Methods and compositions for reduction of side effects of therapeutic treatments
a technology of therapeutic treatment and side effects, applied in the direction of drug compositions, biocide, heterocyclic compound active ingredients, etc., can solve the problems of unsatisfactory side effects, motor abnormalities, affecting the majority of patients, etc., and achieve the effect of reducing or eliminating side effects of dopaminergic agents
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Nicotine Reduced Levodopa-Induced Dyskinesias in Monkeys with Nigrostriatal Damage
Materials and Methods
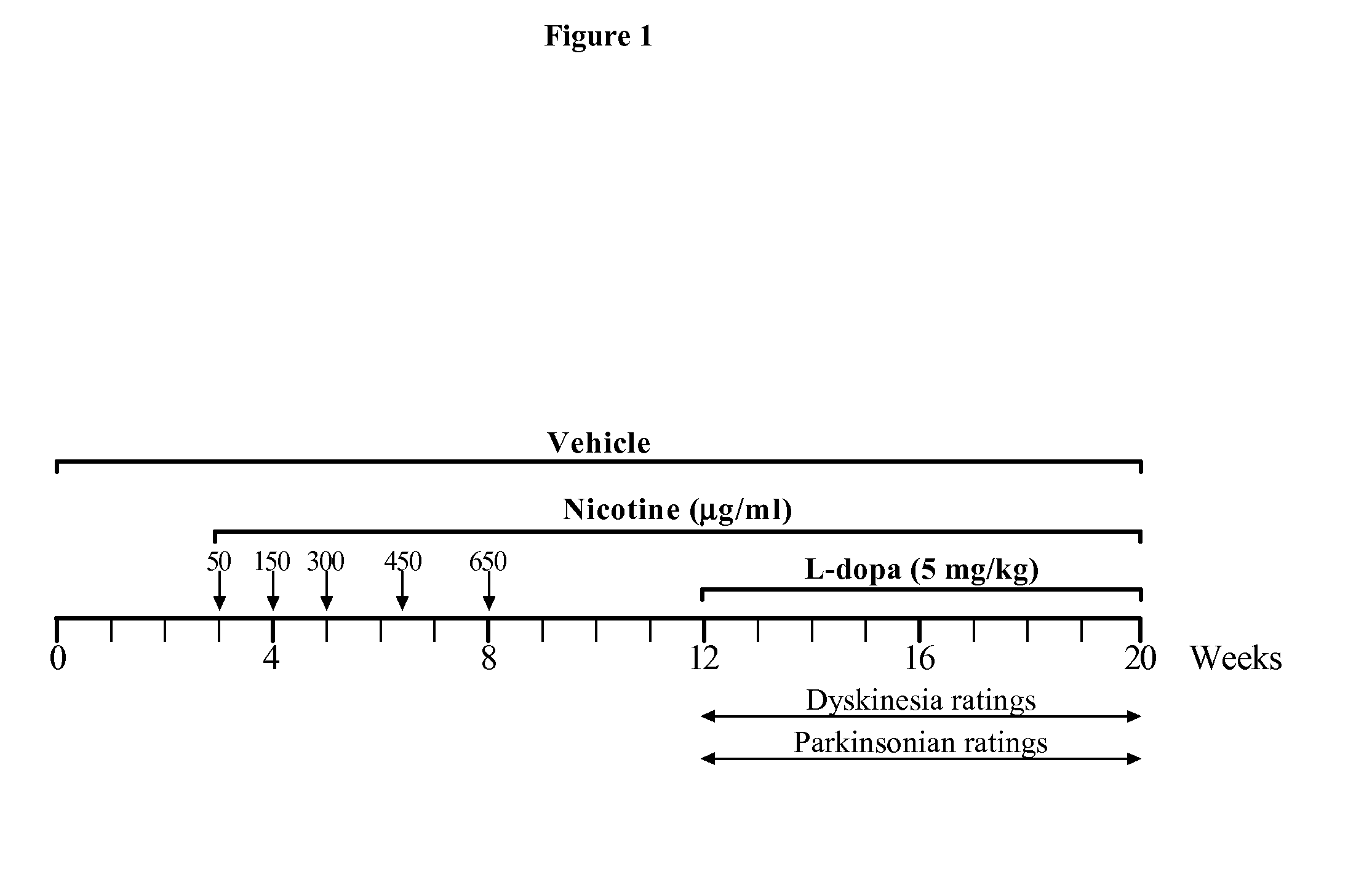
[0242]Animals: Squirrel (Saimiri sciureus) monkeys (n=7) were purchased from World Wide Primates (Miami, Fla.). The animals weighed between 0.6-0.9 kg and were in mid to late adulthood as determined from their general appearance (dentition, fur, other). Female monkeys were used since older animals were available that may better model Parkinson's disease. The animals were placed in quarantine upon arrival, and maintained in a temperature-controlled room (27±3° C.) with a relative humidity>30%, under a 13 / 11-hour light / dark cycle. Monkey food chow and fruits / vegetables were provided once daily, with water provided ad libitum. The monkeys were housed in separate cages to allow for clear behavioral assessments. The animals were released from quarantine after 1 month and treatments initiated. All procedures conformed to the National Institutes of Health Guide for the Care and Use of Lab...
example 2
Nicotine Reduced Dyskinesias in Levodopa-Primed Monkeys
Materials and Methods
[0253]Materials and methods were the same as in example 1.
