Control apparatus for an internal combustion engine and method for controlling the same
a technology of control apparatus and internal combustion engine, which is applied in the direction of electric control, machines/engines, instruments, etc., can solve problems such as burning fuel, and achieve the effect of achieving reliable control of the lift amoun
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
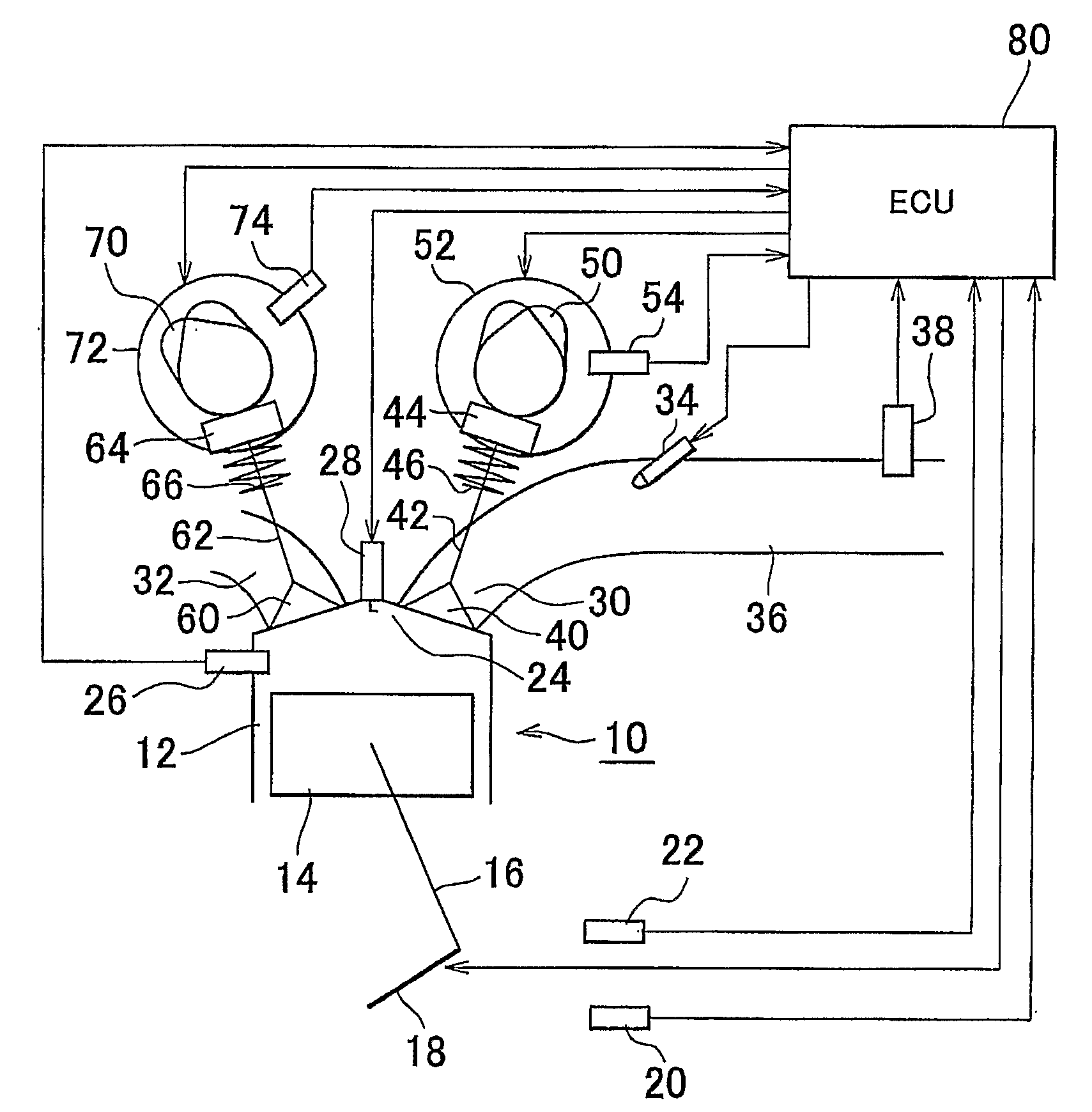
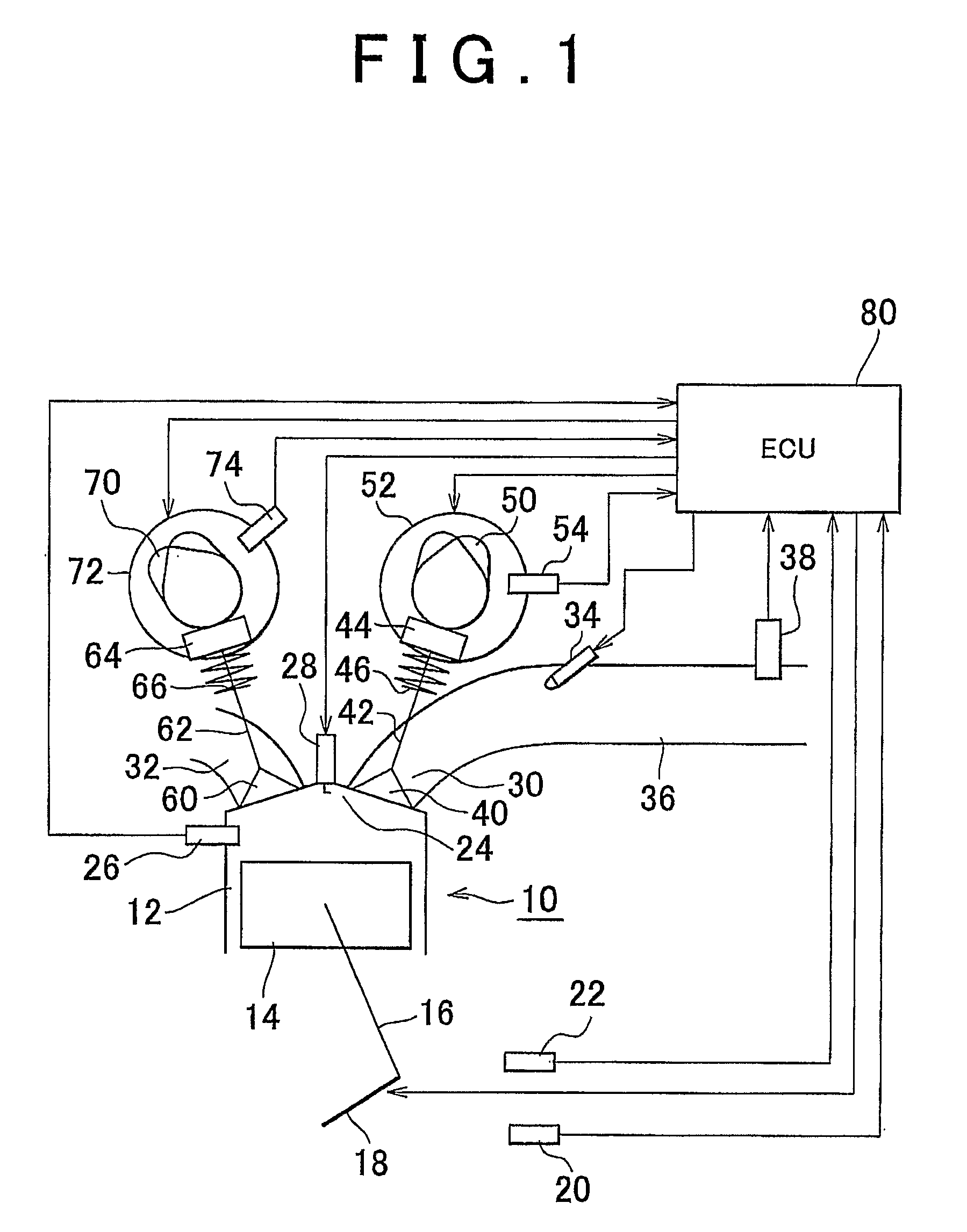
[0043]FIG. 1 is a schematic view showing the configuration of the present invention. The system shown in FIG. 1 has an internal combustion engine 10. The internal combustion engine 10 has a cylinder 12. Although only the cross-section of only one cylinder 12 is shown in FIG. 1, the internal combustion engine 10 actually has a plurality of cylinders 12. A piston 14 is disposed within the cylinder 12. The piston 14 is connected to a crankshaft 18 via a connecting rod 16. A rotational speed sensor 20 that generates an output responsive to the rotational speed of the crankshaft is disposed in the vicinity of the crankshaft 18. A coolant temperature sensor 22 that detects the temperature of the coolant for the internal combustion engine is provided in the internal combustion engine. A combustion chamber 24 is provided at the top of the piston 14. A temperature sensor 26 (temperature detecting means) that generates an output responsive to the temperature within the combustion chamber 24 i...
