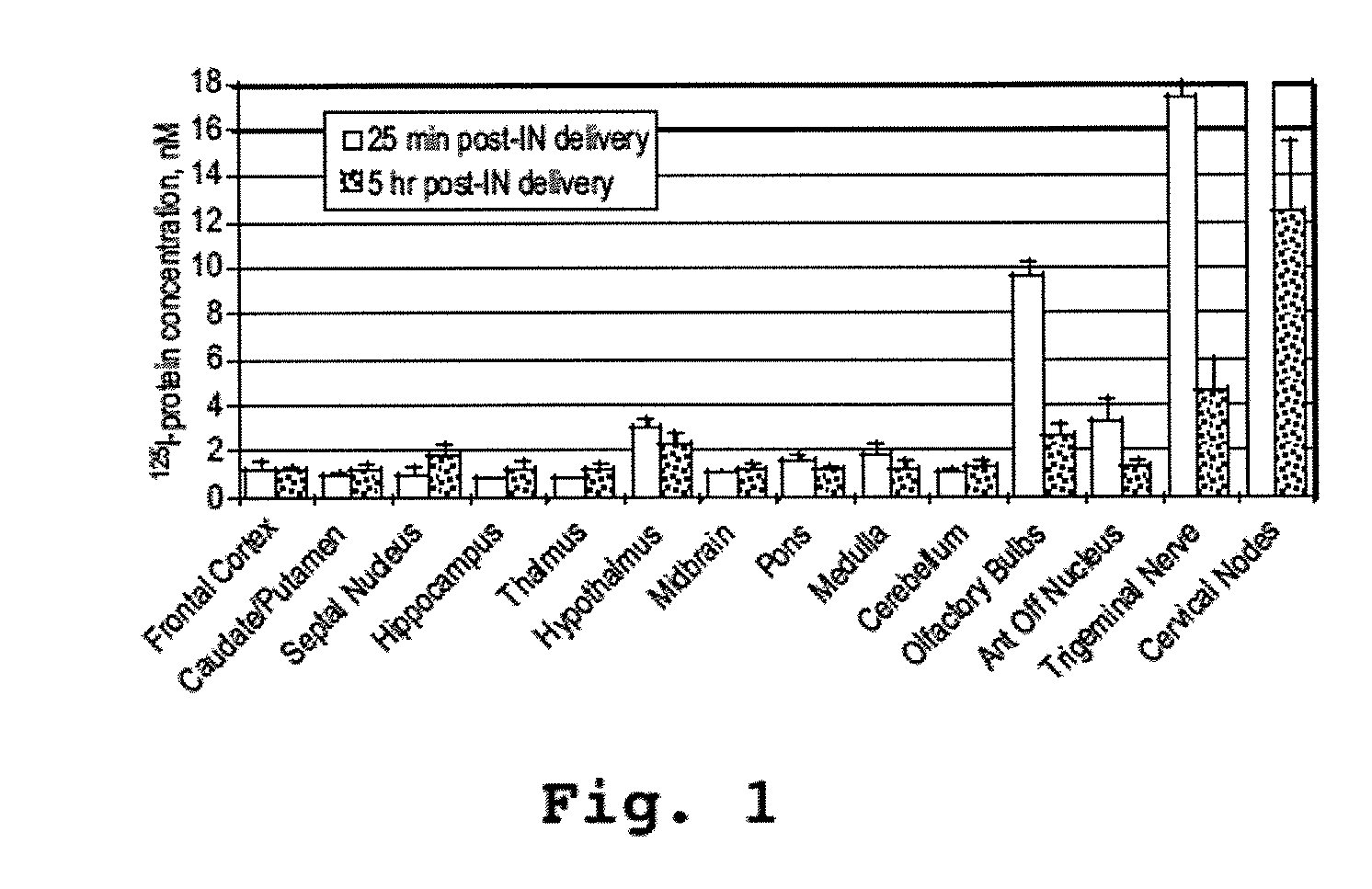
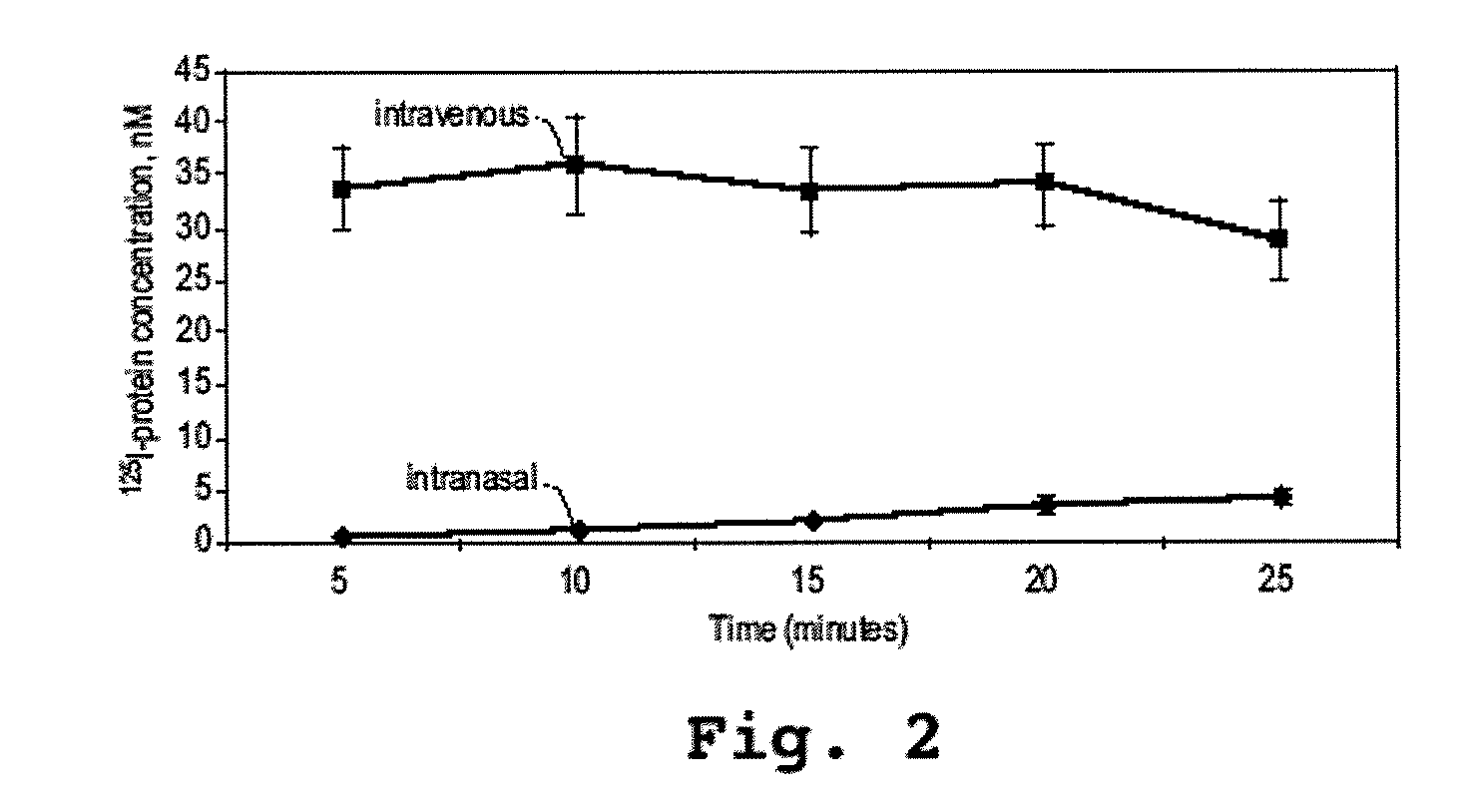
[0133]This example shows that an α-melanocyte stimulating hormone mimetibody (α-MSH mimetibody) is transported to various regions in the brain and was detected at about 25 minutes after intranasal administration while reducing systemic exposure according to the methods of the present invention. The example further shows that the α-MSH mimetibody delivered to the brain is retained in the brain for at least up to 5 hours post-delivery.
Methods
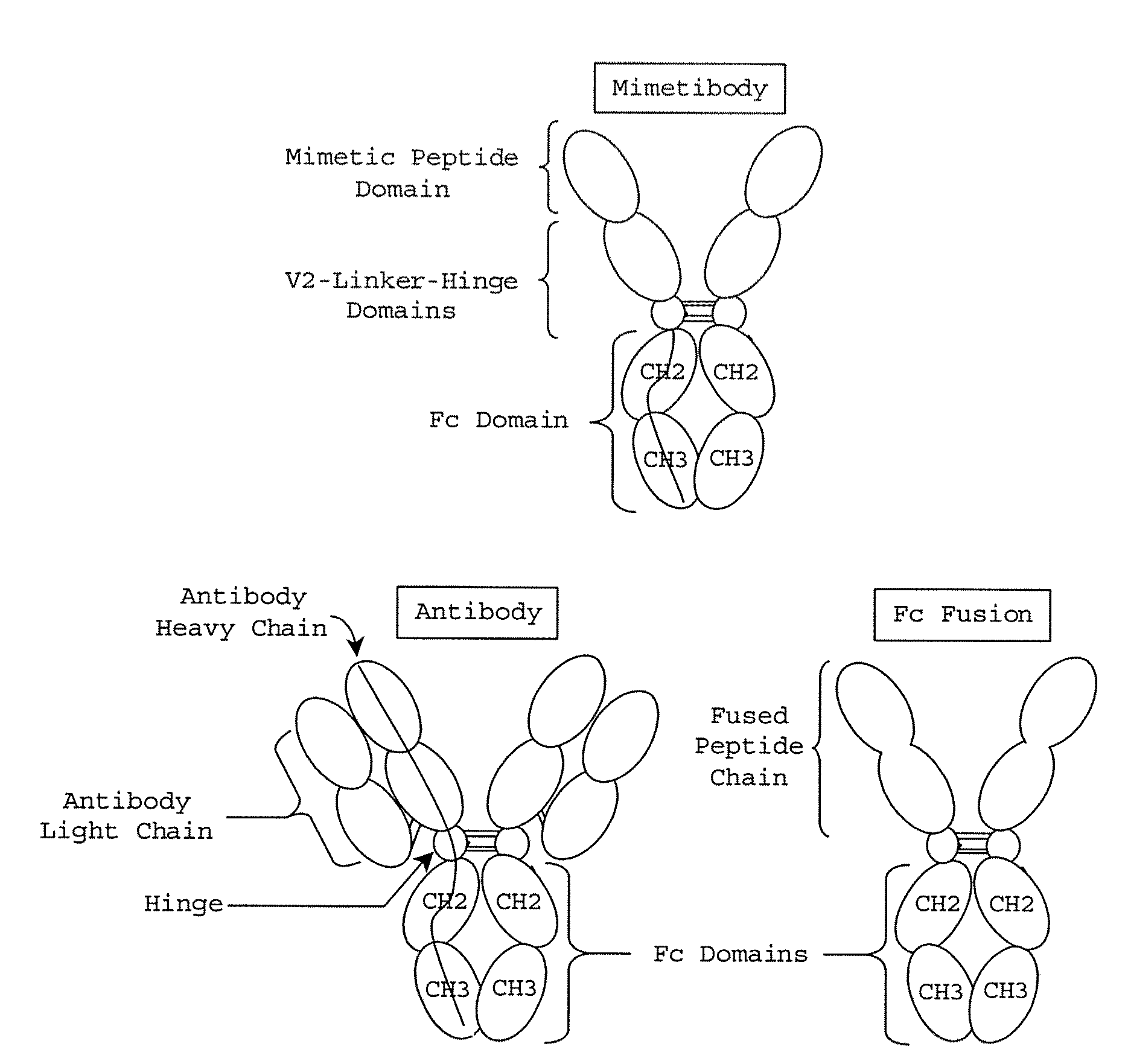
[0134]An α-MSH mimetibody was prepared, to serve as a model and exemplary therapeutic compound to illustrate the claimed method. The α-MSH mimetibody is a homo-dimeric fusion molecule that consists of the therapeutic α-MSH polypeptide, identified herein as SEQ ID NO:1, and the Fc portion of the human immunoglobulin G1 (IgG1) monoclonal antibody. The engineered fusion polypeptide was produced using recombinant DNA methods.
[0135]The α-MSH mimetibody was ...
example 2