Results
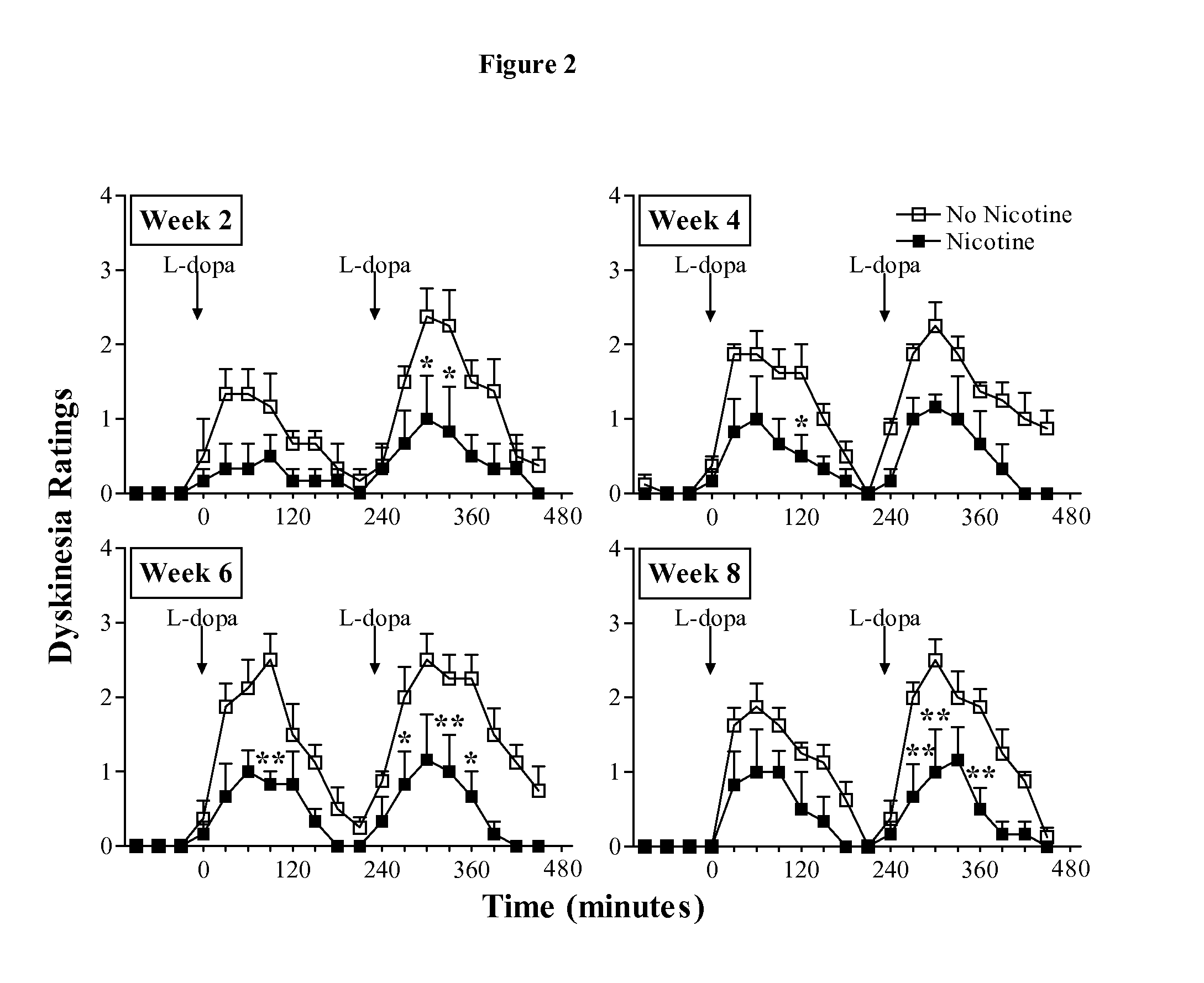
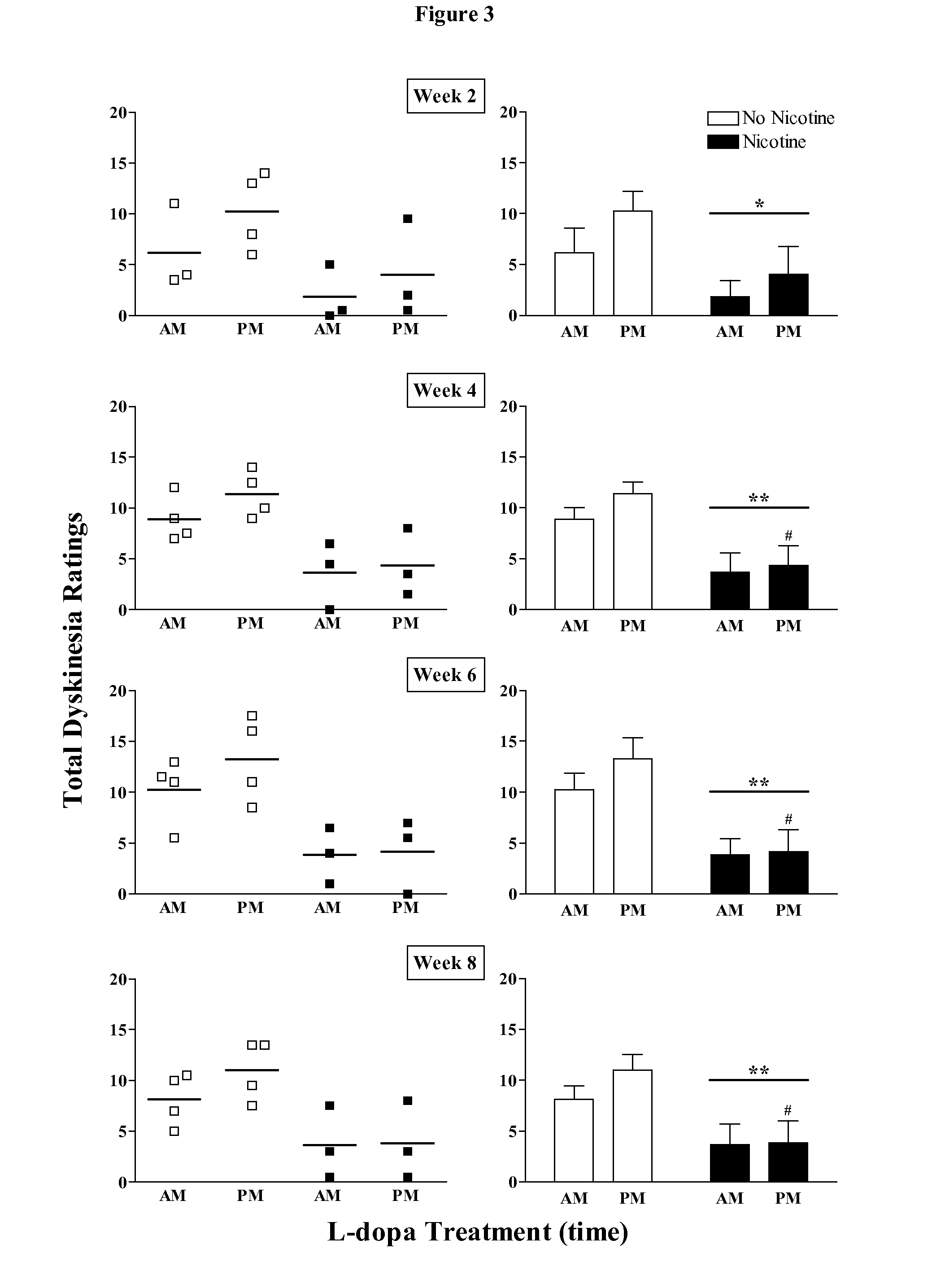
[0254]Crossover study: The data depicted in FIG. 2-4 and Table 1 clearly showed that nicotine administration attenuated levodopa-induced dyskinesias. A crossover study, was then conducted, in which the animals originally receiving nicotine were given vehicle (n=3), while the vehicle-treated animals were now administered nicotine (n=4). Levodopa treatment was stopped. The concentration of nicotine was gradually increased in the drinking water (see FIG. 1) to 650 μg / ml, at which the animals were maintained for 4 weeks. Monkeys that had previously received nicotine were placed on vehicle drinking water for the same time period. All monkeys were then treated with levodopa (5 mg / kg, twice daily 3.5 hours apart) for a subsequent 8-week period. Since both groups of monkeys had previously received levodopa, they were termed levodopa-primed.
[0255]Nicoti...
example 3
Effect of continuous Delivery of Nicotine on its Antidyskinetic Effect
[0260]Animals: Two groups of experimental animals (see Table 3) are required for these experiments to determine the effectiveness of minipump administration in reducing dyskinesias in lesioned monkeys
TABLE 3Groups for experiments in example 3L-dopa treatmentGroupsnNicotine(5 mg / kg orally)(1) MPTP-lesioned8NoYes(2) MPTP-lesioned8YesYes
[0261]MPTP treatment. All animals are lesioned with an injection of MPTP (1.5-2.0 mg / kg, sc). The animals are rated for parkinsonism 3-4 weeks after lesioning according to methods described in example 1. If an animal is not parkinsonian, MPTP injection will be repeated up to 4 times. The lesioning process may therefore require up to 4 months to generate animals with parkinsonism. Eight animals are required per group as our objective is to obtain stably parkinsonian animals. In general 80% of the animals develop stable parkinsonism. The animals are then allowed to recover from the last...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com