Felt with seam for paper manufacture
a technology of paper manufacturing and felt, applied in the field of felt, can solve the problems of increasing the difficulty of insertion of the core line member, increasing the difficulty of insertion of the seam thread s, and difficulty in engaging the seam loop l in an alternating arrangement, so as to achieve smooth intermeshing of the seam loop, stable meshing, and more stably positioned
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
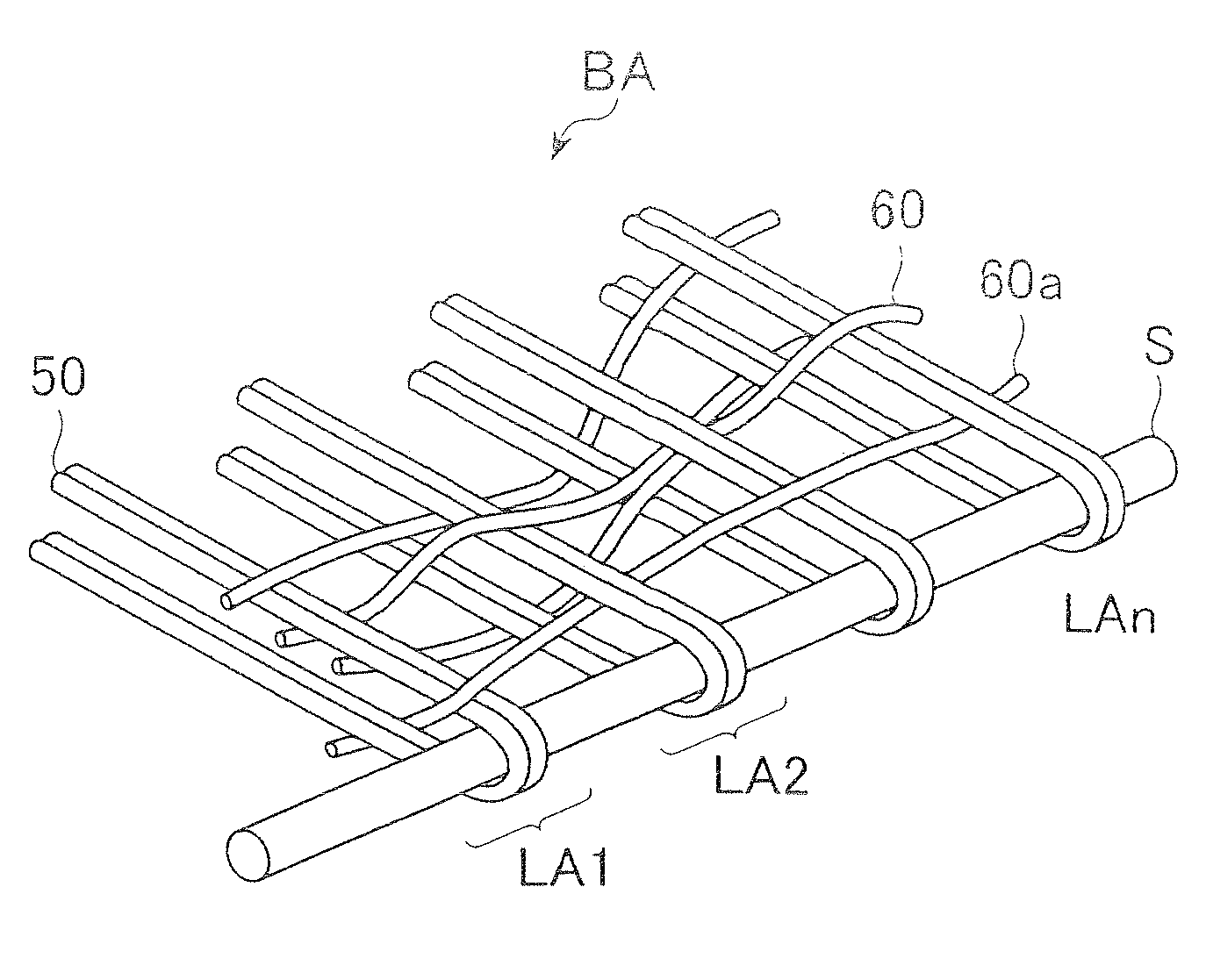
[0049]In this example, yarn A was employed as the MD yarns, and yarn B was used as the CD yarns. The ground fabric BA1 was fabricated by 3 / 1 1 / 3 warp double weaving. A cross-sectional view of the weave in the CD direction is shown in FIG. 6. For the MD yarns, two yarns set side by side were supplied to the weaving machine so that the seam loops are formed with two yarns constituting one group. For the ground fabric BA1, the MD yarns were turned back on themselves at the position of the seam thread S as shown in FIG. 7.
[0050]FIG. 7 is a perspective view of the seaming section of the ground fabric BA1 showing groups LB1 and LA2 of seam loops at one end, and a groups LB1 at the other end, joined together by a seam thread S form and endless felt.
[0051]Following weaving, the ground fabric BA1 was drawn out from the weaving machine, and hung on a pair of rolls. Then, the ground fabric was subjected to heat treatment, using a heating device (not shown). The heating device can be installed ...
example 2
[0054]As in the first example, in this example, yarn A was employed as the MD yarn, and yarn B was used as the CD yarn. The ground fabric was woven in 3 / 1 1 / 3 warp double weave.
[0055]In this case, the supply speed of the CD yarn and the supply speed of the MD yarn were adjusted on the weaving machine so that the seam loops of each group were separated by a distance close to the diameter of yarn A. A ground fabric having a 0.2 mm seam loop interval in the seam loop groups was obtained. The remaining conditions were the same as in Example 1. Thus, the seam felt 2 of the present invention was completed.
example 3
[0056]In this example, yarn C was used as the MD yarn, and yarn B was employed as the CD yarn, the ground fabric was prepared in he same manner as that in Example 1. The ground fabric was then subjected to heat setting, as in example 1, to stabilize the forms of the groups of seam loops. In this example, the heat set temperature was adjusted to at least 180 degrees Celsius, causing the copolymerized nylon sheath of the yarn C to melt, thereby joining the seam loops of each group. In other respects, the process was the same as in Example 1. Thus, the seam felt 3 of the present invention was completed.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com