second embodiment
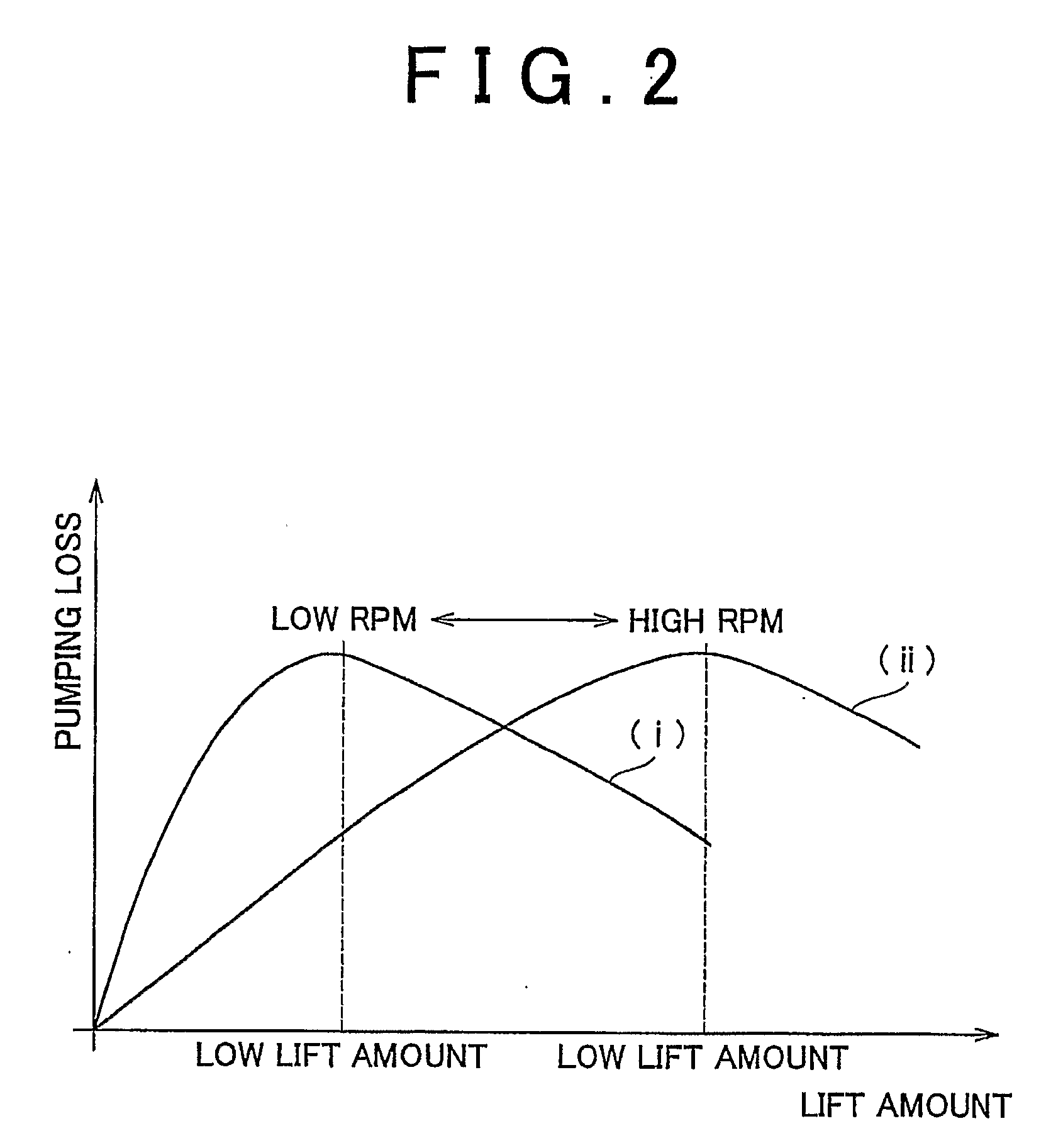
[0082]In six-stroke operation, an increase in the intake temperature makes it easier to burn the fuel. If the engine load becomes large under this condition, abnormal combustion tends to cause knocking. Also, if such abnormal combustion occurs, it can be assumed that the warm-up of the internal combustion engine 10 has progressed to some extent. In the second embodiment, therefore, in order to give priority to suppression of knocking, six-stroke operation is only permitted only when the engine load is within a range that does not cause knocking. The limit value of requested load set in consideration of occurrence of knocking, as indicated by the solid line (ii) in FIG. 5, is smaller than when the temperature of the coolant for the internal combustion engine 10 is high, and becomes higher when the coolant temperature is low. In consideration of suppression of knocking, the rise above the solid line (ii) in FIG. 5 (threshold engine load (ii)) is a second condition for switching from s...
third embodiment
[0093]Specifically, in the system of the third embodiment as well, six-stroke operation is performed at the cold start. It is possible to predict the temperature rise ΔT after the intake stroke in six-stroke operation, based on the air intake amount detected during the six-stroke operation. Therefore, the predicted temperature Tp in the combustion chamber 24 after the second intake stroke in six-stroke operation can be expressed by the current temperature T24 in the combustion chamber and the temperature rise ΔT in the form of Equation (1).
Predicted combustion chamber temperature Tp=Combustion chamber temperature T24+ΔT (1)
[0094]Before starting six-stroke operation, even if the temperature in the combustion chamber 24 is lower than the threshold engine load, there are cases in which an excessive rise occurs in the intake temperature when six-stroke operation is actually performed. If ignition is done under the condition, because it may cause abnormal combustion or knocking to occur...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com