Dose-Dependent Reduction in Cumulative Food Intake in Normal Rats after Intranasal Administration of Alpha-MSH
[0144]This example shows that intranasal administration of a single dose of the N-acetylated α-melanocyte stimulating hormone (Ac-Ser-Tyr-Ser-Met-Glu-His-Phe-Arg-Trp-Gly-Lys-Pro-Val-NH2, SEQ ID NO:1, supplied by Phoenix Pharmaceuticals, INC) was sufficient to achieve a dose dependent, pharmacodynamic response; specifically, a reduction of cumulative food intake, with an ED50 at 24 hours of 6-7 nmol.
Methods
[0145]Two groups of nine rats each were assembled. In a cross-over design, each week one group was dosed with a phosphate buffered saline (PBS) vehicle and the other group was dosed with α-MSH peptide; the following week the treatment administered to each group was reversed. Prior to the study, the light cycle was slowly reversed, within a 2 weeks acclimation period. Rats were fasted for 24 hours prior to each experiment (water was always available), and received anesthesia...
example 3
Reduction in Cumulative Food Intake in Normal Rats after Intranasal Administration of Alpha-MSH Mimetibody
[0148]This example shows that intranasal administration of a single dose of 25 nmols (5 mg / kg) of the α-MSH mimetibody is sufficient to reduce cumulative food intake significantly at 8 and 24 hours. Water consumption and body weight remained unchanged.
Methods
[0149]The study protocol and methods used were the same as described in Example 2. The total number of rats was 14.
Results and Conclusions
[0150]As seen in FIG. 7, a single dose of 25 nmol of intranasally delivered alpha-MSH mimetibody had a significant effect on decreasing cumulative food intake at 8 and 24 hours, with a non-statistically significant trend toward reduction at 48 and 72 hours. The significance at the later time points was likely lost due to the relatively small number of animals used in the study (n=14). The study shows that a 62 kDa large protein, like the α-MSH mimetibody, can be delivered to the CNS via th...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com