Multi-hop wireless backhaul network and method
a backhaul network and multi-hop technology, applied in the field of communication systems, can solve the problems of restrictive and expensive deployment in dense urban areas, wireline and optical links require the expensive installation of physical mediums, placement of supporting equipment and physical mediums
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
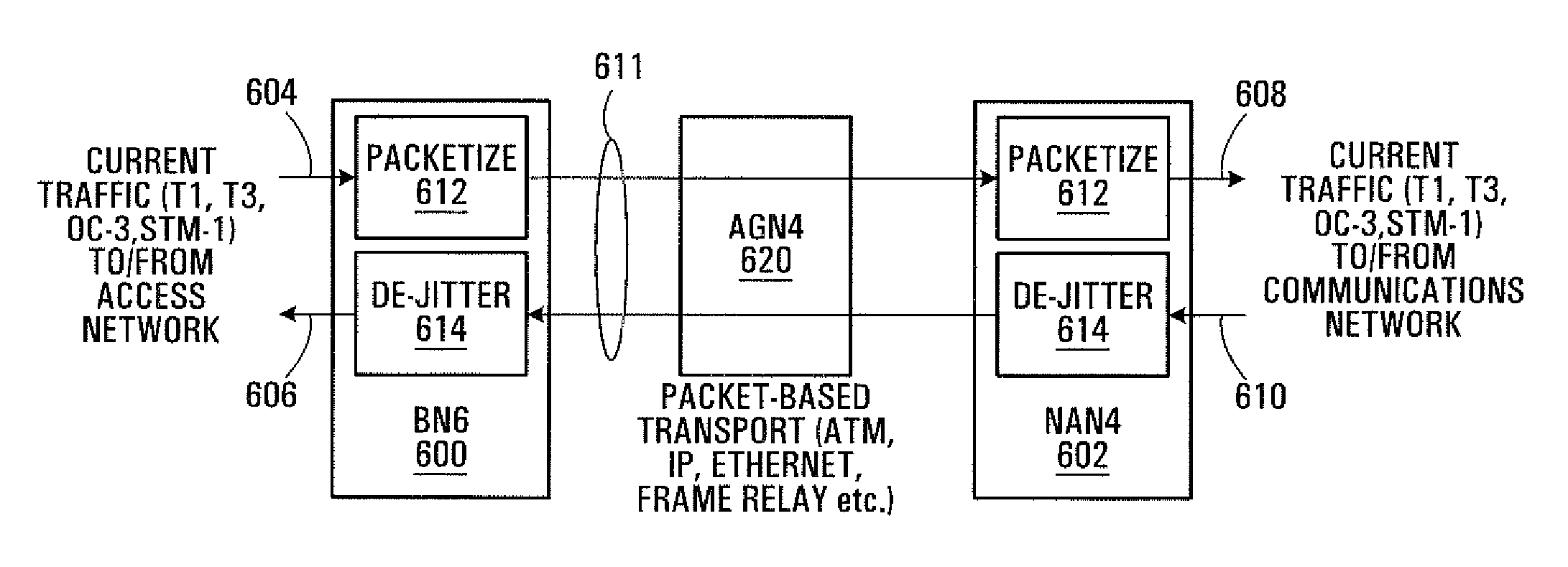
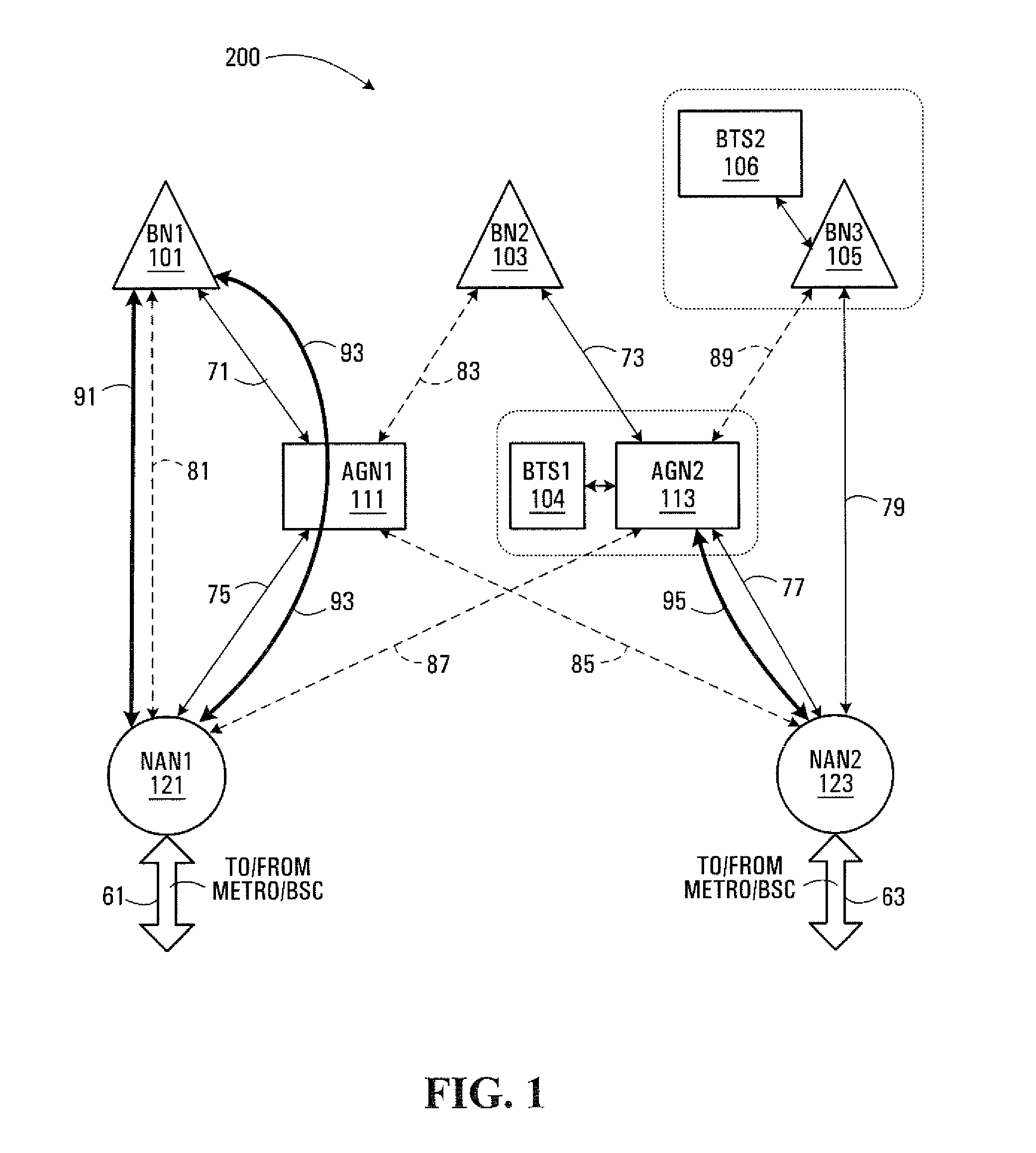
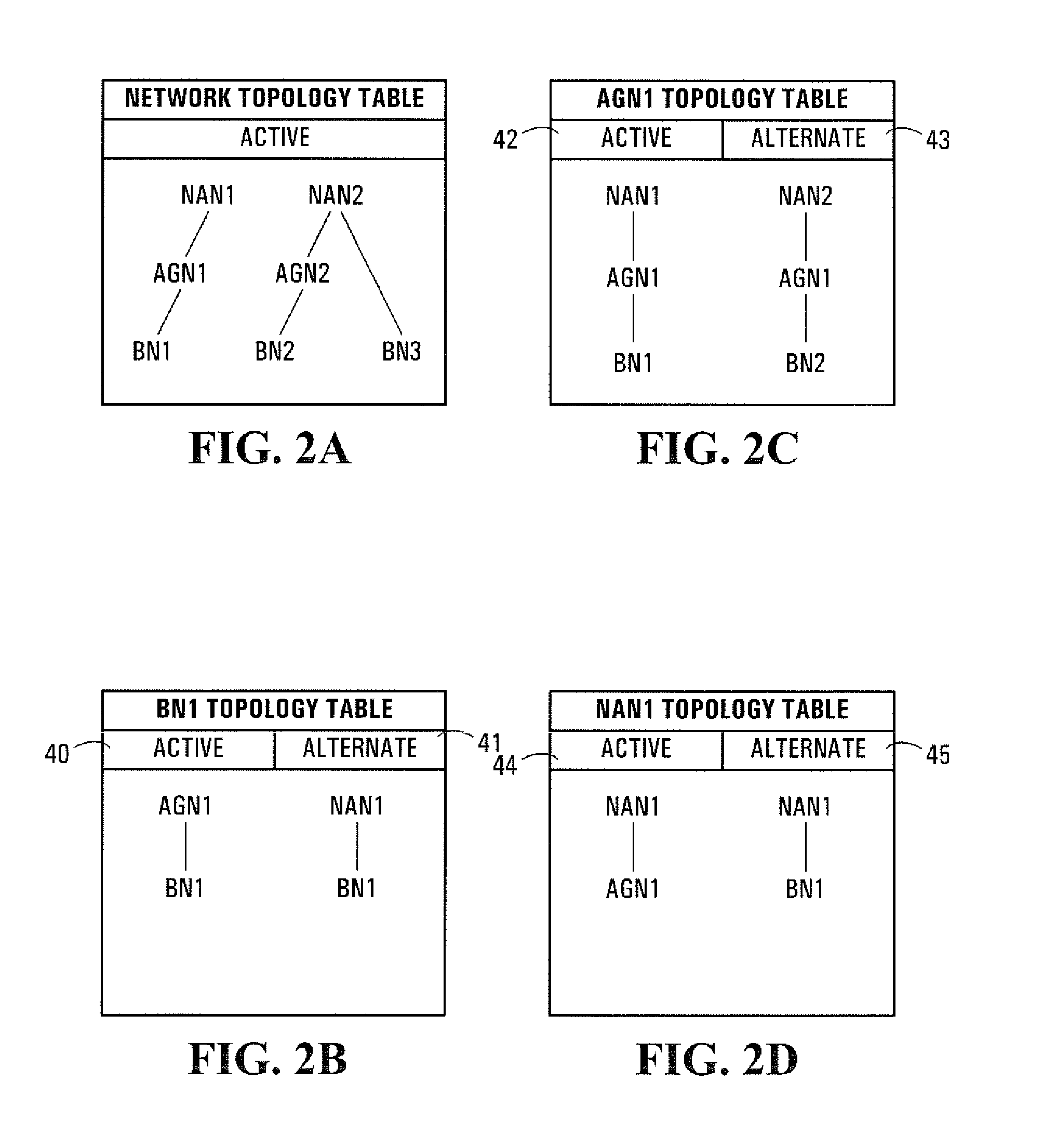
[0103]Conventional multi-hop wireless networks have typically been created for low-capacity, delay tolerant, short-haul data transport to / from consumer electronics and Local Area Network (LAN) and Wide Area Network (WAN) operations. As such, known multi-hop wireless network standards include a number of characteristics which prevent the use of such multi-hop wireless networks in backhaul network design carrying delay sensitive circuit switched traffic.
[0104]For example, conventional multi-hop wireless networks are based on data packet routing. Consequently, each node in a multi-hop wireless network is effectively a router that parses each data packet it receives to determine the data packet's ultimate destination and then re-transmits the data packet as required. The routing functionality requirement alone makes each node relatively complex. Each node in a data packet's path delays the arrival time of the data packet to its ultimate destination, since each node parses the data packe...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com